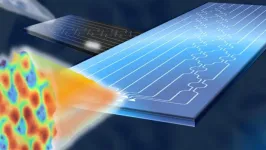
(Press-News.org) Optical wireless may no longer have any obstacles. A study by Politecnico di Milano, conducted together with Scuola Superiore Sant'Anna in Pisa, the University of Glasgow and Stanford University, and published in the prestigious journal Nature Photonics, has made it possible to create photonic chips that mathematically calculate the optimal shape of light to best pass through any environment, even one that is unknown or changing over time.
The problem is well known: light is sensitive to any form of obstacle, even very small ones. Think, for example, of how we see objects when looking through a frosted window or simply when our glasses get foggy. The effect is quite similar on a beam of light carrying data streams in optical wireless systems: the information, while still present, is completely distorted and extremely difficult to retrieve.
The devices developed in this research are small silicon chips that serve as smart transceivers: working in pairs, they can automatically and indipendently 'calculate' what shape a beam of light needs to be in order to pass through a generic environment with maximum efficiency. And that’s not all: they can also generate multiple overlapping beams, each with its own shape, and direct them without them interfering with each other; in this way, the transmission capacity is greatly increased, just as required by next-generation wireless systems.
"Our chips are mathematical processors that make calculations with light very quickly and efficiently, almost with no energy consumption. The optical beams are generated through simple algebraic operations, essentially sums and multiplications, performed directly on the light signals and transmitted by micro-antennas directly integrated on the chips. This technology offers many advantages: extremely easy processing, high energy efficiency and an enormous bandwidth exceeding 5000 GHz”, Francesco Morichetti Head of the Photonic Devices Lab of Politecnico di Milano, explains.
"Today, all information is digital, but in fact, images, sounds and all data are inherently analogue. Digitisation does allow for very complex processing, but as the volume of data increases, these operations become increasingly less sustainable in terms of energy and computation. Today, there is great interest in returning to analogue technologies, through dedicated circuits (analogue co-processors) that will serve as enablers for the 5G and 6G wireless interconnection systems of the future. Our chips work just like that”, Andrea Melloni, Director of Polifab, Politecnico di Milano’s micro and nanotechnology centre, says.
"Analogue computing using optical processors is crucial in numerous application scenarios that include mathematical accelerators for neuromorphic systems, high-performance computing (HPC) and artificial intelligence, quantum computers and cryptography, advanced localisation, positioning and sensor systems, and in general, in all systems where the processing of large amounts of data at very high speed is required”, adds Marc Sorel, Professor of Electronics at the TeCIP Institute (Telecommunications, Computer Engineering, and Photonics Institute) of Scuola Superiore Sant'Anna.
The work is co-funded under the NRRP by the RESTART research and development programme 'RESearch and innovation on future Telecommunications systems and networks, to make Italy more smart'. Within the RESTART programme Prof. Andrea Melloni, Politecnico di Milano, and Prof. Piero Castaldi, Istituto TeCIP, Scuola Superiore Sant’Anna Pisa lead the ‘HePIC’ focused project and 'Rigoletto' structural project, which aim to develop next-generation photonic integrated circuits and optical transport networks that will support the future 6G infrastructure.
END
The chip that makes calculations with light
‘Nature Photonics’ features a study by the Politecnico di Milano in collaboration with Scuola Superiore Sant'Anna in Pisa
2023-11-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Severe weather disproportionately impacts Oklahoma’s native communities, study shows
2023-11-29
As the climate, demographics and land usage continue to change, tribal communities in Oklahoma are increasingly at risk of severe weather. A recent study led by Yang Hong with the University of Oklahoma examines these changes and the risks they pose.
“Indigenous communities are grappling with an imminent climate crisis compounded by systemic injustices. Recognizing their unique connections to their homelands as sovereign peoples is crucial in addressing these pressing issues,” Hong said.
Hong is the corresponding author of the paper, “Future ...
JMIR Publications announces a partnership with leading career center provider Naylor Association Solutions to power a brand-new online career development hub for digital health professionals
2023-11-29
We are thrilled to announce the official launch of the JMIR Career Center on the JMIR Publications website. This pioneering platform is set to revolutionize the way healthcare professionals access career development resources and opportunities within the digital health field.
