(Press-News.org) “Dripstones, or speleothems, are unique natural archives - like Earth’s USB sticks. They store a wealth of information on past climate which helps us to better understand the environment in which early humans lived”, Jenny Maccali explains. She is a scientist at SapienCE Centre of Excellence, and has has lead the study, now published in Climate of the Past.
New perspective to ancient climate
South Africa has a highly dynamic climate resulting from its position at the convergence of two oceanic basins, the Atlantic Ocean to the west and the Indian Ocean to the east. The region is also located at the boundary of different climate zones (subtropical vs. temperate), and the proximity of the Antarctic ice sheet has a direct impact on its climate by influencing the easterlies and westerlies winds position, and hence rainfall pattern.
“All these factors mean that climate in the past could have been different from today and also possibly highly variable”, Jenny Maccali says.
She says that it is particularly important given that the region hosts key archaeological sites with records of significant cognitive, technological, and social developments and it is important to understand the climatic conditions under which these occurred.
Archives for climate reconstruction
A recent study, Multi-proxy speleothem-based reconstruction of mid-MIS 3 climate in South Africa, undertaken by a team of scientists from SapienCE, used new techniques to reconstruct past climate and its variability.
Maccali and her team of researchers have focused on the subterranean world of caves, where they explore dripstones, also known as speleothems, to study past climate. The study is based on scientific analyses of speleothems from Bloukrantz Cave.
“Dripstones forming in caves are excellent archives for climate reconstructions, because their age can be accurately determined and a suite of methods can be used to reconstruct different aspects of past climate”, Maccali says.
Insights to early human occupations
One of the dripstones from Bloukrantz cave, located on the southern coast of South Africa, provided the team with new climate data for a time window of 3000 years during the last glacial period – from around 45,000 years ago. They used different methods that confirmed the average air temperature for this period of 18.8 ± 0.5 ◦C, which was slightly warmer compared to the present day, possibly because the sea level was lower, and the site was further away from the coastline than today. In addition, we could show, again based on multiple methods, that rainfall was highly variable with repeated drying events.
“Combining these insights, our study was able to increase confidence in the methods that were being used and further work will likely provide a detailed picture of the climate around the early human occupations during a crucial time period in South Africa”, Maccali says.
END
Decoding past climates through dripstones
2023-11-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Lower voltage and reduced carbon input for cleaner energy in the works
2023-11-30
There is an ever-present struggle to reduce carbon-based energy sources and replace them with low or no-carbon alternatives. The process of splitting water could be the resolution.
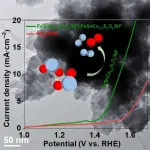
Hydrogen production is a simple, safe, and effective method to produce more energy than gasoline can by the simple process of splitting water. Harvesting energy this way as opposed to relying heavily (or at all) on carbon-based energy sources is increasingly becoming the standard. Researchers have found a method to use transition metal ...
Platoon control of connected vehicles with heterogeneous model structures considering external disturbances
2023-11-30
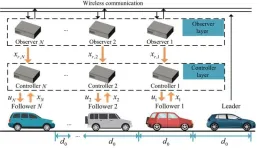
A paper describing the distributed cooperative control problem with the heterogeneous model structures and external disturbances for the connected vehicle (CV) platoon was published in the journal Green Energy and Intelligent Transportation on November 25th, 2022.
In recent decades, the cooperative control problems of CV platoon on highways have attracted widespread interest for their significant impact on road transportation. The platoon control of CV has the advantages of improving the safety of highways, increasing the ...
NCCN and SLACOM host international symposium to improve breast cancer care in Latin America
2023-11-30
BUENOS AIRES, ARGENTINA & PLYMOUTH MEETING, UNITED STATES [November 30, 2023] — Today the Latin American and Caribbean Society of Medical Oncology (SLACOM) and National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®) host the Latin American Regional Breast Cancer Summit: Advocating and Implementing Guideline-Concordant Cancer Care for Patients. Esteemed experts from Argentina, Brazil, Mexico, Columbia, Peru, and the United States will present challenges, barriers, and potential solutions for improving access to guideline-concordant breast cancer care in the Latin American region. The regional summit provides an opportunity for a diverse group ...
