(Press-News.org) Key takeaways
People in parts of Africa communicate with a wild bird, the greater honeyguide, to locate bee colonies and harvest their honey and beeswax.
A study by UCLA anthropologist Brian Wood and other authors show how this partnership is maintained and varies across cultures.
They demonstrate the bird’s ability to learn distinct vocal signals traditionally used by different honey-hunting communities.
In parts of Africa, people communicate with a wild bird — the greater honeyguide — in order to locate bee colonies and harvest their stores of honey and beeswax.
It’s a rare example of cooperation between humans and wild animals, and a potential instance of cultural coevolution.
UCLA anthropologist Brian Wood and University of Cape Town ornithologist Claire Spottiswoode were lead authors on a study showing how this valuable partnership is maintained and varies across cultures. Their article, “Culturally determined interspecies communication between humans and honeyguides,” was published in Science.
“Our study demonstrates the bird’s ability to learn distinct vocal signals that are traditionally used by different honey-hunting communities, expanding possibilities for mutually beneficial cooperation with people,” Wood said.
“Honeyguides seem to know the landscape intimately, gathering knowledge about the location of bee nests, which they then share with people, Spottiswoode said. “People are eager for the bird’s help.”
The honeyguides also benefit from locating the colonies: They eat the leftover honeycomb.
The study’s findings build on research published in 2014 that showed the immense benefits of this relationship for the Hadza people. Honeyguides increased Hadza hunter-gatherers’ rate of finding bee nests by 560% and led them to significantly higher-yielding nests than those found without honeyguides. This prior research also found that 8%–10% of the Hadza's yearly diet was acquired with the help of honeyguides.
Spottiswoode and Wood’s study was done in collaboration with the Hadza in Tanzania, with whom Wood has been conducting research since 2004, and the Yao community of northern Mozambique.
Their prior work in both communities documented differences in how each culture attracts honeyguides. Among the Hadza, a honey-hunter announces a desire to partner with the bird by whistling. (Listen to the Hadza vocal signal.)
In Mozambique, Yao honey-hunters do so with a trilled “Brr! ...” followed by a guttural “ ... hmm!” (Listen to the Yao vocal signal.)
Using mathematical models and audio playback experiments, the team studied these signals, their utility to people and their impacts on birds.
They experimentally exposed honeyguides in Tanzania and Mozambique to the same set of prerecorded sounds. This enabled the researchers to test whether honeyguides had learned to recognize and prefer the specialized signals that local honey-hunters used — or were innately attracted to all such signals.
The honeyguides in Tanzania were over three times more likely to cooperate when hearing the calls of local Hadza people than the calls of ‘foreign’ Yao. The honeyguides in Mozambique were almost twice as likely to cooperate when hearing the local Yao call, compared to the ‘foreign’ Hadza whistles.
The study proposes that differences in honeyguide-attracting signals are not arbitrary, but make practical sense. While honey-hunting, both the Hadza and Yao encounter mammals, but only the Hadza hunt them, using bows and arrows. The Hadza’s hunting might explain the less conspicuous whistles they use. Filmed interviews show Hadza hunters explaining that they can evade being detected by their prey because their whistles “sound like birds.”
“Not just among the Hadza, but in hunting cultures around the world, people use whistles as a form of encrypted communication — to share information while avoiding detection by prey,” Wood said.
Conversely, the guttural trill-grunt signal the Yao use to communicate with the honeyguide can help scare off animals they find dangerous.
Although both humans and birds can learn new signals, the authors propose that the mutually beneficial relationship between birds and people spawns local traditions of human-bird communication that remain stable over time.
“The benefits of the honey-hunter-honeyguide relationship should produce long-lasting, ‘sticky’ traditions,” Wood said.
END
Wild birds lead people to honey — and learn from them
The greater honeyguide can recognize distinct vocal signals to help people in Africa locate bee colonies
2023-12-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Evolving trends in cosmetic breast augmentation: New data
2023-12-07
November 30, 2023 – Ongoing quality improvement data submitted by Board-certified plastic surgeons highlight current trends in surgical technique in cosmetic breast augmentation using implants, reports a study in the December issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"The findings illustrate evolving trends in breast enhancement over the past 16 years, including factors like the location of the incision and the type and positioning of implants," comments lead author Michael J. Stein, ...
Princeton Chemistry develops catalyst for electronically controlled C–H functionalization
2023-12-07
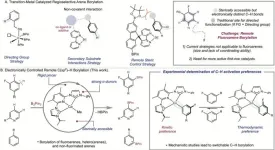
The Chirik Group at the Princeton Department of Chemistry is chipping away at one of the great challenges of metal-catalyzed C–H functionalization with a new method that uses a cobalt catalyst to differentiate between bonds in fluoroarenes, functionalizing them based on their intrinsic electronic properties.