The JMIR Career Center, in collaboration with Naylor Association Solutions, aims to bridge the gap between digital health professionals and their career advancement. As the digital health sector continues to evolve, so too does the demand for skilled and motivated professionals. By providing a dedicated hub for digital health career resources, job ...
Fighting fruit flies help researchers understand why we stay angry
2023-11-29
It’s one of those days. On the drive home from work, the car in the next lane cuts you off. You slam on the brakes, lay on the horn, and yell choice words at the offending driver. When you walk into your house half an hour later, you’re still angry, and snap at your partner when they ask about your day.
Fruit flies may not have to worry about the lingering effects of road rage, but they also experience states of persistent aggression. In the case of female fruit flies, this behavior is a survival mechanism, causing the flies to headbutt, shove, and fence other female fruit flies to guard prime egg-laying territory on a ...
Surgeon supply by county-level rurality and social vulnerability
2023-11-29
About The Study: Between 2010 and 2020, surgeon supply per 100,000 population decreased in rural counties and increased in urban counties, and decreased in socially vulnerable counties and remained unchanged in other counties. Thus, over the past decade, disparities in surgeon supply between rural and urban counties and between socially vulnerable and other counties have widened in the U.S. The largest widening was observed among general surgeons.
Authors: Vishal R. Patel, B.S., of the Dell Medical School in Austin, Texas, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2023.5632)
Editor’s ...
Surgeon sex and health care costs for patients undergoing common surgical procedures
2023-11-29
About The Study: This analysis that included 1.1 million patients found lower 30-day, 90-day, and 1-year health care costs for patients treated by female surgeons compared with those treated by male surgeons. These data further underscore the importance of creating inclusive policies and environments supportive of women surgeons to improve recruitment and retention of a more diverse and representative workforce.
Authors: Christopher J. D. Wallis, M.D., Ph.D., of the University of Toronto, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2023.6031)
Editor’s ...
Google DeepMind adds nearly 400,000 new compounds to Berkeley Lab’s Materials Project
2023-11-29
New technology often calls for new materials – and with supercomputers and simulations, researchers don’t have to wade through inefficient guesswork to invent them from scratch.
The Materials Project, an open-access database founded at the Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) in 2011, computes the properties of both known and predicted materials. Researchers can focus on promising materials for future technologies – think lighter alloys that improve fuel economy in cars, more ...
Tracing the evolution of the “little brain”
2023-11-29
The evolution of higher cognitive functions in human beings has so far mostly been linked to the expansion of the neocortex – a region of the brain that is responsible, inter alia, for conscious thought, movement and sensory perception. Researchers are increasingly realising, however, that the “little brain” or cerebellum also expanded during evolution and probably contributes to the capacities unique to humans, explains Prof. Dr Henrik Kaessmann from the Center for Molecular Biology of Heidelberg University. ...
Bees are still being harmed despite tightened pesticide regulations
2023-11-29
A new study has confirmed that pesticides, commonly used in farmland, significantly harm bumblebees – one of the most important wild pollinators. In a huge study spanning 106 sites across eight European countries, researchers have shown that despite tightened pesticide regulations, far more needs to be done.
While the agricultural uses of insecticides have been in the spotlight for their negative effects on bees, it has remained unknown how the effects scale beyond single substances in focal ...
The Global Biodiversity Data Portal: enabling biodiversity research worldwide
2023-11-29
EMBL’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) has launched the Global Biodiversity Portal – an open access data portal that will consolidate genomic information from different biodiversity projects within the Earth BioGenome Project.
Sequencing and storing the genomic data of all species on Earth is vital for future conservation and biodiversity efforts. In an era where biodiversity is under threat from various environmental pressures, there is an urgent need for centralised, accessible, and actionable data. ...
Doctors call for expanded reporting of medical care given in ICE detention centers
2023-11-29
Embargoed until November 29 11 a.m. ET
A new study led by Dr. Annette Dekker, an assistant professor in the Department of Emergency Medicine at UCLA, calls for the U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) detention centers to increase health outcome reporting for detained immigrants to monitor the quality of medical care. Pulling from three different data sources, the researchers found discrepancies in care reported by emergency medical services (EMS) compared to ICE reports.
Building upon work that reviews deaths that occur at ICE detention centers, Dekker and colleagues sought to address concerns that individuals detained by ICE ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] The chip that makes calculations with light‘Nature Photonics’ features a study by the Politecnico di Milano in collaboration with Scuola Superiore Sant'Anna in Pisa