Innovative gel offers new hope for treating gastrointestinal leaks
2023-11-30
In a major advancement in medical technology, researchers at the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation have developed an adhesive gel, offering a revolutionary treatment for gastrointestinal leaks, a condition clinically known as enterocutaneous fistulas. This development marks a significant milestone in addressing a challenging medical condition that has long plagued patients and clinicians.
Enterocutaneous fistulas, which are abnormal connections between the gastrointestinal tract and the skin, are primarily a ...
Choice of intravenous fluid therapy could improve survival in critically ill patients
2023-11-30
Results of a new meta-analysis in shows that intravenous fluid (IV) therapy using balanced solutions rather than commonly used saline can reduce the risk of in-hospital death of critically ill patients by four percent.
Findings from the BEST-Living Study were presented today at the Critical Care Canada Forum (CCCF 2023) and simultaneously published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine.
Prof Simon Finfer AO, an Intensive Care physician, Professorial Fellow at The George Institute for Global Health, and Adjunct Professor, UNSW Sydney - who was the senior author on the paper - said the results supported the important ...
Recent advances in tree nut research — walnuts, pecans and more
2023-11-30
As the holiday season approaches, many home kitchens will produce the mouthwatering smells of fresh-baked goods and comfort food. From macadamia nut cookies and pecan pies to turkey stuffing, nuts feature heavily in seasonal pastries and dishes. Below are some recent papers published in ACS journals that report new insights into popular tree nuts. Reporters can request free access to these papers by emailing newsroom@acs.org.
“Bulk and Compound-Specific Stable Isotope Analysis for the Authentication of Walnuts (Juglans regia) ...
HRS-AKI treatment options could be expanded
2023-11-30
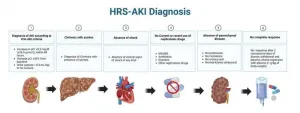
A new study published in the journal eGastroenterology provides an updated assessment of the diagnosis, pathophysiology, and treatment of hepatorenal syndrome-acute kidney injury (HRS-AKI). This severe and often fatal condition can occur in patients with cirrhosis.
HRS-AKI is a functional and progressive kidney failure that is potentially reversible but most often rapidly fatal. It accounts for 11%–20% of all AKI episodes in patients with cirrhosis, and its diagnosis is often challenging to differentiate from prerenal or acute tubular necrosis (ATN).
The study, led by Jorge Arnold, found that early recognition of HRS-AKI is crucial for standard pharmacological treatment with terlipressin ...
A novel targeted molecular therapy for drug-resistant biliary tract cancer
2023-11-30
Biliary tract cancers (BTCs) including cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) and gallbladder cancer (GBC) are becoming more prevalent globally. An effective chemotherapeutic agent for the treatment of BTCs is gemcitabine. Other novel molecular targeted drugs have also been developed; however, they are only effective at treating a few cases of BTCs. In addition, very few drugs are effective against GEM-resistant BTCs. While surgery is the best option for the treatment of BTCs, many patients are diagnosed late, due to a lack of symptoms. ...
Money to burn: Wealthy, white neighborhoods losing their heat shields
2023-11-30
White, wealthy neighborhoods in the LA area are about to start feeling the same heat that has plagued poorer, Hispanic neighborhoods for generations. A new study shows the protective effect of income has largely eroded over the past 40 years, as landscape plants can’t keep up with the pace of climate warming.
Published in the journal Urban Climate, the research cuts across neighborhoods, income levels, and race in the Los Angeles area between 1985 and 2021. It reveals a troubling forecast for city dwellers: it’s becoming unbearably hot, ...
Children who play baseball risk elbow injury
2023-11-30
CHICAGO – Youth baseball players are prone to elbow pain and injuries, including repetitive overuse changes and fractures, based on the maturity of their bones, according to a new study being presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
The repetitive motion and force of throwing a baseball places a large amount of stress on the growing bones, joints and muscles of the elbows of baseball players. Youth baseball players who have not yet reached skeletal maturity might be especially vulnerable to elbow pain and injuries.
“When we look at the forces that baseball players, even ...