(Press-News.org) HOUSTON and SOUTH SAN FRANCISCO, Calif. ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and Rigel Pharmaceuticals, Inc. today announced a multi-year strategic development collaboration to expand the evaluation of olutasidenib in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and other hematologic cancers.
The alliance brings together MD Anderson’s clinical research expertise with Rigel’s differentiated targeted molecule. Under the strategic collaboration, Rigel and MD Anderson will evaluate the potential of olutasidenib to treat newly diagnosed and relapsed or refractory (R/R) patients with AML, higher-risk myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and advanced myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN), in combination with other agents. The collaboration also will support the evaluation of olutasidenib as monotherapy in lower-risk MDS and as maintenance therapy in post-hematopoietic stem cell transplant patients.
“We are excited to enter into this strategic alliance with the exceptional team at MD Anderson to evaluate olutasidenib as a potential therapy for a broad range of IDH1-mutant cancers,” said Raul Rodriguez, president and chief executive officer at Rigel. “We believe olutasidenib has the potential to become a standard of care for patients in urgent need of new hematology-oncology therapies. We look forward to a close collaboration with MD Anderson to advance this as a new therapeutic option for more patients.”
Olutasidenib is a potent, selective, oral, small-molecule inhibitor of mutated IDH1 (mIDH1) designed to bind to and inhibit mIDH1 to reduce 2-hydroxyglutarate levels and restore normal cellular differentiation of myeloid cells. Olutasidenib is approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of adult patients with R/R AML with a susceptible isocitrate dehydrogenase-1 (IDH1) mutation as detected by an FDA-approved test.
“Based on its differentiated profile and compelling clinical data to date, olutasidenib has the potential, beyond its currently approved indication, to benefit patients with various cancers where mutant IDH1 is thought to play a role,” said Courtney DiNardo, M.D., professor of Leukemia. “We look forward to collaborating with Rigel to conduct in-depth studies that will determine the broader potential of olutasidenib in these patient populations.”
Rigel and MD Anderson will jointly lead all clinical development efforts, which will be overseen by a joint steering committee. Rigel will provide $15 million in time-based milestone payments and study material over the five-year collaboration. Rigel will retain all rights to its programs under the collaboration.
Read this press release in the MD Anderson Newsroom.
-30-
About Rigel
Rigel Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (Nasdaq: RIGL) is a biotechnology company dedicated to discovering, developing and providing novel therapies that significantly improve the lives of patients with hematologic disorders and cancer. Founded in 1996, Rigel is based in South San Francisco, California. For more information on Rigel, the Company's marketed products and pipeline of potential products, visit Rigel.com.
About MD Anderson
The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston ranks as one of the world's most respected centers focused on cancer patient care, research, education and prevention. The institution’s sole mission is to end cancer for patients and their families around the world, and, in 1971, it became one of the nation’s first National Cancer Institute (NCI)-designated comprehensive cancer centers. MD Anderson is No. 1 for cancer in U.S. News & World Report’s “Best Hospitals” rankings and has been named one of the nation’s top two hospitals for cancer since the rankings began in 1990. MD Anderson receives a cancer center support grant from the NCI of the National Institutes of Health (P30 CA016672).
END
MD Anderson and Rigel Pharmaceuticals announce strategic alliance to advance olutasidenib in AML and other cancers
2023-12-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New insights into Zebra mussel attachment fibers offer potential solutions to combat invasive species, develop sustainable materials
2023-12-08
A recent study from researchers in Canada and Germany has revealed that an unlikely event, occurring over 12 million years ago played an important role in shaping one of Canada’s most damaging invasive species.
Zebra and quagga mussels, belonging to the Dreissenid family, are widespread freshwater invasive species throughout North America that present a significant danger to native ecosystems by competing for resources. Using a fibrous anchor called a byssus, Dreissenid mussels contribute to biofouling on surfaces and obstruct intake structures in power stations and water treatment plants.
“This new study, which looks into the way these mussels stick to surfaces, may help improve ...
A micro-ring resonator with big potential
2023-12-08
EPFL researchers have developed a hybrid device that significantly improves existing, ubiquitous laser technology.
The team at EPFL’s Photonic Systems Laboratory (PHOSL) has developed a chip-scale laser source that enhances the performance of semiconductor lasers while enabling the generation of shorter wavelengths. This pioneering work, led by Professor Camille Brès and postdoctoral researcher Marco Clementi from EPFL’s School of Engineering represents a significant advance in the field of photonics, with implications for telecommunications, metrology, and other high-precision applications.
