(Press-News.org) In a recent study led by University of Florida astronomer Adam Ginsburg, groundbreaking findings shed light on a mysterious dark region at the center of the Milky Way. The turbulent gas cloud, playfully nicknamed “The Brick” due to its opacity, has sparked lively debates within the scientific community for years.
To decipher its secrets, Ginsburg and his research team, including UF graduate students Desmond Jeff, Savannah Gramze, and Alyssa Bulatek, turned to the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). The implications of their observations, published in The Astrophysical Journal, are monumental. The findings not only unearth a paradox within the center of our galaxy but indicate a critical need to re-evaluate established theories regarding star formation.
The Brick has been one of the most intriguing and highly studied regions of our galaxies, thanks to its unexpectedly low star formation rate. It has challenged scientists’ expectations for decades: as a cloud full of dense gas, it should be ripe for the birth of new stars. However, it demonstrates an unexpectedly low star formation rate.
Using the JWST’s advanced infrared capabilities, the team of researchers peered into the Brick, discovering a substantial presence of frozen carbon monoxide (CO) there. It harbors a significantly larger amount of CO ice than previously anticipated, carrying profound implications for our understanding of star formation processes.
No one knew how much ice there was in the Galactic Center, according to Ginsburg. “Our observations compellingly demonstrate that ice is very prevalent there, to the point that every observation in the future must take it into account,” he said.
Stars typically emerge when gases are cool, and the significant presence of CO ice should suggest a thriving area for star formation in the Brick. Yet, despite this wealth of CO, Ginsburg and the research team found that the structure defies expectations. The gas inside the Brick is warmer than comparable clouds.
These observations challenge our understanding of CO abundance in the center of our galaxy and the critical gas-to-dust ratio there. According to the findings, both measures appear to be lower than previously thought.
“With JWST, we're opening new paths to measure molecules in the solid phase (ice), while previously we were limited to looking at gas,” said Ginsburg. “This new view gives us a more complete look at where molecules exist and how they are transported. “
Traditionally, the observation of CO has been limited to emission from gas. To unveil the distribution of CO ice within this vast cloud, the researchers required intense backlighting from stars and hot gas. Their findings move beyond the limitations of previous measurements, which were confined to around a hundred stars. The new results encompass over ten thousand stars, providing valuable insights into the nature of interstellar ice.
Since the molecules present in our Solar System today were, at some point, likely ice on small dust grains that combined to form planets and comets, the discovery also marks a leap forward toward understanding the origins of the molecules that shape our cosmic surroundings.
These are just the team’s initial findings from a small fraction of their JWST observations of the Brick. Looking ahead, Ginsburg sets his sights on a more extensive survey of celestial ices.
“We don't know, for example, the relative amounts of CO, water, CO2, and complex molecules,” said Ginsburg. “With spectroscopy, we can measure those and get some sense of how chemistry progresses over time in these clouds.”
With the advent of the JWST and its advanced filters, Ginsburg and his colleagues are presented with their most promising opportunity yet to expand our cosmic exploration.
In a recent study led by University of Florida astronomer Adam Ginsburg, groundbreaking findings shed light on a mysterious dark region at the center of the Milky Way. The turbulent gas cloud, playfully nicknamed “The Brick” due to its opacity, has sparked lively debates within the scientific community for years.
To decipher its secrets, Ginsburg and his research team, including UF graduate students Desmond Jeff, Savannah Gramze, and Alyssa Bulatek, turned to the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). The implications of their observations, published in The Astrophysical Journal, are monumental. The findings not only unearth a paradox within the center of our galaxy but indicate a critical need to re-evaluate established theories regarding star formation.
The Brick has been one of the most intriguing and highly studied regions of our galaxies, thanks to its unexpectedly low star formation rate. It has challenged scientists’ expectations for decades: as a cloud full of dense gas, it should be ripe for the birth of new stars. However, it demonstrates an unexpectedly low star formation rate.
Using the JWST’s advanced infrared capabilities, the team of researchers peered into the Brick, discovering a substantial presence of frozen carbon monoxide (CO) there. It harbors a significantly larger amount of CO ice than previously anticipated, carrying profound implications for our understanding of star formation processes.
