(Press-News.org) With the increase in the production of batteries for electric vehicles, demand is also rising for the necessary raw materials. In view of risks to the supply chain, environmental problems and precarious working conditions which are all associated with the mining and transportation of these materials, the recycling of battery materials has become an important issue in research, politics and industry. Prof. Stephan von Delft from the University of Münster (Germany) heads a team of researchers from the fields of science and the automotive and battery industries who have therefore been investigating when the demand for the three most important raw materials for batteries – lithium, cobalt and nickel – can be met entirely through recycling in Europe, the US and China; in other words, when a completely circular economy will be possible in these regions. The team’s conclusion is that China will achieve this first, followed by Europe and the US.
In detail, the results show that China is expected to be able to employ recycling to meet its own demand for primary lithium for electric vehicles, obtained through mining, from 2059 onwards; in Europe and the US, this will not happen until after 2070. As far as cobalt is concerned, recycling is expected to ensure that China will be able to meet its needs after 2045, at the earliest; in Europe this will happen in 2052 and in the US not until 2056. As regards nickel: China can probably meet demand through recycling in 2046 at the earliest, with Europe following in 2058 and the US from 2064 onwards.
Although earlier research looked at the supply of recycled raw materials for batteries and the demand for them, it had not so far been clear when complete circularity would be achieved, with supply and demand being equal (“break-even point”). The team of researchers also looked at the question of whether there are any possibilities of achieving equilibrium sooner than is predicted by current developments. “Yes, there are,” says Stephan von Delft. “Our research shows that, in particular, a faster rate of electrification in the automotive industry, as is currently being discussed in the EU, will play a role in the process. The reason is that the faster electric vehicles spread throughout the automotive market, the sooner there will be sufficient quantities of batteries available for recycling.” As PhD student Jannis Wesselkämper adds, “The demand for raw materials could also be met much earlier by recycling as a result of a reduction in battery size and by avoiding a so-called ‘second life’ for batteries – for example as stationary storage units for solar power.”
The researchers made use of a so-called dynamic material flow analysis to calculate both future demand and the recyclable raw materials then available. The data basis the team used consisted of data from current research work and market forecasts regarding developments in battery production and sales and the associated demand for raw materials.
END
Study on battery recycling shows China is in 1st place
China is ahead of Europe and the US in using recycling to meet its needs for lithium, cobalt and nickel for batteries for electric vehicles
2023-12-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Veins of bacteria could form a self-healing system for concrete infrastructure
2023-12-08
In hopes of producing concrete structures that can repair their cracks, researchers from Drexel University’s College of Engineering are putting a new twist on an old trick for improving the durability of concrete. Fiber reinforcement has been around since the first masons were mixing horsehair into their mud. But the Drexel research team is taking this method to the next level by turning reinforcing fibers into a living tissue system that rushes concrete-healing bacteria to the site of cracks to repair the damage.
Recently reported in the journal Construction ...
First observation of structures resulting from 3D domain swapping in antibody light chains
2023-12-08
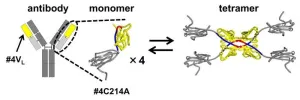
Ikoma, Japan – Antibodies (immunoglobulins) are Y-shaped proteins that recognize and neutralize specific pathogens. Their ability to target specific molecules or cells has made them promising candidates for future drug development. However, their light chains—parts of the antibody that contribute to recognizing and binding to specific antigens—misfold and aggregate, leading to amyloidosis, a condition that brings about complications and tissue dysfunction in the body. In the context of drug development, antibody aggregation can compromise their capacity to bind to antigens ...
Scholars say it's time to declare a new epoch on the moon, the 'lunar Anthropocene'
2023-12-08
LAWRENCE — Human beings first disturbed moon dust on Sept. 13, 1959, when the USSR’s unmanned spacecraft Luna 2 alighted on the lunar surface. In the following decades, more than a hundred other spacecraft have touched the moon — both crewed and uncrewed, sometimes landing and sometimes crashing. The most famous of these were NASA’s Apollo Lunar Modules, which transported humans to the moon’s surface to the astonishment of humankind.
