(Press-News.org) The results are just published in Nature Communications under the title "Enhanced production of mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons from lineage-restricted human undifferentiated stem cells."
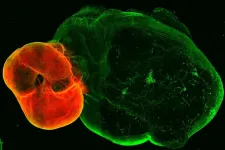
In the new research findings, DANDRITE group leader and Associate Professor Mark Denham has developed a method that ensures much higher purity of the so-called dopamine cells, which are crucial in connection with Parkinson's disease.
"Stem cells offer promising potential for treating Parkinson's disease by transforming into specific nerve cells. However, the precision of this transformation poses a significant challenge with current methods, resulting in low purity," Mark explains.
Achieving high purity is critical for effectively restoring movement in patients.
In the Denham Lab, stem cells were genetically engineered to prevent them from generating the incorrect types of nerve cells. The newly engineered stem cells have an enhanced ability to produce the specific nerve cells required for Parkinson's treatment known as the dopaminergic cells.
Furthermore, the researchers show that the genetically engineered stem cells led to the restoration of movement in animal models. This breakthrough is a potential new therapeutic approach for treating Parkinson's disease patients.
Experiments on rats have shown that both the quantity and purity of cultured stem cells are critical for the number and duration of treatments.
“Using our genetically engineered cells we generate a higher purity of dopamine cells, for patients this will reduce the recovery time and diminish the risk of relapse and medication use. My goal is to help patients stay off their medication, which requires high purity. So, my next step is to transfer my method to clinical trials,” Marks states.
END
A new publication in Nature Communications can revolutionize the treatment of Parkinson's patients
The future treatment of Parkinson’s Disease has undergone tremendous development in recent years. Now, a breakthrough in research has emerged, delivering the strongest results for both side-effect-free and long-lasting treatment effects.
2023-12-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Eye scans provide crucial insights into kidney health, study finds
2023-12-05
3D eye scans can reveal vital clues about kidney health that could help to track the progression of disease, research suggests.
The advance could revolutionise monitoring of kidney disease, which often progresses without symptoms in the early stages.
Experts say the technology has potential to support early diagnosis as current screening tests cannot detect the condition until half of the kidney function has been lost.
Researchers used highly-magnified images to detect changes to the retina – the layer of tissue at the back of the eye that senses light and sends signals to the ...
Diamonds and rust help unveil ‘impossible’ quasi-particles
2023-12-05
Researchers have discovered magnetic monopoles – isolated magnetic charges – in a material closely related to rust, a result that could be used to power greener and faster computing technologies.
Researchers led by the University of Cambridge used a technique known as diamond quantum sensing to observe swirling textures and faint magnetic signals on the surface of hematite, a type of iron oxide.
The researchers observed that magnetic monopoles in hematite emerge through the collective behaviour of many spins (the angular momentum of a particle). These monopoles glide across the swirling textures on the surface of the hematite, like tiny ...
Unlocking the secrets of the brain’s dopaminergic system
2023-12-05
A new organoid model of the dopaminergic system sheds lights on its intricate functionality and potential implications for Parkinson’s disease. The model, developed by the group of Jürgen Knoblich at the Institute of Molecular Biotechnology (IMBA) of the Austrian Academy of Sciences, replicates the dopaminergic system’s structure, connectivity, and functionality. The study, published on December 5 in Nature Methods, also uncovers the enduring effects of chronic cocaine exposure on the dopaminergic circuit, even after withdrawal.
A completed run, the early morning hit of caffeine, the smell of cookies in the oven - these ...
Enhanced AI tracks neurons in moving animals
2023-12-05
Recent advances allow imaging of neurons inside freely moving animals. However, to decode circuit activity, these imaged neurons must be computationally identified and tracked. This becomes particularly challenging when the brain itself moves and deforms inside an organism’s flexible body, e.g. in a worm. Until now, the scientific community has lacked the tools to address the problem.
Now, a team of scientists from EPFL and Harvard have developed a pioneering AI method to track neurons inside moving and deforming animals. The study, now published ...
UC San Diego Health recognized as leader in high quality OB/GYN care
2023-12-05
UC San Diego Health is recognized as a 2023-2024 High Performing Hospital for Maternity Care, which is the highest award a hospital can earn by U.S. News & World Report for obstetric and infant care.
To be recognized as High Performing in Maternity Care, hospitals must meet high standards in caring for patients with uncomplicated pregnancies, such as low cesarean section rates, low newborn complication rates, offering transparency on racial and ethnic disparities, and other measures.
“It is an honor to receive this prominent recognition, ...
Mental health crisis highlights access challenges
2023-12-05
The ongoing mental health crisis is causing significant challenges for many psychologists as they grapple with demand fueled by patients presenting with increasingly severe symptoms year after year, according to APA’s 2023 Practitioner Pulse Survey.
