(Press-News.org) Millions of people are suffering from digital health inequality because of poverty, experts have warned.
A new study says urgent work is needed to ensure those from deprived areas can access healthcare as the NHS increasingly turns to the use of apps and online health portals for the provision of healthcare.
A team of doctors and academics found a “significant association” between increased poverty and reduced use of digital services. Their modelling estimates that this association accounts for 4.27million patients across England who have not downloaded the NHS app. In October 2022 it was estimated more than 37million patients had activated the NHS App - 67.9 per cent of the population.
Researchers used aggregate data about patients and their use of digital resources from 6,356 primary care providers – GP practice centres – in England to measure the link between characteristics such as patient demographics, socio-economic deprivation, disease burden, prescribing burden, geography, and healthcare provider resource, with activation of two universal digital healthcare interventions in the NHS – the NHS App, and online primary care portals.
As the data used was aggregated from national datasets, researchers couldn’t identify any patients during the analysis.
The study was carried out by academics and doctors – Dr Joe Zhang from Imperial College London, , Dr Jack Gallifant from Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Professor Robin L Pierce from the University of Exeter, Dr Aoife Fordham from the Transformation Directorate, NHS England, Professor James T Teo from King’s College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, Professor Leo A Celi from Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, and Professor Hutan Ashrafian from Imperial College London.
Professor Pierce said: “Our results are concerning and show how the use of technology risks widening healthcare inequalities. Digital inequality between those from different socio-economic backgrounds is substantial. The study estimates deprivation is associated with reduced NHS app uptake in 4.27million patients across England.
“What is needed now is for targeted work in communities to prevent digital disparity affecting health outcomes. As the NHS aims to make apps the ‘front door’ to healthcare it is imperative that there is frank and open discussion about equitable digital technology implementation.”
The study says digital literacy and availabilities of devices and infrastructure may account for some of the disparity. It recommends digital transformation must be context-specific, based on local understanding and tailored to specific populations.
Infrastructure, education, and engagement are also important and the roll-out of digital systems should be driven through those who run integrated care systems, who can build strong community links.
Dr Zhang said: “Although we found inequalities this is not necessarily a reason to decelerate. Rather, digitally-enhanced pathways may offer efficiency savings that can be re-directed to vulnerable and excluded populations.”
The study says the NHS should proactively identify those communities at highest risk of digital exclusion, who would then get targeted attention. Dr. Zhang emphasised that a main contribution of this study is the quantification of digital health uptake. He points out that this can allow us to estimate the negative impacts of large scale digital health interventions. It also recommends the NHS should publish data about disparities in uptake and outcomes.
Dr. Zhang said: “We have demonstrated substantial socio-economic inequality in digital health utilisation in NHS England. Such patterns will likely be observable in any health system undergoing rapid digital transformation. An approach that addresses needs of specific groups disadvantaged by the increasing use of digital health technology is urgently required to avoid worsening digital health inequality.”
END
Urgent work needed to tackle “substantial” digital health inequality, study recommends
2023-12-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Unlocking the secret strength of marine mussels
2023-12-01
How do you create strong, yet quick-release connections between living and non-living tissues? This is a question that continues to puzzle bioengineers who aim to create materials that bond together for advanced biomedical applications.
Looking to nature for inspiration, the McGill-led research zeroed in on the marine mussel byssus, a fibrous holdfast, which these bivalve mollusks use to anchor themselves in seashore habitats. The byssus attaches to rocky surfaces using an underwater glue, but the other end (the byssus stem root) is firmly anchored within the mussel’s soft living tissue. This area of contact between the living ...
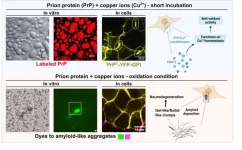
When physics meets biology: prion protein orchestrates liquid-liquid phase separation with copper
2023-12-01
In a groundbreaking study published in Science Advances, researchers from the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro (UFRJ) and the German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases (DZNE-Berlin) shed light on the intricate dance between the prion protein and copper ions in the physiopathology of live cells. The research paves the way for potential treatments addressing copper-bound prion protein clusters to prevent abnormal solid formation and mitigate neurodegenerative outcomes.
Like oil droplets in water, cells harbor membrane-bound organelles that ...
