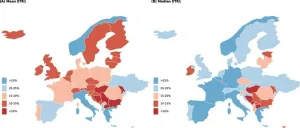
(Press-News.org) Despite a similar statutory tax rate for multinational corporations (MNCs) across many countries, the effective tax rate that MNCs actually pay differs greatly — as low as 1% of gross income in Luxembourg and as high as 67% in Norway. That’s one conclusion of a study published this week in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Javier Garcia-Bernardo of Utrecht University, the Netherlands, Petr Janský of Charles University, Czechia, and Thomas Tørsløv of Danmarks Nationalbank, Denmark. The study comes on the heels of recent European Union legislation that aims to set a minimum effective tax rate across countries and redistribute MNC profits to address tax avoidance.
Tax avoidance by MNCs contributes to inequalities both between and within countries, and understanding the effective tax rates paid by MNCs in different countries is critical to minimizing these inequalities. In the new study, researchers developed a new framework for computing the country-level effective tax rates for MNCs, using MNC income statement data that includes income across countries and taxes paid in different jurisdictions. They applied the framework to MNCs in 47 countries, mostly belonging to the European Union.
The study found that the amount of taxes accrued by MNCs varies considerably from country to country and reveals the extent of the differences between effective tax rates and statutory tax rates for many countries. At the extreme ends of the effective tax rate range were Luxembourg, with MNCs paying a rate of 1-8% of gross income in taxes, and Norway, with MNCs paying as much as 46-67%, despite the two countries having nearly identical statutory tax rates of 28% and 29%.
The authors conclude that statutory rates do not provide a great deal of information on the tax burden that MNCs actually face in many countries, and that better data is needed to obtain more reliable effective tax rate estimates and achieve more informed policy decisions.
The authors add: “We find that effective tax rates substantially differ across countries and from statutory rates for some countries. These findings should be of particular interest in the light of recent changes in the taxation of multinationals worldwide such as the 2021 agreement of more than 100 countries worldwide to a global minimum tax rate of 15%.”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0293552
Citation: Garcia-Bernardo J, Janský P, Tørsløv T (2023) Effective tax rates of multinational corporations: Country-level estimates. PLoS ONE 18(11): e0293552. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0293552
Author Countries: The Netherlands, Czechia, Denmark
Funding: Javier Garcia-Bernardo has received funding from the European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme (grant agreement number 638946). https://erc.europa.eu/ Petr Janský acknowledges support from the Czech Science Foundation (CORPTAX, 21-05547M) (https://gacr.cz/), the Greens/EFA Group in the European Parliament (https://www.greens-efa.eu/) and the H2020-MSCA-RISE project GEMCLIME-2020 GA No. 681228 (https://www.eeas.europa.eu/eeas/horizon-2020_en). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
Study reveals the real tax rate paid by multinational corporations in 47 countries
Calculations of effective tax rates of multinational corporations across countries show drastic differences between those rates and statutory tax rates.
2023-11-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Unknown animals were leaving bird-like footprints in Late Triassic Southern Africa
2023-11-29
Ancient animals were walking around on bird-like feet over 210 million years ago, according to a study published November 29, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Miengah Abrahams and Emese M. Bordy of the University of Cape Town, South Africa.
Numerous fossil sites in southern Africa preserve distinctive three-toed footprints that have been named Trisauropodiscus. For many years, researchers have debated what animals might have left these tracks, as well as precisely how many different species (technically called ichnospecies) of Trisauropodiscus there are.
In this study, the researchers reassessed the ...
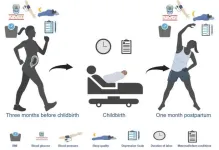
Exercise may reduce postpartum depression, with moderate intensity exercises three to four times a week being especially effective, per meta-analysis
2023-11-29
Exercise may reduce postpartum depression, with moderate intensity exercises three to four times a week being especially effective, per meta-analysis
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0287650
Article Title: Effectiveness of aerobic exercise in the prevention and treatment of postpartum depression: Meta-analysis and network meta-analysis
Author Countries: China
Funding: This work was financially supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities in China (Grant no. CUG150607). The funders did not play a role ...
Breaking down barriers: What happens when the vaginal microbiome attacks
2023-11-29
Bacterial vaginosis is a common condition in which the natural microbiome of the vagina falls out of balance, sometimes leading to complications in sexual and reproductive health. But exactly how these bacterial populations disrupt vaginal health has remained unclear.
Researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine have now found that in bacterial vaginosis, certain bacterial species dismantle protective molecules on the surface of the cells lining the vagina, dysregulating key processes that mediate cell turnover, death and response to surrounding bacteria.
The findings, published November 29, 2023 in Science Translational Medicine, may help explain why bacterial ...
Being prepared for storm surges on the Baltic Sea coast
2023-11-29
The record storm surge in October 2023 caused severe damage to the German Baltic coast. Effective adaptation scenarios to rising sea levels are therefore becoming increasingly urgent. In two recent studies, researchers at Kiel University have modelled both the flooding extent along the Baltic Sea coastal areas and, for the first time, two possible upgrades for current dike lines in high resolution. They modelled various storm surge and sea level rise scenarios. Their results show that, based on the current dike line, neither an increase ...
Findings challenge standard understanding of COVID-19 infection
2023-11-29
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- Some viruses move between species. For example, SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, can spill over from humans to mink, an agricultural species, and then spill back from mink to humans. Spill back is a concern because SARS-CoV-2 can mutate in the mink and come back to humans in a more virulent form. Both spill over and spill back of SARS-CoV-2 have been reported on mink farms in the United States and Europe.
To address these issues, a research team at the University of California, Riverside, has ...
Building the digital replica of our seas: an open call for crucial biodiversity data to restore ocean ecosystems
2023-11-29
The Horizon Europe DTO-BioFlow project (https://dto-bioflow.eu) has launched an Open Call offering up to 60,000€ for institutions that manage marine biodiversity data, to invite them to contribute to the European Digital Twin of the Ocean (EU DTO) by making these data available to the public domain through EMODnet Biology, the portal that provides open and free access to interoperable data and data products on temporal and spatial distribution of marine species (angiosperms, benthos, birds, fish, macroalgae, mammals, reptiles, phyto- and zooplankton) from European regional seas. Published officially on Tuesday, October 31st, this single-stage call is open to a wide ...
New research sheds light on Bantu-speaking populations' expansion in Africa
2023-11-29
About 350 million people across Africa speak one or more of the 500 Bantu languages. New genetic analysis of modern and ancient individuals suggests that these populations probably originated in western Africa and then moved south and east in several waves. The study has been published in the scientific journal Nature.
The expansion of people speaking Bantu languages is considered one of the most dramatic demographic events in Late Holocene Africa, which began 6,000 to 4,000 years ago in western Africa. This new study generated and analysed a comprehensive dataset, including genomic data of modern-day populations from 1,763 participants ...
Popularity matters more than compatibility on dating apps
2023-11-29
A new study has found that algorithms used by online dating platforms have popularity bias - meaning that they recommend more popular, attractive users over less popular, less attractive users. Researchers at Carnegie Mellon University and the University of Washington published their findings in Manufacturing & Service Operations Management.
They evaluated data from over 240,000 users of a major online dating platform in Asia over three months. They found that a user's chance of being recommended by the platform's algorithm ...
Markey Cancer Center research highlights need for education to combat cancer in Appalachia
2023-11-29
LEXINGTON, Ky. (Nov. 29, 2023) — University of Kentucky Markey Cancer Center research underscores the need for interventions to increase educational attainment and knowledge of cancer in Appalachian Kentucky.
Kentucky has the highest rate of cancer incidence and mortality in the country, with the Eastern Appalachian region bearing the highest burden due to health, socioeconomic and education disparities including decreased education attainment levels that cause lower health ...
Contraception: hormonal and copper coil only show minor differences
2023-11-29
In the “ThemenCheck Medizin” procedure offered by the German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG), interested members of the public can submit proposals for the assessment of medical procedures and technologies. On behalf of IQWiG, an interdisciplinary team of researchers led by Share to Care GmbH in Cologne investigated the advantages and disadvantages of two types of contraceptive coils (also known as intrauterine devices, IUDs) for preventing unwanted pregnancies, the copper IUD and the hormonal IUD.
Their conclusion: both types of IUDs are very safe and, compared to condoms or the pill, cost-effective contraceptive ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
[Press-News.org] Study reveals the real tax rate paid by multinational corporations in 47 countriesCalculations of effective tax rates of multinational corporations across countries show drastic differences between those rates and statutory tax rates.