No one knew how much ice there was in the Galactic Center, according to Ginsburg. “Our observations compellingly demonstrate that ice is very prevalent there, to the point that every observation in the future must take it into account,” he said.
Stars typically emerge when gases are cool, and the significant presence of CO ice should suggest a thriving area for star formation in the Brick. Yet, despite this wealth of CO, Ginsburg and the research team found that the structure defies expectations. The gas inside the Brick is warmer than comparable clouds.
These observations challenge our understanding of CO abundance in the center of our galaxy and the critical gas-to-dust ratio there. According to the findings, both measures appear to be lower than previously thought.
“With JWST, we're opening new paths to measure molecules in the solid phase (ice), while previously we were limited to looking at gas,” said Ginsburg. “This new view gives us a more complete look at where molecules exist and how they are transported. “
Traditionally, the observation of CO has been limited to emission from gas. To unveil the distribution of CO ice within this vast cloud, the researchers required intense backlighting from stars and hot gas. Their findings move beyond the limitations of previous measurements, which were confined to around a hundred stars. The new results encompass over ten thousand stars, providing valuable insights into the nature of interstellar ice.
Since the molecules present in our Solar System today were, at some point, likely ice on small dust grains that combined to form planets and comets, the discovery also marks a leap forward toward understanding the origins of the molecules that shape our cosmic surroundings.
These are just the team’s initial findings from a small fraction of their JWST observations of the Brick. Looking ahead, Ginsburg sets his sights on a more extensive survey of celestial ices.
“We don't know, for example, the relative amounts of CO, water, CO2, and complex molecules,” said Ginsburg. “With spectroscopy, we can measure those and get some sense of how chemistry progresses over time in these clouds.”
With the advent of the JWST and its advanced filters, Ginsburg and his colleagues are presented with their most promising opportunity yet to expand our cosmic exploration.
END
Dark galactic region nicknamed "The Brick" explained with Webb telescope findings
UF astronomer Adam Ginsburg harnesses the James Webb Space Telescope to explore a galactic enigma
2023-12-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Awareness, accessibility, and affordability are crucial for the early detection of thalassemia
2023-12-04
- Interviewing Dr. Androulla Eleftheriou, Executive Director at TIF, and Dr. Zhiyu Peng, Deputy GM at BGI Genomics, Head of the World Hemoglobinopathy Foundation
Thalassemia, a hereditary hemoglobinopathy, occurs in 4.4 out of every 10,000 live births and is prevalent in Mediterranean coastal areas, Africa, the Middle East, Southeast Asia, and southern China.
Screening and antenatal diagnosis reduced the frequency of β-thalassemia in many Mediterranean countries. Focusing on other regions with high thalassemia prevalence, BGI Genomics has launched the Global 2023 State of Thalassemia Awareness Report, covering 1,847 ...
Complications from flu largely preventable with annual flu vaccine
2023-12-04
ARLINGTON, Va., BETHESDA, Md., CHICAGO and DALLAS, Dec. 4, 2023 — During National Influenza Vaccination Week (December 4-8, 2023), leading public health organizations are encouraging everyone to get a flu shot if they have not already done so. The flu is more than an inconvenience: it can lead to hospitalization, worsening of chronic medical conditions or even death. An annual flu vaccine is the best way to help prevent complications from the flu. [1]
The American Heart Association®, the American Lung Association,® the American ...
Soil drought weakens forest microclimatic cooling
2023-12-04
Scientists from Stockholm University have investigated the mechanisms that create cool microclimates beneath forest canopies during warm and dry summer days. The study reveals how canopy shading and water evaporation together create cooler forest microclimates compared to temperatures outside forests. The article is published in Agricultural and Forest Meteorology.
”The findings are alarming in the context of climate change as more frequent and more severe droughts may threaten the cooling functions of forests,” says Caroline Greiser, researcher at the Physical Geography Department, Stockholm ...
