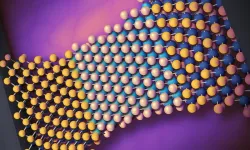
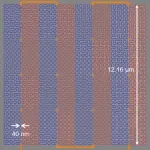
(Press-News.org) By strategically straining materials that are as thin as a single layer of atoms, University of Rochester scientists have developed a new form of computing memory that is at once fast, dense, and low-power. The researchers outline their new hybrid resistive switches in a study published in Nature Electronics.
Developed in the lab of Stephen M. Wu, an assistant professor of electrical and computer engineering and of physics, the approach marries the best qualities of two existing forms of resistive switches used for memory: memristors and phase-change materials. Both forms have been explored for their advantages over today’s most prevalent forms of memory, including dynamic random access memory (DRAM) and flash memory, but have their drawbacks.
Wu says that memristors, which operate by applying voltage to a thin filament between two electrodes, tend to suffer from a relative lack of reliability compared to other forms of memory. Meanwhile, phase-change materials, which involve selectively melting a material into either an amorphous state or a crystalline state, require too much power.
“We’ve combined the idea of a memristor and a phase-change device in a way that can go beyond the limitations of either device,” says Wu. “We’re making a two-terminal memristor device, which drives one type of crystal to another type of crystal phase. Those two crystal phases have different resistance that you can then story as memory.”
The key is leveraging 2D materials that can be strained to the point where they lie precariously between two different crystal phases and can be nudged in either direction with relatively little power.
“We engineered it by essentially just stretching the material in one direction and compressing it in another,” says Wu. “By doing that, you enhance the performance by orders of magnitude. I see a path where this could end up in home computers as a form of memory that’s ultra-fast and ultra-efficient. That could have big implications for computing in general.”
Wu and his team of graduate students conducted the experimental work and partnered with researchers from Rochester’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, including assistant professors Hesam Askari and Sobhit Singh, to identify where and how to strain the material. According to Wu, the biggest hurdle remaining to making the phase-change memristors is continuing to improve their overall reliability—but he is nonetheless encouraged by the team’s progress to date.
END
Straining memory leads to new computing possibilities
Researchers develop hybrid phase-change memristors that offer fast, low-power, and high-density computing memory
2023-11-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Antarctica's ancient ice sheets foreshadow dynamic changes in Earth’s future
2023-11-30
MADISON – Nineteen million years ago, during a time known as the early Miocene, massive ice sheets in Antarctica rapidly and repeatedly grew and receded. The Miocene is widely considered a potential analog for Earth's climate in the coming century, should humanity remain on its current carbon emissions trajectory.
Identifying how and why Antarctica's major ice sheets behaved the way they did in the early Miocene could help inform understanding of the sheets' behavior under a warming climate. Together, the ice sheets lock a volume of water equivalent to more than 50 meters of sea level rise and influence ocean currents that affect marine food webs and regional climates. ...
Modular chimeric cytokine receptors improve CAR T–cell therapy for solid tumors
2023-11-30
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – November 30, 2023) Immunotherapy using modified chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells has greatly improved survival rates for pediatric patients with relapsed and recurrent leukemia. However, these therapies are not as effective in treating solid tumors and can have significant toxicity. Findings from St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital showed that adding a modular chimeric cytokine receptor to CAR T cells increased their efficacy in multiple solid tumor models. The study was published today in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
“We designed modular chimeric cytokine receptors and showed that ...
Climate: why disinformation is so persistent
2023-11-30
Melting of glaciers, rising sea levels, extreme heat waves: the consequences of climate change are more visible than ever, and the scientific community has confirmed that humans are responsible. Yet studies show that a third of the population still doubts or disputes these facts. The cause is disinformation spread by certain vested interests. To try and prevent this phenomenon, a team from the University of Geneva (UNIGE) has developed and tested six psychological interventions on nearly 7,000 participants from twelve countries. The research, published in ...
Early body contact develops premature babies' social skills
2023-11-30
Skin-to-skin contact between parent and infant during the first hours after a very premature birth helps develop the child's social skills. This is according to a new study published in JAMA Network Open by researchers from Karolinska Institutet and others. The study also shows that fathers may play a more important role than previous research has shown.
In current practice, very premature babies are usually placed in an incubator to keep them warm and to stabilize them during the first hours after birth. In the “Immediate parent-infant skin-to-skin study” (IPISTOSS), 91 premature babies born at 28 to 33 weeks were randomized to either ...
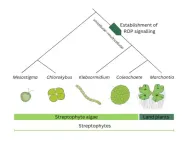
ROP signaling: Origin at dawn of multicellular plant life
2023-11-30
Plants regulate their development with a distinct group of molecular players. ROP proteins, a group of plant-specific proteins, are known to control plant tissue formation. Now, Hugh Mulvey and Liam Dolan at the GMI show that ROP proteins evolved at the transition between unicellular and multicellular plant life. The findings are published on November 30 in the journal Current Biology.
