(Press-News.org) Medicare is the single largest provider of health insurance in the United States, serving 63.8 million senior citizens as of 2022. Three-quarters of these recipients are enrolled in optional Medicare Part D plans, which provide outpatient prescription drug coverage to seniors through private insurance companies. In 2022, Medicare paid more than $160 Billion for prescription drugs, making it the single largest payer of pharmaceuticals in the US.
While Medicare is meant to keep healthcare affordable for seniors, millions of Americans still face steep costs for prescription medications. Researchers at University of California San Diego, West Health, and the University of Washington have now explained part of the problem.
The researchers found evidence that the private insurers that sponsor Medicare Part D are artificially inflating the costs of certain generic drugs by overpaying pharmacies. The findings published December 5, 2023 in the Journal of the American Medical Association.
Generic over-reimbursement is one of the areas targeted for reform by the United States Senate, after anecdotal evidence submitted earlier this year by the non-profit manufacturer CivicaRx raised concerns about Part D sponsors potentially over-reimbursing pharmacies for abiraterone, a cancer drug. The concern: that patients are ultimately impacted by these reimbursement practices because of how out-of-pocket costs, such as copayments and deductibles) are calculated.
“For instance, if a patient pays 30% as a copayment for a drug, that 30% would be applied to the inflated price, which could mean higher out-of-pocket costs for seniors,” said corresponding author Inmaculada Hernandez, PharmD, PhD, professor at UC San Diego Skaggs School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Science.
However, whether Part D Plan sponsors are engaging in generic over-reimbursement has been an outstanding question until now.
“This is the first study to investigate whether these practices actually take place in the Medicare Part D program,” added Hernandez.
To fill prescriptions, pharmacies purchase drugs wholesale and are reimbursed by insurers. In order to be reimbursed, pharmacies must adhere to contractual obligations that allow insurers to take back money in certain circumstances, such as when the reimbursement to the pharmacy is higher than a certain threshold or if the pharmacy’s cost of acquisition is very low. These ‘clawbacks’ by Part D Plans can be financially devastating to a pharmacy.
“It doesn’t make sense that insurers would overpay for drugs, then use clawbacks to retroactively adjust payments after the patient has paid their co-payment,” said co-author Sean D. Sullivan, PhD, professor of pharmacy at the University of Washington. “This practice is opaque and ultimately harms patients and pharmacies.”
The researchers gathered and analyzed data from the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), focusing on spending and reimbursement data for the 50 generic drugs that Medicare Part D spent the most on in 2021. They found that some Medicare Part D sponsors were reimbursing at much higher rates than what pharmacies spent to acquire the drugs.
“The results are alarming,” said Hernandez. “We are talking about markups of 6000% or 7000% in some cases.”
In one of the most dramatic examples, the researchers found that insurers were reimbursing pharmacies an average of $126 per tablet for a cancer drug that cost $4.20 per tablet to the pharmacy. This corresponds to an average markup of 3000%, or $3600 per 30-day prescription. Some insurers paid even more.
“Seniors are clearly paying more for their medications as a result of these markups,” said Hernandez. “More research is needed to confirm the scope of these practices, but the evidence is concerning.”
Co-authors include: Nico Gabriel at UC San Diego, Anna Kaltenboeck at ATI Advisory, Cristina Boccuti at West Health Policy Center and Ryan N. Hansen at the CHOICE Institute, School of Pharmacy, University of Washington.
This study was funded by West Health Policy Center.
###
END
Medicare is overpaying for generic drugs
Disturbing financial practice by Medicare Part D sponsors revealed in UC San Diego study of data from the Centers for Medicaid and Medicare Services
2023-12-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Forecasting forest health using models to predict tree canopy height
2023-12-05
Tree height is an important indicator of a forest’s maturity and overall health. Forest restoration projects rely on tree height as a predictor and measurement of success, but forecasting a forest’s future tree height based on observations alone is almost impossible. There are too many factors that contribute to the growth and health of trees.
Because so many factors can impact how a tree develops, researchers enhanced a predictive model called the Allometric Scaling and Resource Limitations (ASRL) model and then deployed it using ...
Green macroalga caulerpa has replaced seagrass in Florida’s Indian River Lagoon
2023-12-05
The Indian River Lagoon was considered one of the last “unpolluted coastal lagoons” in Florida in the 1970s. Fast forward to today and most of the 156-mile lagoon is now considered impaired because of external sources of nutrients including human waste, fertilizers, stormwater runoff, agriculture, rainfall and sub-marine groundwater discharge.
As a result, the lagoon – especially the Northern Indian River Lagoon and Banana River – has experienced various harmful algal blooms, catastrophic seagrass losses, and is the epicenter of Florida ...
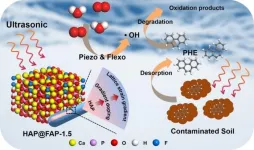
Novel mineral piezocatalysts offer innovative approaches for soil remediation
2023-12-05
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) removal in the soil environment is of great significance for repairing the long-term damaged ecosystem. However, the poor mass transfer process and low catalytic activity in most conventional methods lead to limited removal efficiency. A team of scientists has constructed a gradient F-doping hydroxyapatite core-shell structure (HAP@FAP) with the coupling effect of flexoelectricity and piezoelectricity for degradation of PAHs in soil that provide innovative approaches for soil remediation. Their work was published in the journal Industrial Chemistry & Materials in October 2023.
The poor mass ...
Florida wildflowers and pollinators get a boost with two grants
2023-12-05
The Daniels Lab at the Florida Museum of Natural History was recently awarded two grants to help support pollinators in Florida. The Florida Department of Transportation has set aside $155,002 for the team to plant and monitor thousands of milkweeds along roads in North Florida, and Duke Energy Florida will distribute $144,421 over three years to evaluate the establishment of pollinator habitat at its new solar site Alachua County.