The survey, which was completed by 561 licensed practicing psychologists between Aug. 30 and Sept. 29, 2023, found that not only did more than half of psychologists (52%) say that they were seeing an increase in severity of symptoms among their patients, but 41% said that they were seeing ...
Wearable ultrasound monitor can aid rehabilitation from injury #Acoustics23
2023-12-05
SYDNEY, Dec. 5, 2023 – Millions suffer from musculoskeletal injuries every year, and the recovery process can often be long and difficult. Patients typically undergo rehabilitation, slowly rebuilding muscle strength as their injuries heal. Medical professionals routinely evaluate a patient’s progress via a series of tasks and exercises. However, because of the dynamic nature of these exercises, obtaining a clear picture of real-time muscle function is extremely challenging.
Parag Chitnis of George Mason University led a team that developed a wearable ultrasound system that can produce clinically relevant information about muscle function during dynamic physical activity. He ...
Bird feeding may give humans something to chirp about
2023-12-05
Ashley Dayer hopes to peck away at the notion that bird feeding is simply for the birds.
Associate professor in the Department of Fish and Wildlife Conservation at Virginia Tech, Dayer is the lead author of an article published in People and Nature that argues not only for the acknowledgment of the activity’s benefit to humans, but that it should play a role in public guidance and policy.
“Wildlife agencies and others making decisions on managing bird feeding need to be considering not only what the science is behind what’s going on with birds, but also the science behind what’s going on with people,” ...
Using AI to find microplastics
2023-12-05
An interdisciplinary research team from the University of Waterloo is using artificial intelligence (AI) to identify microplastics faster and more accurately than ever before.
Microplastics are commonly found in food and are dangerous pollutants that cause severe environmental damage – finding them is the key to getting rid of them.
The research team’s advanced imaging identification system could help wastewater treatment plants and food production industries make informed decisions ...
Eco-friendly glue breakthrough designed by Cal Poly chemistry team receives patent
2023-12-05
An innovative, ecofriendly glue designed by a Cal Poly chemistry research team in collaboration with an East Coast company has been approved for a U.S. government patent.
The patent, approved Nov. 21, creates a pathway for proprietary commercial production of the glue innovation under the direction of the Massachusetts-based company Geisys Ventures with involvement of Cal Poly chemistry faculty and students in research and development as part of a memorandum of understanding between the university and Geisys. The new adhesive has potential to reduce landfill waste and positively impact the environment on a broad scale.
The product, to be formally commercialized under the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ASU researchers showcase scalable tech solutions for older adults living alone with cognitive decline at AAAS 2026
Scientists identify smooth regional trends in fruit fly survival strategies
Antipathy toward snakes? Your parents likely talked you into that at an early age
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for Feb. 2026
Online exposure to medical misinformation concentrated among older adults
Telehealth improves access to genetic services for adult survivors of childhood cancers
Outdated mortality benchmarks risk missing early signs of famine and delay recognizing mass starvation
Newly discovered bacterium converts carbon dioxide into chemicals using electricity
Flipping and reversing mini-proteins could improve disease treatment
Scientists reveal major hidden source of atmospheric nitrogen pollution in fragile lake basin
Biochar emerges as a powerful tool for soil carbon neutrality and climate mitigation
Tiny cell messengers show big promise for safer protein and gene delivery
AMS releases statement regarding the decision to rescind EPA’s 2009 Endangerment Finding
Parents’ alcohol and drug use influences their children’s consumption, research shows
Modular assembly of chiral nitrogen-bridged rings achieved by palladium-catalyzed diastereoselective and enantioselective cascade cyclization reactions
Promoting civic engagement
AMS Science Preview: Hurricane slowdown, school snow days
Deforestation in the Amazon raises the surface temperature by 3 °C during the dry season
Model more accurately maps the impact of frost on corn crops
How did humans develop sharp vision? Lab-grown retinas show likely answer
Sour grapes? Taste, experience of sour foods depends on individual consumer
At AAAS, professor Krystal Tsosie argues the future of science must be Indigenous-led
From the lab to the living room: Decoding Parkinson’s patients movements in the real world
Research advances in porous materials, as highlighted in the 2025 Nobel Prize in Chemistry
Sally C. Morton, executive vice president of ASU Knowledge Enterprise, presents a bold and practical framework for moving research from discovery to real-world impact
Biochemical parameters in patients with diabetic nephropathy versus individuals with diabetes alone, non-diabetic nephropathy, and healthy controls
Muscular strength and mortality in women ages 63 to 99
Adolescent and young adult requests for medication abortion through online telemedicine
Researchers want a better whiff of plant-based proteins
Pioneering a new generation of lithium battery cathode materials
[Press-News.org] A new publication in Nature Communications can revolutionize the treatment of Parkinson's patientsThe future treatment of Parkinson’s Disease has undergone tremendous development in recent years. Now, a breakthrough in research has emerged, delivering the strongest results for both side-effect-free and long-lasting treatment effects.