(Press-News.org) An international team has shown that the injection of a type of stem cell into the brains of patients living with progressive multiple sclerosis (MS) is safe, well tolerated and has a long-lasting effect that appears to protect the brain from further damage.
The study, led by scientists at the University of Cambridge, University of Milan Bicocca and Hospital Casa Sollievo della Sofferenza (Italy), is a step towards developing an advanced cell therapy treatment for progressive MS.
Over 2 million people live with MS worldwide, and while treatments exist that can reduce the severity and frequency of relapses, two-thirds of MS patients still transition into a debilitating secondary progressive phase of disease within 25-30 years of diagnosis, where disability grows steadily worse.
In MS, the body’s own immune system attacks and damages myelin, the protective sheath around nerve fibres, causing disruption to messages sent around the brain and spinal cord.
Key immune cells involved in this process are macrophages (literally ‘big eaters’), which ordinarily attack and rid the body of unwanted intruders. A particular type of macrophage known as a microglial cell is found throughout the brain and spinal cord. In progressive forms of MS, they attack the central nervous system (CNS), causing chronic inflammation and damage to nerve cells.
Recent advances have raised expectations that stem cell therapies might help ameliorate this damage. These involve the transplantation of stem cells, the body’s ‘master cells’, which can be programmed to develop into almost any type of cell within the body.
Previous work from the Cambridge team has shown in mice that skin cells re-programmed into brain stem cells, transplanted into the central nervous system, can help reduce inflammation and may be able to help repair damage caused by MS.
Now, in research published in the Cell Stem Cell, scientists have completed a first-in-man, early-stage clinical trial that involved injecting neural stem cells directly into the brains of 15 patients with secondary MS recruited from two hospitals in Italy. The trial was conducted by teams at the University of Cambridge, Milan Bicocca and the Hospitals Casa Sollievo della Sofferenza and S. Maria Terni (IT) and Ente Ospedaliero Cantonale (Lugano, Switzerland) and the University of Colorado (USA).
The stem cells were derived from cells taken from brain tissue from a single, miscarried foetal donor. The Italian team had previously shown that it would be possible to produce a virtually limitless supply of these stem cells from a single donor – and in future it may be possible to derive these cells directly from the patient – helping to overcome practical problems associated with the use of allogeneic foetal tissue.
The team followed the patients over 12 months, during which time they observed no treatment-related deaths or serious adverse events. While some side-effects were observed, all were either temporary or reversible.
All the patients showed high levels of disability at the start of the trial – most required a wheelchair, for example – but during the 12 month follow up period none showed any increase in disability or a worsening of symptoms. None of the patients reported symptoms that suggested a relapse and nor did their cognitive function worsen significantly during the study. Overall, say the researchers, this points to a substantial stability of the disease, without signs of progression, though the high levels of disability at the start of the trial make this difficult to confirm.
The researchers assessed a subgroup of patients for changes in the volume of brain tissue associated with disease progression. They found that the larger the dose of injected stem cells, the smaller the reduction in this brain volume over time. They speculate that this may be because the stem cell transplant dampened inflammation.
The team also looked for signs that the stem cells were having a neuroprotective effect – that is, protecting nerve cells from further damage. Their previous work showed how tweaking metabolism – how the body produces energy – can in turn reprogram microglia from ‘bad’ to ‘good’. In this new study, they looked at how the brain's metabolism changes after the treatment. They measured changes in the fluid around the brain and in the blood over time and found certain signs that are linked to how the brain processes fatty acids. These signs were connected to how well the treatment works and how the disease develops. The higher the dose of stem cells, the greater the levels of fatty acids, which also persisted over the 12-month period.
Professor Stefano Pluchino from the University of Cambridge, who co-led the study, said: “We desperately need to develop new treatments for secondary progressive MS, and I am cautiously very excited about our findings, which are a step towards developing a cell therapy for treating MS.
“We recognise that our study has limitations – it was only a small study and there may have been confounding effects from the immunosuppressant drugs, for example – but the fact that our treatment was safe and that its effects lasted over the 12 months of the trial means that we can proceed to the next stage of clinical trials.”
Co-leader Professor Angelo Vescovi from the University of Milano-Bicocca said: “It has taken nearly three decades to translate the discovery of brain stem cells into this experimental therapeutic treatment This study will add to the increasing excitement in this field and pave the way to broader efficacy studies, soon to come.”
Caitlin Astbury, Research Communications Manager at the MS Society, says: “This is a really exciting study which builds on previous research funded by us. These results show that special stem cells injected into the brain were safe and well-tolerated by people with secondary progressive MS. They also suggest this treatment approach might even stabilise disability progression. We’ve known for some time that this method has the potential to help protect the brain from progression in MS.
“This was a very small, early-stage study and we need further clinical trials to find out if this treatment has a beneficial effect on the condition. But this is an encouraging step towards a new way of treating some people with MS.”
Reference
Leone, MA, Gelati, M & Profico, DC et al. Intracerebroventricular Transplantation of Foetal Allogeneic Neural Stem Cells in Patients with Secondary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis (hNSC-SPMS): a phase I dose escalation clinical trial. Cell Stem Cell; 7 Dec 2023; DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2023.11.001
END
Early-stage stem cell therapy trial shows promise for treating progressive MS
2023-11-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Irritability, agitation, and anxiety in Alzheimer’s patients caused by brain inflammation, study says
2023-11-27
PITTSBURGH, Nov. 27, 2023 – Common neuropsychiatric symptoms that doctors see in Alzheimer’s disease patients originate from brain inflammation rather than amyloid and tau proteins, report University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine researchers today in JAMA Network Open.
