(Press-News.org) The ongoing mental health crisis is causing significant challenges for many psychologists as they grapple with demand fueled by patients presenting with increasingly severe symptoms year after year, according to APA’s 2023 Practitioner Pulse Survey.
The survey, which was completed by 561 licensed practicing psychologists between Aug. 30 and Sept. 29, 2023, found that not only did more than half of psychologists (52%) say that they were seeing an increase in severity of symptoms among their patients, but 41% said that they were seeing an increase in the number of sessions spent treating each patient, which may reduce their capacity to accept new patients.
Similarly, more than half (56%) said that they had no openings for new patients. And more than two-thirds (69%) of psychologists who maintained a waitlist said that the average wait was up to three months for a first appointment, while 31% said average wait times were longer than three months. Psychologists reported increasing demand for treatment of certain mental health conditions, including anxiety disorders (68%) and trauma- and stressor-related disorders (50%), among those who treat those disorders.
"As the mental health crisis continues, psychologists are under pressure,” said APA CEO Arthur C. Evans Jr., PhD. "These findings underscore the sustained demand for care, led by increased severity of symptoms and extended treatment courses, compounded by increases year after year. This paints a clear picture of psychologists operating at the brink of their capacity. To better meet demand, it is essential that we develop comprehensive public health strategies that reach people throughout their lifespan and robustly address behavioral health alongside physical health.”
The survey found that the psychologist workforce is already adapting to meet the changing needs of the population -- for example, as part of integrated care teams or in medical settings. More than 4 in 5 psychologists (86%) said they have worked alongside other health care providers, with 59% saying they do so frequently or very frequently. Collaborating providers included psychiatrists (76% of psychologists said they worked with them, with 38% doing so frequently); other physicians (45%, with 17% doing so frequently); occupational therapists (30%, with 6% doing so frequently); physician assistants (41%, with 11% doing so frequently); community health workers (30%, with 4% doing so frequently); and speech language pathologists (28%, with 5% frequent collaborators). Alongside mental health concerns, psychologists reported treating patients with physical conditions, including 50% treating patients with chronic pain, 42% treating obesity or weight conditions, 27% some symptoms of cancer, and 25% high blood pressure.
“Integrated care, where psychologists work on health care teams with other providers, is one way that we can expand access to care, prioritize preventive care and find ways to better meet the biological, psychological and social needs of the patients,” said Evans. “We must also support and expand the mental health workforce, foster innovation and technology, and support psychologists in extending their reach in the communities in which they live and work.”
Psychologists have shown themselves to be adaptable, changing their work habits during the pandemic to include fully remote or hybrid practices. Only 21% are now offering fully remote practices (down from a peak of 64% in 2020), according to the poll, yet more than two-thirds (67%) are now working in hybrid practices seeing some patients in person and others remotely.
More than one-third (36%) of psychologists reported experiencing burnout and 1 in 5 psychologists (21%) said that they were planning to reduce their practice hours in the next 12 months. Yet nearly three-quarters (73%) said that they were able to practice self-care and nearly two-thirds (63%) said that they were able to maintain a positive work-life balance.
METHODOLOGY
APA’s 2023 Practitioner Pulse Survey is one in a series of surveys conducted annually since 2020. This year’s survey was distributed via email to a random sample of 16,557 licensed psychologists in the United States from Aug. 30 to Sept. 29, 2023. A total of 561 responded to the survey.
A full methodology is available.
END
Mental health crisis highlights access challenges
Poll finds many psychologists face capacity strains as patients present with increasingly severe symptoms
2023-12-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Wearable ultrasound monitor can aid rehabilitation from injury #Acoustics23
2023-12-05
SYDNEY, Dec. 5, 2023 – Millions suffer from musculoskeletal injuries every year, and the recovery process can often be long and difficult. Patients typically undergo rehabilitation, slowly rebuilding muscle strength as their injuries heal. Medical professionals routinely evaluate a patient’s progress via a series of tasks and exercises. However, because of the dynamic nature of these exercises, obtaining a clear picture of real-time muscle function is extremely challenging.
Parag Chitnis of George Mason University led a team that developed a wearable ultrasound system that can produce clinically relevant information about muscle function during dynamic physical activity. He ...
Bird feeding may give humans something to chirp about
2023-12-05
Ashley Dayer hopes to peck away at the notion that bird feeding is simply for the birds.
Associate professor in the Department of Fish and Wildlife Conservation at Virginia Tech, Dayer is the lead author of an article published in People and Nature that argues not only for the acknowledgment of the activity’s benefit to humans, but that it should play a role in public guidance and policy.
“Wildlife agencies and others making decisions on managing bird feeding need to be considering not only what the science is behind what’s going on with birds, but also the science behind what’s going on with people,” ...
