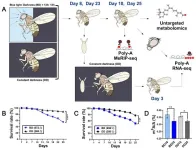
(Press-News.org) In a study on fruit flies, daily low-intensity blue light exposure (BLE), similar to that experienced daily by billions of humans in the form of LED lighting and device screens, changed flies at the sub-cellular level, affecting processes related to aging and circadian rhythms. Xiaoyun Wang and colleagues exposed fruit flies (Drosophila melanogaster) to different durations of daily low-intensity BLE and then analysed the consequences to the cellular makeup of the insects, as compared to flies raised in darkness. The authors paid particular attention to blue light’s effects on N6-Methyladenosine (m6A), a modification of RNA common across the tree of life that plays a role in a wide range of processes. The authors found that blue light induced transcriptomic, m6A epitranscriptomic and metabolomic reprogramming. Ten-day old flies could be differentiated from 25-day old flies by each age group’s m6A epitranscriptomic profiles, showing the link between m6A and aging. RNA profiles between 25-day old male blue light exposed flies’ heads were significantly different from 25-day-old male dark-raised flies’ heads. According to the authors, the types of genes up- and down-regulated suggest that blue light exposure can damage neuronal function. In comparisons of whole-body transcriptomes, however, age created bigger differences between groups than light exposure, suggesting that eye and brain tissues of Drosophila are the major tissues affected by blue light. Differences in mRNA m6A levels and other m6A-related markers between light and dark raised flies indicate that m6A methylation was involved in the impacts of BLE on Drosophila. According to the authors, attention should be paid to the potential hazards of cumulative blue light exposure in humans.
END
Blue light exposure and aging
2023-12-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Toxicity at Wikipedia
2023-12-05
A study links hostility on Wikipedia to lost productivity on the site. Wikipedia, the largest reference work ever created, is written and edited by tens of thousands of volunteers, known as Wikipedians. Despite the fact that anyone can edit any page, studies show that Wikipedia is generally a reliable source of information. Ivan Smirnov and colleagues studied how the volunteer labor that keeps the site working is affected by hostile comments in the “user talk” pages connected to each editor. Toxic comments were identified by a toxicity detection algorithm devised by the Perspective API ...
Reliable research and evidence-based recommendations scarce for women who exercise according to menstrual cycle
2023-12-05
Hamilton, ON, December 5, 2023 – There is no shortage of advice for women on what to eat, how to train, or what supplements to take during their menstrual cycles, but a new review by an international team of scientists has found little evidence to support such recommendations.
In fact, they found sparse research on women and exercise at all, and even less on the effect of their periods on sports performance, physiology, or physical fitness.
The authors of the paper, from McMaster University, Manchester Metropolitan University and the Australian Catholic University in Melbourne, are calling for much more high quality, standardized research ...
New Alzheimer Europe publication highlights continuing inequalities in access to dementia care and treatment across Europe
2023-12-05
Brussels, 5 December 2023 – In a report launched today at a lunch debate hosted by Deirdre Clune MEP (Ireland), Alzheimer Europe highlighted the continuing inequalities in access to dementia care and treatment across Europe.
The objective of the report entitled “European Dementia Monitor” was to provide a benchmark of national dementia policies in order to compare and rate the responses of European countries to the dementia challenge. The survey covered all Member States of the European Union (with the exception of Latvia), as well as Armenia, Iceland, Israel, Jersey, North Macedonia, Norway, Serbia, Switzerland, Turkey, United ...
Both virtual and in-person nutrition visits help to lower cholesterol, study finds
2023-12-05
Despite an end to the national public health emergency in May 2023, the use of telehealth remains high, with over 20% of American adults taking appointments online.
These visits include video calls with registered dietitian nutritionists, who have a critical role in helping patients take on lifestyle changes through medical nutrition therapy.
With a focus on the changing digital landscape, researchers at Michigan Medicine found that telemedicine patients with hyperlipidemia — an excess of cholesterol or fats in the blood ...
USC Norris Cancer Hospital earns Leapfrog Top Teaching Hospital award for third year in a row
2023-12-05
LOS ANGELES — The Leapfrog Group, a national hospital watchdog organization, has named USC Norris Cancer Hospital a 2023 Top Teaching Hospital. This is the third year in a row the hospital has received this distinction.
“I am incredibly proud that once again, USC Norris Cancer Hospital ranked among the top hospitals in the country,” said Marty Sargeant, MBA, CEO of USC Norris Cancer Hospital and Keck Hospital of USC. “This prestigious honor reflects our rigorous safety and quality standards and our continuous commitment to our ...
Exposure to soft robots decreases human fears about working with them
2023-12-05
VANCOUVER, Wash. – Seeing robots made with soft, flexible parts in action appears to lower people’s anxiety about working with them or even being replaced by them.
A Washington State University study found that watching videos of a soft robot working with a person at picking and placing tasks lowered the viewers’ safety concerns and feelings of job insecurity. This was true even when the soft robot was shown working in close proximity to the person. This finding shows soft robots hold ...
Study proposes new explanation for California anchovy booms and busts
2023-12-05
New research from Scripps and NOAA scientists has discovered ecological correlations that could help explain the booms and busts of California’s anchovy population. If the correlations hold up to further research, they could one day help inform management of California’s anchovy fishery and improve conservation.
The Northern Anchovy (Engraulis mordax) is a crucial food source for much of California’s most conspicuous marine life – including droves of sea lions, pods of dolphins, lucrative tuna fisheries, and throngs of whales. But one of the hallmarks of the anchovy population off California ...
A new publication in Nature Communications can revolutionize the treatment of Parkinson's patients
2023-12-05
The results are just published in Nature Communications under the title "Enhanced production of mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons from lineage-restricted human undifferentiated stem cells."
In the new research findings, DANDRITE group leader and Associate Professor Mark Denham has developed a method that ensures much higher purity of the so-called dopamine cells, which are crucial in connection with Parkinson's disease.
"Stem cells offer promising potential for treating Parkinson's disease by transforming into specific nerve cells. However, the precision of this transformation poses a significant challenge with current methods, resulting in low purity," ...
Eye scans provide crucial insights into kidney health, study finds
2023-12-05
3D eye scans can reveal vital clues about kidney health that could help to track the progression of disease, research suggests.
The advance could revolutionise monitoring of kidney disease, which often progresses without symptoms in the early stages.
Experts say the technology has potential to support early diagnosis as current screening tests cannot detect the condition until half of the kidney function has been lost.
Researchers used highly-magnified images to detect changes to the retina – the layer of tissue at the back of the eye that senses light and sends signals to the ...
Diamonds and rust help unveil ‘impossible’ quasi-particles
2023-12-05
Researchers have discovered magnetic monopoles – isolated magnetic charges – in a material closely related to rust, a result that could be used to power greener and faster computing technologies.
Researchers led by the University of Cambridge used a technique known as diamond quantum sensing to observe swirling textures and faint magnetic signals on the surface of hematite, a type of iron oxide.
The researchers observed that magnetic monopoles in hematite emerge through the collective behaviour of many spins (the angular momentum of a particle). These monopoles glide across the swirling textures on the surface of the hematite, like tiny ...