The finding strengthens mounting evidence for the role of neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s progression and suggests new pathways for the development of therapies targeting neurological symptoms of the disease.
“Neuropsychiatric symptoms such as irritability, agitation, anxiety and depression are among the most difficult ...
Sensitive ecosystems at risk from mine waste
2023-11-27
Nearly a third of the world’s mine tailings are stored within or near protected conservation areas, University of Queensland research has found.
A study led by UQ’s Bora Aska, from the Sustainable Minerals Institute and School of the Environment, said these waste facilities pose an enormous risk to some of earth’s most precious species and landscapes.
“Mine tailings contain the waste and residue that remains after mineral processing, and the storage facilities built to contain it are some of the world’s largest engineered structures,” Ms Aska said.
“We found of the 1,721 disclosed tailings ...
Genes influence whether infants prefer to look at faces or non-social objects
2023-11-27
Whether infants at five months of age look mostly at faces or non-social objects such as cars or mobile phones is largely determined by genes. This has now been demonstrated by researchers at Uppsala University and Karolinska Institutet. The findings suggest that there is a biological basis for how infants create their unique visual experiences and which things they learn most about. The study has been published in the scientific journal Nature Human Behaviour.
The way in which we explore our environment with our eyes affects what we notice, think about and learn. The new study analysed preference for faces versus non-social objects in ...
Collaboration between women helps close the gender gap in ice core science
2023-11-27
A Perspective article published today in Nature Geoscience tackles the longstanding issue of gender representation in science, focusing on the field of ice core science. Prior work has shown that despite progress toward gender parity over the past fifty years1, women continue to be significantly underrepresented within the discipline of Earth sciences2 and receive disproportionately fewer opportunities for recognition, such as invited talks, awards, and nominations3. This lack of opportunity can have long-term negative impacts on women’s careers. To help address these persistent gender gaps, the study evaluates patterns related to women’s publication in ice core science over the ...
Stanford Medicine study reveals why we value things more when they cost us more
2023-11-27
Ahab hunting down Moby Dick. Wile E. Coyote chasing the Road Runner. Learning Latin. Walking over hot coals. Standing in a long line for boba tea or entrance to a small, overpriced clothing retail store. Forking up for luxury nonsense.
What do these activities have in common? They’re all examples of the overvaluation of what economists call “sunk costs”: the price you’ve already irretrievably paid in time, money, effort, suffering or any combination of them for an item, an experience or a sense of self-esteem.
It’s a ...
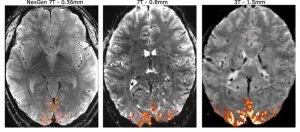
Innovative design achieves tenfold better resolution for functional MRI brain imaging
2023-11-27
An intense international effort to improve the resolution of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for studying the human brain has culminated in an ultra-high resolution 7 Tesla scanner that records up to 10 times more detail than current 7T scanners and over 50 times more detail than current 3T scanners, the mainstay of most hospitals.
The dramatically improved resolution means that scientists can see functional MRI (fMRI) features 0.4 millimeters across, compared to the 2 or 3 millimeters typical of today's standard 3T fMRIs.
"The NexGen 7T scanner is a new tool that allows us to look at the brain circuitry underlying different diseases of the brain with ...
Hamburg collaboration paves the way to cleaner technologies for industry
2023-11-27
During the nearly five decades of its operation, the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Hamburg has developed many fruitful collaborations with other scientific institutions located in the Hamburg metropolitan area. One example is the long-lasting collaboration between researchers at EMBL Hamburg and the Center for Biobased Solutions (CBBS) at the Hamburg University of Technology (TUHH), which has recently yielded new insights into the structure and function of a lipid-degrading enzyme found in a microbe adapted to living in extreme conditions. The findings could help improve ...
Pioneering research method reveals bluefin tuna’s fate
2023-11-27
The return of bluefin tuna to Northern European waters is a conservation success story, but rising sea temperatures in their Mediterranean nursery grounds mean this recovery may be short-lived, according to new research led by the University of Southampton.
Temperatures expected in the Mediterranean within the next 50 years are expected to drive juvenile tuna out of the Mediterranean, where they may be accidentally caught in existing sardine and anchovy fisheries – requiring fishery managers to adapt their methods to allow tuna nurseries to establish.
Outlining the research, published in Nature, lead author Clive Trueman, Professor of Geochemical Ecology ...
New study sheds light on the link between lipids and cholelithiasis
2023-11-27
A new study published in the journal Gut has shed light on the complex relationship between serum lipids, lipid-modifying targets, and cholelithiasis, a common condition characterized by the formation of gallstones. The study, led by researchers at the First Hospital of Jilin University, employed a combination of observational and Mendelian randomization (MR) approaches to comprehensively assess these associations.
Cholelithiasis is a prevalent hepatobiliary disorder that primarily affects Western populations. It is a significant risk factor for cholangiocarcinoma, ...
Honeybee cluster—not insulation but stressful heat sink
2023-11-27
With images - the visual assets can be downloaded by clicking on this WeTransfer link:https://we.tl/t-mbRtSW5BzO
*See further information at end of release for captions and required pic credits
A Leeds researcher is keen to help beekeepers shape their practices following his study which appears to disprove the widespread belief that honeybees naturally insulate their colonies against the cold. His findings suggest that the creatures are potentially being subjected to thermally-induced ...