Gaining more control over the fabrication of surface micro/nano structures using ultrafast lasers
2023-11-28
(Press-News.org)
Surface functionalization via micro/nano structuring is not only a thriving research area inspired by bionics but also of great importance for various practical applications. The key to achieving various surface functions is the fabrication of surface micro/nano structures with controlled dimensions, hierarchies, and compositions, which is driving the continuous progress of micro/nano fabrication techniques. Researchers from the Laser Materials Processing Research Center at the School of Materials Science and Engineering of Tsinghua University, China, have spent years in developing laser-enabled fabrication techniques for preparing surface micro/nano structures and exploring their functional applications. We have established the capabilities to separately and finely control the micro- and nanoscale features as well as control how they are combined to form different types of multi-level structures. The functions and applications we have studied include extreme wettability, anti-icing, broadband light absorption, structural colors, solar water evaporation, thermal interface management, tribological properties, surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy, and photoelectrocatalysis for energy applications, etc.
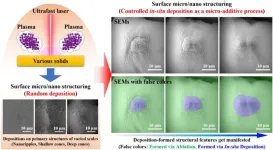
Gaining more control over the structure fabrication using ultrafast lasers and developing more flexible fabrication approaches is one of our continuous research focuses. In addition to controlling the ultrafast laser ablation process, we recently demonstrated that the in-situ deposition of particles following ultrafast laser ablation of solid surfaces could also be controlled and used as a localized micro-additive process to pile up hierarchical surface structures. The plasma plume formation is a universal phenomenon during pulsed laser ablation of solids. The products (e.g., nanoparticles) from the plasma plumes can be collected for usage by external liquids (e.g., in the case of laser ablation in liquids) or substrates (e.g., in the case of pulsed laser deposition). In contrast, some of the nanoparticles from the plasma plumes in-situ deposit back to the irradiated surfaces during ultrafast laser surface structuring. For specific applications, the in-situ deposited structural features play a significant role for enhancing surface properties like light absorption, sensibility, and energy conversion. However, whether and how the in-situ deposition process can be controlled remains an open question. Our recent studies showed a capability of controlling the in-situ deposition process, e.g., to build fort-like structures on top of micro cone arrays rather than just producing randomly distributed nanoparticles. The revealed laser-matter interaction mechanism can motivate future research interests to explore new possibilities in the fabrication of functional surface micro/nano structures using ultrafast lasers. The work entitled “Localized in-situ deposition: a new dimension to control in fabricating surface micro/nano structures via ultrafast laser ablation” was published on Frontiers of Optoelectronics (published on Nov. 17, 2023).
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-11-28
1 Overview
A number of open source resources, in the form of curated datasets, web-based databases, stand-alone software, or library packages have been floating in various forms online. These codes are useful in computer science research works, and engineering practices. The application of these resources requires instructions. Traditional scientific publications usually focus on the algorithms, principles, theoretical proofs, benchmarking evaluations and comparisons that is in the background or in the generation process of these resources. The instructions, case studies, application examples and sample codes, which help users and other practitioners to utilize these ...
2023-11-28
Particle accelerators hold great potential for semiconductor applications, medical imaging and therapy, and research in materials, energy and medicine. But conventional accelerators require plenty of elbow room — kilometers — making them expensive and limiting their presence to a handful of national labs and universities.
Researchers from The University of Texas at Austin, several national laboratories, European universities and the Texas-based company TAU Systems Inc. have demonstrated a compact particle accelerator less than 20 meters long that produces ...
2023-11-28
University of Birmingham Press Release
STRICTLY EMBARGOED UNTIL 00.01 Tuesday 28th November UK TIME/ 19.01 Monday 27th November EASTERN TIME
Experts from the University of Birmingham are calling for global cooling and cold chain to be considered as critical infrastructure as the planet continues to heat.
The report, The Hot Reality: Living in a +50°C World, comes as world leaders, businesses, scientists, and environmental agencies gather in Dubai for the start of COP 28.