Study shows advanced footwear technology positively impacts elite sprint performances
2023-12-04
A scientific study published in PeerJ Life & Environment sheds light on the potential game-changing impact of advanced footwear technology (AFT) on elite sprint performances in track and field. The research, titled "The Potential Impact of Advanced Footwear Technology on the Recent Evolution of Elite Sprint Performances," reveals the significant strides made in sprint performance and suggests that AFT has played a pivotal role in these improvements.
Elite track ...
What's behind the holiday-suicide myth
2023-12-04
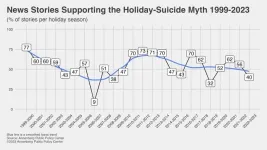
PHILADELPHIA – For more than two decades, the Annenberg Public Policy Center has tracked the ways in which news organizations erroneously link the year-end holiday season with suicide, perpetuating the false holiday-suicide myth. But as years of national data show, the winter holiday months usually have low average daily suicide rates, with December the lowest of all.
In our new media analysis, we find that of the newspaper stories during the 2022-23 holiday season that explicitly connected the holidays with suicide, 60% correctly debunked the myth while 40% incorrectly supported it.
But it’s not just the media that ...
More than a meteorite: New clues about the demise of dinosaurs
2023-12-04
What wiped out the dinosaurs? A meteorite plummeting to Earth is only part of the story, a new study suggests. Climate change triggered by massive volcanic eruptions may have ultimately set the stage for the dinosaur extinction, challenging the traditional narrative that a meteorite alone delivered the final blow to the ancient giants.
That’s according to a study published in Science Advances, co-authored by Don Baker, a professor in McGill University’s Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences.
The research team delved into volcanic eruptions of the Deccan Traps—a ...
INU scientists propose a model to predict personal learning performance for virtual reality-based safety training
2023-12-04
In Korea, occupational hazards are on the rise, particularly in the construction sector. According to a report on the ‘Occupational Safety Accident Status’ by Korea’s Ministry of Employment and Labor, the industry accounted for the highest number of accidents and fatalities among all sectors in 2021. To address this rise, the Korea Occupational Safety and Health Agency has been providing virtual reality (VR)-based construction safety content to daily workers as part of their educational training initiatives.
Nevertheless, ...
Placing nanoparticles in the palm of your hand
2023-12-04
Nanoparticles are super tiny―as small as one nanometer, or one billionth of a meter―and are of keen interest to materials scientists for their unique physical and chemical properties. They cannot be detected by the naked eye and require a highly specialized electron microscope to be seen.
In fact, advancements in imaging technologies through the 1990s and early 2000s are what made the field of nanoscience possible, says Anne Bentley, a faculty member in the Department of Chemistry at Lewis & Clark College in Portland, Oregon.
“I ...
Rice engineers tackle hard-to-map class of materials
2023-12-04
HOUSTON – (Dec. 4th, 2023) – The properties that make materials like semiconductors so sought after result from the way their atoms are connected, and insight into these atomic configurations can help scientists design new materials or use existing materials in new, unforeseen ways.
Rice University materials scientist Yimo Han and collaborators mapped out the structural features of a 2D ferroelectric material made of tin and selenium atoms, showing how domains ⎯ areas of the ...
Unravelling the mechanism of urticaria from eruption shapes
2023-12-04
The skin is the largest organ in the human body and plays an important role in maintaining homeostasis as well as protecting the body from the outside environment. Skin diseases can be life-threatening or heavily impair patients’ quality of life. Urticaria (also called “hives”) is common, affecting at least one in five people in their lifetime, and can persist for years or even decades. Many skin diseases are unique to humans, and their pathogenesis often remains unclear due to the lack of an appropriate experimental animal model and limited clinical data. One such human-specific disease is chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU), which is characterized by the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
Heat does not reduce prosociality
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
How AI is integrated into clinical workflow lowers medical liability perception
New biotech company to accelerate treatments for heart disease
One gene makes the difference: research team achieves breakthrough in breeding winter-hardy faba beans
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
[Press-News.org] Dark galactic region nicknamed "The Brick" explained with Webb telescope findingsUF astronomer Adam Ginsburg harnesses the James Webb Space Telescope to explore a galactic enigma