(Press-News.org) Ancient animals were walking around on bird-like feet over 210 million years ago, according to a study published November 29, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Miengah Abrahams and Emese M. Bordy of the University of Cape Town, South Africa.
Numerous fossil sites in southern Africa preserve distinctive three-toed footprints that have been named Trisauropodiscus. For many years, researchers have debated what animals might have left these tracks, as well as precisely how many different species (technically called ichnospecies) of Trisauropodiscus there are.
In this study, the researchers reassessed the fossil record of these footprints, examining physical fossil traces alongside published materials documenting Trisauropodiscus at four sites in Lesotho dating to the Late Triassic and Early Jurassic Periods. The authors also provided a detailed field-based description of footprints from an 80-meter-long tracksite in Maphutseng. They identified two distinct morphologies among Trisauropodiscus footprints, the first of which is similar to certain non-bird dinosaur tracks, and the second of which is very similar in size and proportions to the footprints of birds.
These tracks aren’t a direct match for any fossil animals known from this region and time period. The most ancient of these footprints, at over 210 million years old, are 60 million years older than the earliest known body fossils of true birds. It’s possible that these tracks were produced by early dinosaurs, and potentially even early members of a near-bird lineage, but the authors note that there could also have been other reptiles, cousins of dinosaurs, that convergently evolved bird-like feet. Whoever the trackmakers are, these footprints establish the origin of bird-like feet at least as early as the Late Triassic Period.
The authors add: “Trisauropodiscus tracks are known from numerous southern African sites dating back to approximately 215 million years ago. The shape of the tracks is consistent with modern and more recent fossil bird tracks, but it is likely a dinosaur with a bird-like foot produced Trisauropodiscus.”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0293021
Citation: Abrahams M, Bordy EM (2023) The oldest fossil bird-like footprints from the upper Triassic of southern Africa. PLoS ONE 18(11): e0293021. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0293021
Author Countries: South Africa
Funding: This work was supported by the following grants: EMB (as PI) – National Research Foundation of South Africa Competitive Programme for Rated Researchers [93544, 113394], African Origins Platform [98825]; MA (as PI) – UCT Research Development Grant [2021, 2022], DSI – NRF Centre of Excellence in Palaeosciences (Genus) We Dig Fossils [86073]. MA also acknowledges DSI – NRF Centre of Excellence in Palaeosciences (Genus) postgraduate funding [2016 – 2018]. The funders had no role in the study design, data collection, analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. https://www.nrf.ac.za ; https://www.genus.africa.
END
Unknown animals were leaving bird-like footprints in Late Triassic Southern Africa
These tracks pre-date the oldest bird bone by around 60 million years
2023-11-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
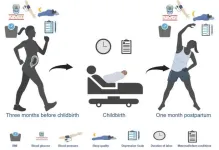
Exercise may reduce postpartum depression, with moderate intensity exercises three to four times a week being especially effective, per meta-analysis
2023-11-29
Exercise may reduce postpartum depression, with moderate intensity exercises three to four times a week being especially effective, per meta-analysis
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0287650
Article Title: Effectiveness of aerobic exercise in the prevention and treatment of postpartum depression: Meta-analysis and network meta-analysis
Author Countries: China
Funding: This work was financially supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities in China (Grant no. CUG150607). The funders did not play a role ...
Breaking down barriers: What happens when the vaginal microbiome attacks
2023-11-29
Bacterial vaginosis is a common condition in which the natural microbiome of the vagina falls out of balance, sometimes leading to complications in sexual and reproductive health. But exactly how these bacterial populations disrupt vaginal health has remained unclear.
Researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine have now found that in bacterial vaginosis, certain bacterial species dismantle protective molecules on the surface of the cells lining the vagina, dysregulating key processes that mediate cell turnover, death and response to surrounding bacteria.
The findings, published November 29, 2023 in Science Translational Medicine, may help explain why bacterial ...
Being prepared for storm surges on the Baltic Sea coast
2023-11-29
The record storm surge in October 2023 caused severe damage to the German Baltic coast. Effective adaptation scenarios to rising sea levels are therefore becoming increasingly urgent. In two recent studies, researchers at Kiel University have modelled both the flooding extent along the Baltic Sea coastal areas and, for the first time, two possible upgrades for current dike lines in high resolution. They modelled various storm surge and sea level rise scenarios. Their results show that, based on the current dike line, neither an increase ...