Being non-mobile, plants follow a very different lifestyle from us animals. To grow and develop, plants also need a distinct ...
Twin research indicates that that a vegan diet improves cardiovascular health
2023-11-30
In a study with 22 pairs of identical twins, Stanford Medicine researchers and their colleagues have found that a vegan diet improves cardiovascular health in as little as eight weeks.
Although it’s well-known that eating less meat improves cardiovascular health, diet studies are often hampered by factors such as genetic differences, upbringing and lifestyle choices. By studying identical twins, however, the researchers were able to control for genetics and limit the other factors, as the twins grew up in the same households ...
A mineral produced by plate tectonics has a global cooling effect, study finds
2023-11-30
MIT geologists have found that a clay mineral on the seafloor, called smectite, has a surprisingly powerful ability to sequester carbon over millions of years.
Under a microscope, a single grain of the clay resembles the folds of an accordion. These folds are known to be effective traps for organic carbon.
Now, the MIT team has shown that the carbon-trapping clays are a product of plate tectonics: When oceanic crust crushes against a continental plate, it can bring rocks to the surface that, over ...
Age disparities in prevalence of anxiety and depression among adults during the pandemic
2023-11-30
About The Study: In this study of 3 million U.S. adults, anxiety and depression were significantly higher among adults ages 18 to 39 compared with adults age 40 and older during the COVID-19 pandemic. Less favorable economic conditions and responses to social upheaval may have contributed to young adults’ worse mental well-being. These findings suggest a need for greater mental health care and economic policies targeted toward younger adults.
Authors: Sarah Collier Villaume, Ph.D., of Northwestern University in Evanston, ...
Structural racism and lung cancer risk
2023-11-30
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that structural racism must be considered as a fundamental contributor to the unequal distribution of lung cancer risk factors and thus disparate lung cancer risk across different racial and ethnic groups. Additional research is needed to better identify mechanisms contributing to inequitable lung cancer risk and tailor preventive interventions.
Authors: Sidra N. Bonner, M.D., M.P.H., M.Sc., of the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
Traumatic memories are represented differently than regular sad memories in the brains of people with PTSD, new research shows
2023-11-30
A new analysis of the brain activity of people with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is the first to reveal that traumatic memories are represented in the brain in an entirely different way than sad autobiographical memories.
This finding supports the notion that traumatic memories in PTSD are an alternate cognitive entity that deviates from regular memory, and may provide a biological explanation for why the recall of traumatic memories often displays as intrusions that differ profoundly from “regular” negative memories for patients with PTSD.
The study, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Gibson Oncology, NIH to begin Phase 2 trials of LMP744 for treatment of first-time recurrent glioblastoma
Researchers develop a high-efficiency photocatalyst using iron instead of rare metals
Study finds no evidence of persistent tick-borne infection in people who link chronic illness to ticks
New system tracks blockchain money laundering faster and more accurately
In vitro antibacterial activity of crude extracts from Tithonia diversifolia (asteraceae) and Solanum torvum (solanaceae) against selected shigella species
Qiliang (Andy) Ding, PhD, named recipient of the 2026 ACMG Foundation Rising Scholar Trainee Award
Heat-free gas sensing: LED-driven electronic nose technology enhances multi-gas detection
Women more likely to choose wine from female winemakers
E-waste chemicals are appearing in dolphins and porpoises
Researchers warn: opioids aren’t effective for many acute pain conditions
Largest image of its kind shows hidden chemistry at the heart of the Milky Way
JBNU researchers review advances in pyrochlore oxide-based dielectric energy storage technology
Novel cellular phenomenon reveals how immune cells extract nuclear DNA from dying cells
Printable enzyme ink powers next-generation wearable biosensors
6 in 10 US women projected to have at least one type of cardiovascular disease by 2050
People’s gut bacteria worse in areas with higher social deprivation
Unique analysis shows air-con heat relief significantly worsens climate change
Keto diet may restore exercise benefits in people with high blood sugar
Manchester researchers challenge misleading language around plastic waste solutions
Vessel traffic alters behavior, stress and population trends of marine megafauna
Your car’s tire sensors could be used to track you
Research confirms that ocean warming causes an annual decline in fish biomass of up to 19.8%
Local water supply crucial to success of hydrogen initiative in Europe
New blood test score detects hidden alcohol-related liver disease
High risk of readmission and death among heart failure patients
Code for Earth launches 2026 climate and weather data challenges
Three women named Britain’s Brightest Young Scientists, each winning ‘unrestricted’ £100,000 Blavatnik Awards prize
Have abortion-related laws affected broader access to maternal health care?
Do muscles remember being weak?
Do certain circulating small non-coding RNAs affect longevity?
[Press-News.org] Straining memory leads to new computing possibilitiesResearchers develop hybrid phase-change memristors that offer fast, low-power, and high-density computing memory