Using AI to find microplastics
2023-12-05
An interdisciplinary research team from the University of Waterloo is using artificial intelligence (AI) to identify microplastics faster and more accurately than ever before.
Microplastics are commonly found in food and are dangerous pollutants that cause severe environmental damage – finding them is the key to getting rid of them.
The research team’s advanced imaging identification system could help wastewater treatment plants and food production industries make informed decisions ...
Eco-friendly glue breakthrough designed by Cal Poly chemistry team receives patent
2023-12-05
An innovative, ecofriendly glue designed by a Cal Poly chemistry research team in collaboration with an East Coast company has been approved for a U.S. government patent.
The patent, approved Nov. 21, creates a pathway for proprietary commercial production of the glue innovation under the direction of the Massachusetts-based company Geisys Ventures with involvement of Cal Poly chemistry faculty and students in research and development as part of a memorandum of understanding between the university and Geisys. The new adhesive has potential to reduce landfill waste and positively impact the environment on a broad scale.
The product, to be formally commercialized under the ...
Underwater vehicle AI model could be used in other adaptive control systems
2023-12-05
Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUVs) are used around the world to conduct difficult environmental, remote, oceanic, defence and rescue missions in often unpredictable and harsh conditions.
A new study led by Flinders University and French researchers has now used a novel bio-inspired computing artificial intelligence solution to improve the potential of UUVs and other adaptive control systems to operate more reliability in rough seas and other unpredictable conditions.
This innovative approach, using the Biologically-Inspired Experience Replay (BIER) method, has been published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers journal IEEE Access.
Unlike conventional ...
Sugar permeation discovered in plant aquaporins
2023-12-05
Aquaporins, which move water through membranes of plant cells, were not thought to be able to permeate sugar molecules, but University of Adelaide researchers have observed sucrose transport in plant aquaporins for the first time, challenging this theory.
The finding, made by researchers from the School of Agriculture, Food and Wine, widens the concept of aquaporins’ role in plant biology and will have implications for the bioengineering of plants for food production and plant survival.
Aquaporins, which belong to a class of membrane ...
American Eel as an emerging consumer target
2023-12-05
Research led by Hiromi Shiraishi, researcher at Chuo University, indicated a steep rise in the importation of American Eel (Anguilla rostrata) live fry to East Asia for aquaculture purposes. This surge poses a potential threat to the already endangered species, further depleting the resources of this species. Japan relies on imports for two-thirds of its eel consumption and it is believed that a significant quantity of American Eel is included in these imports. As a major consumer of eels, Japan is urged to take a leading role in ensuring the sustainable utilisation of eel species, including ...
New implants linked to less infection and better recovery from orthopedic surgery
2023-12-05
Superior knee and hip replacements are a step closer after Flinders University and Chinese researchers further test and develop a new orthopedic implant coating which has the strong ability to ward off infection – as well as stimulate bone growth.
The technology, which has been patented after more promising results just detailed in the lead scientific journal Advanced Functional Materials, consists of novel Silver-Gallium (Ag-Ga) nano-amalgamated particles that can be easily applied to medical device surfaces.
“The antibacterial capabilities of compounds derived from silver have been extensively researched. ...
Recycling concrete using carbon can reduce emissions and waste
2023-12-05
Amid the rubble of large-sale earthquake, war or other disaster – and as ageing buildings and infrastructure are replaced – mountains of concrete are often taken to landfill or pounded into rubble for roads.
For a more sustainable approach, Flinders University and The University of Melbourne experts are developing a ‘value add’ for old broken concrete to ‘upcycling’ coarse aggregate to produce a strong, durable and workable concrete using a small amount of a secret ingredient – graphene.
The novel method is gaining ground ...
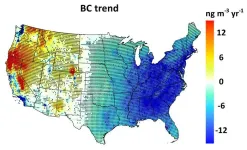
Wildfires have erased two decades’ worth of air quality gains in western United States
2023-12-05
You need only to remember last summer’s wildfires in the United States and Canada, which fouled the air from coast to coast, to know the effects these blazes can have on the environment and human health.
A new study has tabulated the toll from two decades of wildfires on air quality and human health in the continental U.S. The authors report that from 2000 to 2020, the air has worsened in the western U.S., mainly due to the increase in frequency and ferocity of wildfires causing an increase of 670 premature deaths per year in the region during that time period. Overall, the study’s authors report fires have undercut ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
Psilocybin trends in states that decriminalized use
New data signals high demand in aesthetic surgery in southern, rural U.S. despite access issues
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
[Press-News.org] Mental health crisis highlights access challengesPoll finds many psychologists face capacity strains as patients present with increasingly severe symptoms