The ...
Skipping adjuvant radiotherapy may not impact risk of recurrence or progression in patients with low-risk DCIS
2023-12-08
SAN ANTONIO – Patients with low-risk ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) who skipped adjuvant radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery had comparable five-year outcomes to those with high-risk DCIS who received adjuvant radiotherapy, according to results from the E4112 clinical trial presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, held December 5-9, 2023.
“Nearly all women with DCIS—a noninvasive form of breast cancer—will have their cancer successfully removed, but some women will have a high risk of the disease returning or progressing to invasive breast cancer,” said Seema A. Khan, MD, a professor of surgery and the Bluhm Family ...
Some breast cancer survivors may safely de-escalate mammography three years after surgery
2023-12-08
Women 50 or older who de-escalated to less-frequent mammography three years after curative surgery for early-stage breast cancer had similar outcomes to women who received annual mammography, according to results from the Mammo-50 trial presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, held December 5-9, 2023.
Both U.S. and U.K. guidelines recommend annual breast cancer screening following surgery to remove early-stage breast cancer; in the U.S., annual mammography is recommended indefinitely, and in the U.K., it is recommended for five years, followed by screening every three years for patients 50 years and older.
However, the optimal screening schedule has yet to ...
Potentially targetable fusion RNAs may be more common in metastatic breast cancer than previously realized
2023-12-08
SAN ANTONIO – Comprehensive profiling of fusion RNAs present in a large cohort of metastatic breast tumors revealed unique fusion mutations that may be therapeutically targetable, according to results presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, held December 5-9, 2023.
Fusion mutations occur when a portion of one gene becomes fused to a portion of another, which can create gene products with new functions. They are common in cancer types that are characterized by genomic rearrangements and structural damage to the DNA, including breast cancer.
“Fusion RNAs may serve as ...
Study reveals insights into tacking diabetic kidney disease - with a side order of how anti-obesity drugs work
2023-12-08
Data from Australian researchers could partly explain why a trial of a new drug for diabetes, was recently halted because it was found to be so effective. Importantly, the data also reveals how anti-obesity drugs like Ozempic, actually work, which to date have been a mystery.
In early November the FLOW trial of the drug semaglutide on the progression of renal impairment in people with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease was halted ahead of schedule because of the drug’s efficacy.
Part of the rationale for the cessation of the trial could be explained by ...
Study on battery recycling shows China is in 1st place
2023-12-08
With the increase in the production of batteries for electric vehicles, demand is also rising for the necessary raw materials. In view of risks to the supply chain, environmental problems and precarious working conditions which are all associated with the mining and transportation of these materials, the recycling of battery materials has become an important issue in research, politics and industry. Prof. Stephan von Delft from the University of Münster (Germany) heads a team of researchers from the fields of science ...
Veins of bacteria could form a self-healing system for concrete infrastructure
2023-12-08
In hopes of producing concrete structures that can repair their cracks, researchers from Drexel University’s College of Engineering are putting a new twist on an old trick for improving the durability of concrete. Fiber reinforcement has been around since the first masons were mixing horsehair into their mud. But the Drexel research team is taking this method to the next level by turning reinforcing fibers into a living tissue system that rushes concrete-healing bacteria to the site of cracks to repair the damage.
Recently reported in the journal Construction ...
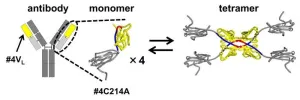
First observation of structures resulting from 3D domain swapping in antibody light chains
2023-12-08
Ikoma, Japan – Antibodies (immunoglobulins) are Y-shaped proteins that recognize and neutralize specific pathogens. Their ability to target specific molecules or cells has made them promising candidates for future drug development. However, their light chains—parts of the antibody that contribute to recognizing and binding to specific antigens—misfold and aggregate, leading to amyloidosis, a condition that brings about complications and tissue dysfunction in the body. In the context of drug development, antibody aggregation can compromise their capacity to bind to antigens ...
Scholars say it's time to declare a new epoch on the moon, the 'lunar Anthropocene'
2023-12-08
LAWRENCE — Human beings first disturbed moon dust on Sept. 13, 1959, when the USSR’s unmanned spacecraft Luna 2 alighted on the lunar surface. In the following decades, more than a hundred other spacecraft have touched the moon — both crewed and uncrewed, sometimes landing and sometimes crashing. The most famous of these were NASA’s Apollo Lunar Modules, which transported humans to the moon’s surface to the astonishment of humankind.
In the coming years, missions and projects already planned will change the face of the moon ...