Pollinators are declining on a global scale, the collateral damage of continued habitat destruction and urbanization, among other stressors. ...
Glyphosphate: a silver-bullet weed killer no more
2023-12-05
For decades, corn and soy farmers have heavily relied on one herbicide: glyphosate. Crops bred to resist glyphosate have been extremely successful, with over 90% of corn and soy hectares planted with glyphosate-resistant varieties by 2014. But as Christopher Landau and colleagues document, the chemical was not quite the “silver bullet” it was promised to be. With an entire industry using the same chemical—the US and Canada alone apply more than 130 million kg annually—evolutionary selection pressures on weed plants have been intense. Since 1996, there have been 354 confirmed cases of glyphosate ...
Blue light exposure and aging
2023-12-05
In a study on fruit flies, daily low-intensity blue light exposure (BLE), similar to that experienced daily by billions of humans in the form of LED lighting and device screens, changed flies at the sub-cellular level, affecting processes related to aging and circadian rhythms. Xiaoyun Wang and colleagues exposed fruit flies (Drosophila melanogaster) to different durations of daily low-intensity BLE and then analysed the consequences to the cellular makeup of the insects, as compared to flies raised in darkness. The authors paid particular attention to ...
Toxicity at Wikipedia
2023-12-05
A study links hostility on Wikipedia to lost productivity on the site. Wikipedia, the largest reference work ever created, is written and edited by tens of thousands of volunteers, known as Wikipedians. Despite the fact that anyone can edit any page, studies show that Wikipedia is generally a reliable source of information. Ivan Smirnov and colleagues studied how the volunteer labor that keeps the site working is affected by hostile comments in the “user talk” pages connected to each editor. Toxic comments were identified by a toxicity detection algorithm devised by the Perspective API ...
Reliable research and evidence-based recommendations scarce for women who exercise according to menstrual cycle
2023-12-05
Hamilton, ON, December 5, 2023 – There is no shortage of advice for women on what to eat, how to train, or what supplements to take during their menstrual cycles, but a new review by an international team of scientists has found little evidence to support such recommendations.
In fact, they found sparse research on women and exercise at all, and even less on the effect of their periods on sports performance, physiology, or physical fitness.
The authors of the paper, from McMaster University, Manchester Metropolitan University and the Australian Catholic University in Melbourne, are calling for much more high quality, standardized research ...
New Alzheimer Europe publication highlights continuing inequalities in access to dementia care and treatment across Europe
2023-12-05
Brussels, 5 December 2023 – In a report launched today at a lunch debate hosted by Deirdre Clune MEP (Ireland), Alzheimer Europe highlighted the continuing inequalities in access to dementia care and treatment across Europe.
The objective of the report entitled “European Dementia Monitor” was to provide a benchmark of national dementia policies in order to compare and rate the responses of European countries to the dementia challenge. The survey covered all Member States of the European Union (with the exception of Latvia), as well as Armenia, Iceland, Israel, Jersey, North Macedonia, Norway, Serbia, Switzerland, Turkey, United ...
Both virtual and in-person nutrition visits help to lower cholesterol, study finds
2023-12-05
Despite an end to the national public health emergency in May 2023, the use of telehealth remains high, with over 20% of American adults taking appointments online.
These visits include video calls with registered dietitian nutritionists, who have a critical role in helping patients take on lifestyle changes through medical nutrition therapy.
With a focus on the changing digital landscape, researchers at Michigan Medicine found that telemedicine patients with hyperlipidemia — an excess of cholesterol or fats in the blood ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
Anxiety, depression, and care barriers in adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities
Study: Anxiety, gloom often accompany intellectual deficits
Massage Therapy Foundation awards $300,000 research grant to the University of Denver
Gastrointestinal toxicity linked to targeted cancer therapies in the United States
Countdown to the Bial Award in Biomedicine 2025
Blood marker from dementia research could help track aging across the animal world
Birds change altitude to survive epic journeys across deserts and seas
Here's why you need a backup for the map on your phone
ACS Central Science | Researchers from Insilico Medicine and Lilly publish foundational vision for fully autonomous “Prompt-to-Drug” pharmaceutical R&D
Increasing the number of coronary interventions in patients with acute myocardial infarction does not appear to reduce death rates
Tackling uplift resistance in tall infrastructures sustainably
Novel wireless origami-inspired smart cushioning device for safer logistics
Hidden genetic mismatch, which triples the risk of a life-threatening immune attack after cord blood transplantation
Physical function is a crucial predictor of survival after heart failure
Striking genomic architecture discovered in embryonic reproductive cells before they start developing into sperm and eggs
Screening improves early detection of colorectal cancer
New data on spontaneous coronary artery dissection (SCAD) – a common cause of heart attacks in younger women
How root growth is stimulated by nitrate: Researchers decipher signalling chain
Scientists reveal our best- and worst-case scenarios for a warming Antarctica
Cleaner fish show intelligence typical of mammals
AABNet and partners launch landmark guide on the conservation of African livestock genetic resources and sustainable breeding strategies
Produce hydrogen and oxygen simultaneously from a single atom! Achieve carbon neutrality with an 'All-in-one' single-atom water electrolysis catalyst
Sleep loss linked to higher atrial fibrillation risk in working-age adults
Visible light-driven deracemization of α-aryl ketones synergistically catalyzed by thiophenols and chiral phosphoric acid
Most AI bots lack basic safety disclosures, study finds
How competitive gaming on discord fosters social connections
[Press-News.org] Medicare is overpaying for generic drugsDisturbing financial practice by Medicare Part D sponsors revealed in UC San Diego study of data from the Centers for Medicaid and Medicare Services