Findings challenge standard understanding of COVID-19 infection
2023-11-29
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- Some viruses move between species. For example, SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, can spill over from humans to mink, an agricultural species, and then spill back from mink to humans. Spill back is a concern because SARS-CoV-2 can mutate in the mink and come back to humans in a more virulent form. Both spill over and spill back of SARS-CoV-2 have been reported on mink farms in the United States and Europe.
To address these issues, a research team at the University of California, Riverside, has ...
Building the digital replica of our seas: an open call for crucial biodiversity data to restore ocean ecosystems
2023-11-29
The Horizon Europe DTO-BioFlow project (https://dto-bioflow.eu) has launched an Open Call offering up to 60,000€ for institutions that manage marine biodiversity data, to invite them to contribute to the European Digital Twin of the Ocean (EU DTO) by making these data available to the public domain through EMODnet Biology, the portal that provides open and free access to interoperable data and data products on temporal and spatial distribution of marine species (angiosperms, benthos, birds, fish, macroalgae, mammals, reptiles, phyto- and zooplankton) from European regional seas. Published officially on Tuesday, October 31st, this single-stage call is open to a wide ...
New research sheds light on Bantu-speaking populations' expansion in Africa
2023-11-29
About 350 million people across Africa speak one or more of the 500 Bantu languages. New genetic analysis of modern and ancient individuals suggests that these populations probably originated in western Africa and then moved south and east in several waves. The study has been published in the scientific journal Nature.
The expansion of people speaking Bantu languages is considered one of the most dramatic demographic events in Late Holocene Africa, which began 6,000 to 4,000 years ago in western Africa. This new study generated and analysed a comprehensive dataset, including genomic data of modern-day populations from 1,763 participants ...
Popularity matters more than compatibility on dating apps
2023-11-29
A new study has found that algorithms used by online dating platforms have popularity bias - meaning that they recommend more popular, attractive users over less popular, less attractive users. Researchers at Carnegie Mellon University and the University of Washington published their findings in Manufacturing & Service Operations Management.
They evaluated data from over 240,000 users of a major online dating platform in Asia over three months. They found that a user's chance of being recommended by the platform's algorithm ...
Markey Cancer Center research highlights need for education to combat cancer in Appalachia
2023-11-29
LEXINGTON, Ky. (Nov. 29, 2023) — University of Kentucky Markey Cancer Center research underscores the need for interventions to increase educational attainment and knowledge of cancer in Appalachian Kentucky.
Kentucky has the highest rate of cancer incidence and mortality in the country, with the Eastern Appalachian region bearing the highest burden due to health, socioeconomic and education disparities including decreased education attainment levels that cause lower health ...
Contraception: hormonal and copper coil only show minor differences
2023-11-29
In the “ThemenCheck Medizin” procedure offered by the German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG), interested members of the public can submit proposals for the assessment of medical procedures and technologies. On behalf of IQWiG, an interdisciplinary team of researchers led by Share to Care GmbH in Cologne investigated the advantages and disadvantages of two types of contraceptive coils (also known as intrauterine devices, IUDs) for preventing unwanted pregnancies, the copper IUD and the hormonal IUD.
Their conclusion: both types of IUDs are very safe and, compared to condoms or the pill, cost-effective contraceptive ...
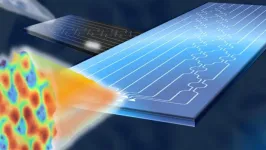
The chip that makes calculations with light
2023-11-29
Optical wireless may no longer have any obstacles. A study by Politecnico di Milano, conducted together with Scuola Superiore Sant'Anna in Pisa, the University of Glasgow and Stanford University, and published in the prestigious journal Nature Photonics, has made it possible to create photonic chips that mathematically calculate the optimal shape of light to best pass through any environment, even one that is unknown or changing over time.
The problem is well known: light is sensitive to any form of obstacle, even very small ones. Think, for example, of how we see objects when looking through a frosted window ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Governing with AI: a new AI implementation blueprint for policymakers
Recent pandemic viruses jumped to humans without prior adaptation, UC San Diego study finds
Exercise triggers memory-related brain 'ripples' in humans, researchers report
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
[Press-News.org] Unknown animals were leaving bird-like footprints in Late Triassic Southern AfricaThese tracks pre-date the oldest bird bone by around 60 million years