Eminent scientists say a child-centric approach is the blueprint to improve communities
2023-12-01
Communities can prosper by providing attentive education and social services to their youngest residents — but the challenge is for leaders to work together.
That is the message of Craig Ramey and Sharon Ramey, Virginia Tech distinguished research professors of the Fralin Biomedical Research Institute at VTC, who today (Dec. 1, 2023) presented details of a decades-long study that focuses on early childhood education and development.
In a research article in the journal Medical Research Archives, the official journal of the European Society of Medicine, the scientists discuss lessons ...
Adverse childhood experiences linked to muscle dysmorphia
2023-12-01
Toronto, ON – A new study published in Clinical Social Work Journal found that adolescents and young adults who experienced adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) before the age of 18 were significantly more likely to experience symptoms of muscle dysmorphia.
With previous research showing that more than half of North American children and adolescents experience at least one adverse childhood experience in their lifetime, these new findings highlight the need for greater awareness of how adverse experiences in childhood (such as domestic violence, emotional abuse, and sexual abuse) and muscle dysmorphia (the pathological ...
New health problems emerge after COVID-19 for those who lack quality housing, health care
2023-12-01
New research from the Texas A&M University School of Public Health suggests that those who live with ongoing poverty and poor housing conditions are more likely to develop new mobility issues following a COVID-19 infection.
This study, published in Preventive Medicine, is the first to examine the relationship between social vulnerability and persistent COVID-19 symptoms. In it, researchers analyzed data about socially vulnerable Michigan residents who experienced new difficulty in walking or climbing stairs after ...
Two leading standards bodies launch Neuroscience Community, powering a global data network that will speed up answers in autism, Parkinson’s, addiction, and more
2023-12-01
The Global Alliance for Genomics and Health (GA4GH) and the International Neuroinformatics Coordinating Facility (INCF) launched a new group to lay the groundwork for connecting global neuroscience and genomic data.
Answering data-driven questions in neuroscience means dealing with complexity: in types of data, data management systems, the number and variety of conditions, ethical and legal requirements, and the genetic and biological conditions themselves. Even just aligning industry standards for neuroimaging and genomics can be a struggle.
To improve life for people with neurological conditions, we need to tackle the complexity together.
The new GA4GH & INCF Neuroscience ...
Novel screening tool and recovery program may help reduce mental health problems after trauma
2023-12-01
Key takeaways
A new mental health screening tool accurately predicts mental health outcomes for hospitalized trauma patients.
To be sustainable, mental health screening and recovery programs should be tailored to each trauma center, with the engagement of all stakeholders, a related study finds.
Studies shed light on the need for trauma centers to provide injured patients with mental health resources, such as online education, support, and referrals to mental healthcare providers when needed.
CHICAGO (December 1, 2023): A novel screening ...
Black men with advanced prostate cancer less likely to receive crucial treatment, study finds
2023-12-01
A new study led by investigators at the UCLA Health Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center found Black men diagnosed with more advanced stages of prostate cancer are significantly less likely to be prescribed novel hormone therapy than other racial and ethnic groups – including white or Latino men – despite the therapy being proven to effectively control the growth of prostate tumors and extend the lives of men with the disease.
The findings, published in JAMA Network Open, reveal a concerning racial disparity in the utilization of the crucial therapy for the treatment of the disease.
“This revelation is particularly concerning ...
Trends in adult smoking prevalence
2023-12-01
About The Study: This analysis of survey data from 353,000 U.S. adults found that smoking prevalence decreased from 2011 to 2022 in all age groups except adults 65 years or older, with faster decreases among younger than older adults. These findings suggest that the greatest gains in terms of reducing smoking-attributable morbidity and mortality could be achieved by focusing on individuals with low socioeconomic status, as this population has the highest smoking rates and the worst health prospects.
Authors: Rafael ...
Racial and ethnic disparities in use of recommended therapies for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, 1999-2020
2023-12-01
About The Study: In this study of 5,218 adults with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, significant disparities persisted between current care and optimal care, surpassing any differences observed among demographic groups. These findings highlight the critical need for sustained efforts to bridge these gaps and achieve better outcomes for all patients, regardless of their racial and ethnic backgrounds.
Authors: Harlan M. Krumholz, M.D., S.M., of Yale New Haven Hospital in New Haven, Connecticut, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.45964)
Editor’s ...