In the coming years, missions and projects already planned will change the face of the moon ...
Researchers safely integrate fragile 2D materials into devices
2023-12-08
Two-dimensional materials, which are only a few atoms thick, can exhibit some incredible properties, such as the ability to carry electric charge extremely efficiently, which could boost the performance of next-generation electronic devices.
But integrating 2D materials into devices and systems like computer chips is notoriously difficult. These ultrathin structures can be damaged by conventional fabrication techniques, which often rely on the use of chemicals, high temperatures, or destructive processes like etching.
To overcome this challenge, researchers from MIT and elsewhere have developed a new technique to integrate 2D materials into devices in a single ...
Digital multi-sided platforms transform traditional value chains in business-to-business service sales
2023-12-08
Various digital platforms are becoming increasingly common in business-to-business (B2B) activities. They enable building competitiveness and boosting selling and buying. The platforms also offer different ways of building long-term customer relationships in B2B service sales. A recent study found that digital platforms are transforming traditional value chains based on linear value creation towards a platform-based, multi-sided, digital value network.
“The network is administered and orchestrated by the platform owner, who must attract a sufficient number ...
The first European manifesto for more sustainable museums
2023-12-08
Venice, Amsterdam, Paris, December 8, 2023 – Today, the Center for Cultural Heritage Technologies of the Italian Institute of Technology (CCHT-IIT), the University of Amsterdam/Rijksmuseum, and CNRS/École Normale Supérieure de Paris-Saclay launch the first manifesto for sustainable conservation of cultural heritage. The manifesto aims to improve conservation practices and promote more sustainable and ecological methods in museum practices.
During the COP28 in Dubai, the United Nations event on ...
Atlantic Ocean near Bermuda is warmer and more acidic than ever, 40 years of observation show
2023-12-08
Decade-long ocean warming which impacts ocean circulation, a decrease in oxygen levels that contributes to changes in salinification and nutrient supply, and ocean acidification are just some of the challenges the world’s oceans are facing.
In 1988, a comprehensive sustained ocean time-series of observations, called the Bermuda Atlantic Time-series Study (BATS), began at a site about 80 km southeast of the island of Bermuda. There, scientists take monthly samples of the physics, biology, and chemistry of the ocean’s surface and depths. In a new paper published in Frontiers in Marine Science, researchers have now presented the latest findings from ...
Battle of the AIs in medical research: ChatGPT vs Elicit
2023-12-08
Can AI save us from the arduous and time-consuming task of academic research collection? An international team of researchers investigated the credibility and efficiency of generative AI as an information-gathering tool in the medical field.
The research team, led by Professor Masaru Enomoto of the Graduate School of Medicine at Osaka Metropolitan University, fed identical clinical questions and literature selection criteria to two generative AIs; ChatGPT and Elicit. The results showed that while ChatGPT suggested fictitious articles, Elicit was efficient, suggesting multiple references within a few minutes with the same level of accuracy as the researchers.
“This ...
Aston University research finds peer support vital for those taking medication for severe mental illness
2023-12-08
Research has found many challenges to medication adherence in people living with severe mental illness
Talking to those with similar conditions on similar medication may offer more reassurance and useful advice
The researchers worked with people with severe mental illness to better understand their lived experience.
Researchers at Aston Pharmacy School have found that people with severe mental illness could benefit from peer support to help them manage their medication and improve their health and quality of life.
The study, which was set up to review the complexities ...
Even small amounts of physical activity could be valuable in late-stage lung cancer
2023-12-08
Lung cancer kills more people globally each year than any other type of cancer, however new Curtin University-led research has found less than five minutes of daily physical activity could be linked with prolonged life in people living with inoperable forms of the disease.
The team from Curtin School of Allied Health, Curtin enAble Institute and other research organisations measured the daily activity of 89 people living with inoperable lung cancer, from the time of their diagnosis.
They then compared the mortality rates after 12 months between those who engaged in more moderate-to-vigorous ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Study on battery recycling shows China is in 1st placeChina is ahead of Europe and the US in using recycling to meet its needs for lithium, cobalt and nickel for batteries for electric vehicles