(Press-News.org) (Boston)—Alcohol is the most common addictive substance in the world. Every year in the U.S. excessive alcohol use costs $249 billion and causes approximately 88,000 deaths, as well as various chronic diseases and social issues. Alcohol use disorder, a highly prevalent, chronic, relapsing disorder, affects more than 14 million people in the U.S. alone, in addition to being severely under-treated, with only three modestly effective pharmacological therapies available.
Chronic exposure to alcohol has been shown to produce profound neuroadaptations in specific brain regions, including the recruitment of key stress neurotransmitters, ultimately causing changes in the body that sustain excessive drinking. The area of the brain known as the “bed nucleus of the stria terminalis” (BNST) is critically involved in the behavioral response to stress as well as in chronic, pathological alcohol use.
Researchers from Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine have identified that a peptide called pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide (PACAP), is involved in heavy alcohol drinking. In addition, they have discovered that this peptide acts in the BNST area.
Using an established experimental model for heavy, intermittent alcohol drinking, the researchers observed that during withdrawal this model showed increased levels of the stress neuropeptide PACAP selectively in the BNST, compared to the control model.
Interestingly, a similar increase was also observed in the levels of another stress neuropeptide closely related to PACAP, the calcitonin gene-related peptide, or CGRP. Both peptides have been implicated in stress as well as pain sensitivity, but their role in alcohol addiction is less established.
The researchers then used a virus in a transgenic model to block the neural pathways containing PACAP that specifically arrive to the BNST. "We found that inhibiting PACAP to the BNST dramatically reduced heavy ethanol drinking," explained co-corresponding author Valentina Sabino, PhD, co-director of the School’s Laboratory of Addictive Disorders as well as professor of pharmacology, physiology & biophysics.
According to the researchers, these results provide evidence that this protein mediates the addictive properties of alcohol. "We found a key player, PACAP, driving heavy alcohol drinking, which can be targeted for the development of novel pharmacological therapies," added co-corresponding author Pietro Cottone, PhD, associate professor of pharmacology, physiology & biophysics and co-director of the Laboratory of Addictive Disorders.
These findings appear online in the journal eNeuro.
Funding for this study was to grants number AA026051 (PC), AA025038 (VS), and AA024439 (VS) from the National Institute on Alcohol and Alcoholism (NIAAA), the Boston University Undergraduate Research Opportunities Program (UROP), the Boston University Micro and Nano Imaging Facility and the Office of the Director of the National Institutes of Health (S10OD024993).
END
Study identifies peptide as key mediator in heavy alcohol drinking
2023-12-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New understanding of oobleck-like fluids contributes to smart material design
2023-12-01
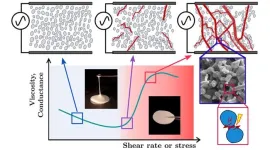
If you mix cornstarch and water in the right proportions, you get something that seems not-quite-liquid but also not-quite-solid. Oobleck flows and settles like a liquid when untouched, but stiffens when you try to pick it up or stir it with a spoon. The properties of oobleck and other non-Newtonian fluids — including Silly Putty, quicksand, paint, and yogurt — change under stress or pressure and scientists have long struggled to prove exactly why.
Now, researchers at the University of Chicago’s Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering (PME) have used piezoelectric nanoparticles, which themselves change in response to pressure, to investigate the fundamental physics of non-Newtonian ...
Brainstorming with a bot
2023-12-01
A researcher has just finished writing a scientific paper. She knows her work could benefit from another perspective. Did she overlook something? Or perhaps there's an application of her research she hadn't thought of. A second set of eyes would be great, but even the friendliest of collaborators might not be able to spare the time to read all the required background publications to catch up.
Kevin Yager—leader of the electronic nanomaterials group at the Center for Functional Nanomaterials (CFN), a U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science User Facility ...
Hip hop dancing promotes awareness of disability rights and performance equality, study shows
2023-12-01
Hip hop dancing can be used to spread awareness of disability rights and help those with sight problems to participate in performance equally, a new study says.
Breakin’ – which is commonly referred to as breakdancing - is good for mobility and helps promote balance and stability as well as wellbeing.