The Hot Reality: Living in a +50°C World project is led by the Centre for Sustainable Cooling and the Africa Centre of Excellence for Sustainable Cooling ...
2023-11-28
Greater adherence to the World Cancer Research Fund/American Institute for Cancer Research (WCRF/AICR) cancer prevention recommendations — which encourage a healthy lifestyle — is associated with a lower risk of all cancers combined and some individual cancers such as breast cancer. The findings are published in BMC Medicine.
The 2018 WCRF/AICR cancer prevention recommendations aim to reduce the risk of cancer by encouraging individuals to maintain a healthy weight, be physically active, and eat a diet rich in wholegrains, vegetables, fruit, and beans, but low in highly processed foods, red and processed meat, sugar-sweetened drinks, and alcohol.
John Mathers and ...
2023-11-28
[Jerusalem, Israel]
Professor Asaf Hellman and his research team at the Hebrew University-Hadassah Medical School have unveiled new findings in the realm of methylation-directed regulatory networks. Their study sheds light on the mechanisms governing the activation and suppression of mutation-driven disease genes, particularly in cases like glioblastoma, offering insights into variations in disease expression among patients. This research has the potential to revolutionize disease research and clinical applications, paving the way for personalized medicine, diagnostic biomarkers, and improved patient care. Currently, 98% of individuals hospitalized ...
2023-11-28
A groundbreaking study co-authored by Rachita Sumbria, associate professor in the Chapman University School of Pharmacy, has uncovered a new contributor to the formation of brain hemorrhages. Contrary to previous beliefs that such hemorrhages were solely linked to blood vessel injuries, the research reveals that increased interactions between aged red blood cells and brain capillaries can lead to brain microhemorrhages. This discovery not only enhances new understandings of the mechanisms behind these microhemorrhages but also opens up new possibilities ...
2023-11-28
A new study zooming in on how smartphones influence our photography habits found Australians aged 20 to 40 years old take more selfies than teenagers and older Australians.
The research, from RMIT University and the Pathshala South Asian Media Institute, studied over 1,200 smartphone photos taken during a two-week period by 30 participants and found older participants overall took more photos than teenage participants.
Research lead and RMIT Senior Lecturer Dr TJ Thomson said older participants often used their smartphone cameras in more functional ways, such as capturing information ...
2023-11-28
It’s well-known that when those around us get sick, there’s a good chance we’ll catch what they have, but new research reveals that simply observing a sick individual triggers a biological response.
Patricia Lopes, an assistant professor of biology at Chapman University, is studying how the body anticipates the possibility of infection just by witnessing someone else's symptoms. This phenomenon raises questions about the interconnectedness of individuals within a social group and how the perception of sickness can influence the health and behavior of others.
Her recent work showed that when healthy ...
2023-11-28
Life on Earth is facing the greatest rate of extinction in history – and humans are the disruptive force, according to a leading ecologist.
Protecting biodiversity, according to consultant ecologist Nigel Dudley who has worked with international organizations including WWF International and UNESCO, does not mean prioritizing animal lives at all costs or focusing narrowly on nature’s economic values.
The author defines biodiversity rights here as ‘the right of all species to continue their natural span of existence within a functioning ecosystem’.
Dudley says the failure of some governments to respect biodiversity ...
2023-11-28
University of Oxford News Release
Oxford Internet Institute
Strict Embargo until 00.01 GMT Tuesday, 28 November 2023
No ‘smoking gun’ mental health harm from internet: landmark Oxford survey
Study of two million individuals’ psychological well-being from 2005 to 2022 in 168 countries, in relation to country-level internet-use and mobile broadband statistics
Negative and positive experiences had increased on average, but little to no evidence suggesting (mobile) internet use was associated with these changes
Links between internet adoption ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Gaining more control over the fabrication of surface micro/nano structures using ultrafast lasers