In a paper published this week in Science, researchers show they are able to bypass the need for steric control and directing groups to induce cobalt-catalyzed borylation that is meta-selective.
The lab’s research ...
Llama power: Tiny llama nanobodies neutralize different noroviruses. Can they improve human anti-viral therapies?
2023-12-07
Human noroviruses cause acute gastroenteritis, a global health problem for which there are no vaccines or antiviral drugs. Although most healthy patients recover completely from the infection, norovirus can be life-threatening in infants, the elderly and people with underlying diseases. Estimates indicate that human noroviruses cause approximately 684 million illnesses and 212,000 deaths annually.
“Human noroviruses are highly diverse,” said first author Dr. Wilhelm Salmen, a graduate student in Dr. B V Venkataram Prasad’s lab while he was working ...
Less ice on the road leads to more salt in the soil, air, and water
2023-12-07
When temperatures drop and roads get slick, rock salt is an important safety precaution used by individuals, businesses, and local and state governments to keep walkers, cyclists, and drivers safe. However, according to a new scientific review paper from a team of researchers at Virginia Tech and the University of Maryland, the human demand for salt comes at a cost to the environment.
Published in the journal Nature Reviews Earth & Environment with researchers Stanley Grant, Megan Rippy, and Shantanu Bhide from Virginia Tech’s Occoquan Watershed Monitoring Laboratory, ...
Very early treatment of newborns with HIV could result in medication-free remission for many babies
2023-12-07
An unexpectedly high percentage of children, who were born with HIV and started treatment within 48 hours of life, exhibit biomarkers by 2 years of age that may make them eligible to test for medication-free remission, according to a multinational study published in Lancet HIV.
“Moving away from reliance on daily antiretroviral therapy (ART) to control HIV would be a huge improvement to the quality of life of these children,” said Protocol Co-Chair and senior author Ellen Chadwick, MD, former Director of Section ...
Sister climate cities, utility data predict future water, electricity demands
2023-12-07
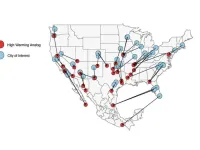
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. – Modern-day Ciudad Mante, Mexico, could help Tampa, Florida, plan for shifting water and electricity demands due to climate change, according to an international team of researchers. Led by Renee Obringer, assistant professor of energy and mineral engineering at Penn State, the researchers used utilities data and climate analogs — contemporary cities with climates close to what other cities are predicted to experience in the future — to assess how climate change may impact residential water and electricity use across 46 cities in the United States.
Their computationally efficient model projected strong regional differences for future water and electricity ...
New target found for treatment of spinal muscular atrophy
2023-12-07
The lab of Yongchao C. Ma, PhD, at Stanley Manne Children’s Research Institute at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago uncovered a novel mechanism that leads to motor neuron degeneration in spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). This discovery offers a new target for treatment that overcomes important limitations of gene therapy and other current therapies for SMA.
SMA is a genetic disease that disrupts the nerve cells that control voluntary muscle movement. Symptoms of motor neuron degeneration could start at as early as 3 months of ...
Mass General Cancer Center researchers present key findings at American Society of Hematology (ASH) Meeting
2023-12-07
Investigators from the Mass General Cancer Center, a part of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, will present research discoveries and outcomes from clinical trials at the 2023 American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting, held December 9-12, 2023 in San Diego.
ASH brings together leading experts in classical and malignant blood diseases to share the latest breakthroughs, clinical studies and research impacting the field and patient care. Mass General Cancer Center researchers will cover a wide range of topics, including ...
Thermal impact of 3D stacking photonic and electronic chips
2023-12-07
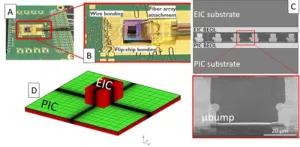
Recent advancements in AI and more specifically large language models such as ChatGPT have put a strain on data centers. AI models require huge amounts of data to train, and in order to move data between the processing units and memory, efficient communication links become necessary. For long distance communication, fiber optics has already been the go-to solution for decades. For short distance intra-data center communication, the industry is now also starting to adopt fiber optics due to its great performance compared to classical electrical links. Recent technological developments now even enable the switch from electrical to optical interconnect for very small distances, ...
Protein found in brain linked to frontotemporal dementia
2023-12-07
INDIANAPOLIS—An international team of researchers including experts at the Indiana University School of Medicine has identified a protein found in the brains of people with frontotemporal dementia (FTD), discovering a new target for potential treatments for the disease.
According to the National Institutes of Health, FTD results from damage to neurons in the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain. People with this type of dementia typically present symptoms, including unusual behaviors, emotional problems, trouble communicating, difficulty with work or in some cases difficulty with walking, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
[Press-News.org] Wild birds lead people to honey — and learn from themThe greater honeyguide can recognize distinct vocal signals to help people in Africa locate bee colonies