It also offers an important opportunity for people to slow down and to connect with their inner selves, their feelings, their bodies, and their peers, according to researchers. It has been used to treat symptoms of depression, anxiety and PTSD.
Nathan Geering, ...
Urgent work needed to tackle “substantial” digital health inequality, study recommends
2023-12-01
Millions of people are suffering from digital health inequality because of poverty, experts have warned.
A new study says urgent work is needed to ensure those from deprived areas can access healthcare as the NHS increasingly turns to the use of apps and online health portals for the provision of healthcare.
A team of doctors and academics found a “significant association” between increased poverty and reduced use of digital services. Their modelling estimates that this association accounts for 4.27million patients across England who have not downloaded the NHS app. In October 2022 it was estimated more than 37million patients had activated ...
Unlocking the secret strength of marine mussels
2023-12-01
How do you create strong, yet quick-release connections between living and non-living tissues? This is a question that continues to puzzle bioengineers who aim to create materials that bond together for advanced biomedical applications.
Looking to nature for inspiration, the McGill-led research zeroed in on the marine mussel byssus, a fibrous holdfast, which these bivalve mollusks use to anchor themselves in seashore habitats. The byssus attaches to rocky surfaces using an underwater glue, but the other end (the byssus stem root) is firmly anchored within the mussel’s soft living tissue. This area of contact between the living ...
When physics meets biology: prion protein orchestrates liquid-liquid phase separation with copper
2023-12-01
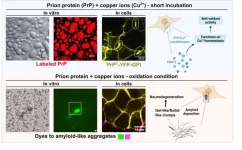
In a groundbreaking study published in Science Advances, researchers from the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro (UFRJ) and the German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases (DZNE-Berlin) shed light on the intricate dance between the prion protein and copper ions in the physiopathology of live cells. The research paves the way for potential treatments addressing copper-bound prion protein clusters to prevent abnormal solid formation and mitigate neurodegenerative outcomes.
Like oil droplets in water, cells harbor membrane-bound organelles that ...
Eminent scientists say a child-centric approach is the blueprint to improve communities
2023-12-01
Communities can prosper by providing attentive education and social services to their youngest residents — but the challenge is for leaders to work together.
That is the message of Craig Ramey and Sharon Ramey, Virginia Tech distinguished research professors of the Fralin Biomedical Research Institute at VTC, who today (Dec. 1, 2023) presented details of a decades-long study that focuses on early childhood education and development.
In a research article in the journal Medical Research Archives, the official journal of the European Society of Medicine, the scientists discuss lessons ...
Adverse childhood experiences linked to muscle dysmorphia
2023-12-01
Toronto, ON – A new study published in Clinical Social Work Journal found that adolescents and young adults who experienced adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) before the age of 18 were significantly more likely to experience symptoms of muscle dysmorphia.
With previous research showing that more than half of North American children and adolescents experience at least one adverse childhood experience in their lifetime, these new findings highlight the need for greater awareness of how adverse experiences in childhood (such as domestic violence, emotional abuse, and sexual abuse) and muscle dysmorphia (the pathological ...
New health problems emerge after COVID-19 for those who lack quality housing, health care
2023-12-01
New research from the Texas A&M University School of Public Health suggests that those who live with ongoing poverty and poor housing conditions are more likely to develop new mobility issues following a COVID-19 infection.
This study, published in Preventive Medicine, is the first to examine the relationship between social vulnerability and persistent COVID-19 symptoms. In it, researchers analyzed data about socially vulnerable Michigan residents who experienced new difficulty in walking or climbing stairs after ...
Two leading standards bodies launch Neuroscience Community, powering a global data network that will speed up answers in autism, Parkinson’s, addiction, and more
2023-12-01
The Global Alliance for Genomics and Health (GA4GH) and the International Neuroinformatics Coordinating Facility (INCF) launched a new group to lay the groundwork for connecting global neuroscience and genomic data.
Answering data-driven questions in neuroscience means dealing with complexity: in types of data, data management systems, the number and variety of conditions, ethical and legal requirements, and the genetic and biological conditions themselves. Even just aligning industry standards for neuroimaging and genomics can be a struggle.
To improve life for people with neurological conditions, we need to tackle the complexity together.
The new GA4GH & INCF Neuroscience ...