(Press-News.org) BUFFALO, N.Y. – University at Buffalo research has identified how a misstep in the genesis of a key component of the kidney causes infantile cystinosis, a rare disease that significantly shortens the lifespan of patients. Published Nov. 30 in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences, the work reveals that the mechanisms that cause the disease could be addressed and potentially cured through the genome-editing technique CRISPR. That could make kidney transplants, the most effective treatment currently available for these patients, unnecessary.
Infantile cystinosis, the most common and most severe type of cystinosis, occurs as the result of an accumulation in the body’s cells of cystine, an amino acid. The buildup damages cells throughout the body, especially the kidneys and the eyes. Treatment consists of medications that work to lower the level of cystine in the body, as well as therapies that address the impaired growth of these children due to the inability to properly absorb nutrients. Some children require feeding tubes. Eventually, patients with infantile cystinosis, also called nephropathic cystinosis, will require dialysis and a kidney transplant.
Promise of stem cells
Human-induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) are stem cells that can differentiate into many different cell types. They hold tremendous potential for studying genetic diseases; the drawback has been that differentiation into certain cell types has been problematic. Such is the case with many cell types found in the kidney.
But a new protocol developed by this research team was successful.
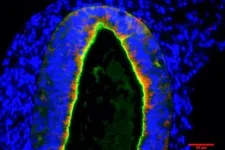
“When our normal human-induced pluripotent stem cells were subjected to the differentiation protocol we developed, we were able to demonstrate extensive expression of physiologically important markers of the renal proximal tubule, the specific nephron segment that is altered in this disease,” says Mary L. Taub, PhD, senior author on the paper and professor of biochemistry in the Jacobs School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences at UB.
Ramkumar Thiyagarajan, PhD, assistant professor of geriatric studies at the University of Kansas and formerly a postdoctoral fellow at UB, is first author on the paper.
The protocol involved extracting stem cells from a healthy individual and an individual with infantile cystinosis. The researchers developed a culture medium to grow stem cells that included a small number of defined components present in blood, including insulin, specific proteins, growth factors and others. “Conducting the differentiation protocol under these conditions occurred in a timely manner,” says Taub, “we didn’t have to wait for weeks on end, and it occurred in a reproducible manner.”
The researchers were able to efficiently differentiate the hiPSCs into the kidney proximal tubule, the type of nephron in the kidney that is impaired in infantile cystinosis, as well as in other kidney diseases.
“Unlike in other studies, we were able to retain a number of markers in the tubule that are physiologically important in the kidney’s reabsorptive functions,” says Taub. “Although these markers were expressed in both the normal and the cystinosis-derived hiPSCs, the genesis of the tubule was impaired in the cystinosis-derived cells, mimicking what happens in infantile cystinosis.”
A potential cure
That finding means that the CRISPR genome-editing technique could be used to repair the defective genome and potentially cure the disease. “The normal gene can be introduced in the genome of cystinotic hiPSCs, which can then be injected in the kidney to replace the defective proximal tubules of individuals with infantile cystinosis,” Taub says.
“In cystinotic individuals, it is the renal proximal tubule that degenerates, presumably due to programmed cell death,” explains Taub, “so the entire kidney would not need to be replaced. The defective renal proximal tubules of individuals with this disease can be replaced with normal tubules following the introduction of the normal gene into cystinotic hiPSCs obtained from the patient. And because these tubules are from cells derived from the patient, there should be no problem with tissue rejection.”
The findings are applicable to other kidney diseases where the renal proximal tubule is damaged, including acute kidney injury that can lead to chronic kidney disease and renal failure, and can be fatal.
Initial studies will need to be conducted with animal models as well as with in vitro tissue culture cells.
The research was funded by UB’s WNYSTEM and The Cystinosis Research Foundation.
END
Stem cell study reveals how infantile cystinosis causes kidney failure – and how to cure it
Research demonstrates how the genetic defect causing this rare, congenital disease could be repaired through CRISPR
2023-12-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Raz developing advanced model-based tools for portfolio management
2023-12-11
Raz Developing Advanced Model-Based Tools For Portfolio Management
Ali Raz, Professor, Systems Engineering and Operations Research (SEOR), received funding for the project: "Advanced Model-Based Tools for Portfolio Management and Analytic: System Architecture and Multi-Attribute Decision Making for Integrating Autonomy Phase 2 (AIRC RT-1081.07.5)."
Raz is supporting Purdue University and Georgia Tech Research Institute (GTRI) in the enhancement of the IAPR System-of-systems (SoS) tool suite.
Raz received $20,500 from Stevens Institute of Technology on a subaward from the U.S. Department of Defense for ...
SETI Institute unveils two prestigious postdoctoral fellowships: the Baruch S. Blumberg Fellowship and the William J. Welch Fellowship
2023-12-11
December 11, 2023, Mountain View, CA -- The SETI Institute announced today the establishment of a new postdoctoral research fellowship program funded by its transformative bequest from Qualcomm Co-founder, Franklin Antonio. The first two fellowships are being announced in conjunction with the American Geophysical Union Conference (AGU) being held this week in San Francisco. The Baruch S. Blumberg Postdoctoral Fellowship for Astrobiology and the William J. Welch Postdoctoral Fellowship for SETI and Technosignatures ...
Alaskan allies: Communities unite to protect the areas they love
2023-12-11
URBANA, Ill. — Natural resource management decisions in protected areas impact more than the wildlife and landscapes they’re charged to conserve. They also affect neighbors, who could otherwise hunt, build, or recreate as they choose on their own land. For decades, community members primarily voiced their opinions through brief and impersonal public comment periods. But an initiative led by environmental social scientists at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign is putting a new spin on neighborly communication.
“Historically, public land management ...
Researchers find promising candidate to treat irreversible lung and eye diseases in extremely premature infants
2023-12-11
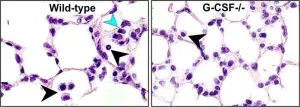
Philadelphia, December 11, 2023 – Advancements in the care of premature babies are leading to improved survival rates. However, the incidence of neonatal diseases with life-long consequences such as bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) and retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) is increasing. A novel study has implicated granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) in both BPD and ROP, making it a promising therapeutic candidate. The results appear in The American Journal of Pathology, published by Elsevier.
BPD, also called chronic lung disease of immaturity, afflicts approximately one third of all extremely ...
Public bodies “overwhelmed” at having to implement human rights laws, study warns
2023-12-11
Statt at public bodies can be “overwhelmed” by having to implement human rights laws into the working of their organisation when staff are in “awe” of legislation, a new study warns.
When laws are viewed as sacrosanct control over interpretation and implementation can be seen as the responsibility of a privileged few, according to the research.
This leads to staff placing greater weight on implementation through processes. Laws are seen as so specialist staff feel they do not have the perceived required knowledge and expertise and cannot be trusted to implement them.
Those who see equality and human rights law as malleable believe they should ...
If a piece of Turkey gets stuck in your throat this Christmas, there is no point in trying to free it with Cola
2023-12-11
Cola. A drink forever associated with the Christmas season. And also, for many, a liquid that can help clear a blocked oesophagus. Something that may be a bit more likely at this time of year. However, research from Amsterdam UMC, published today in the BMJ Christmas Issue, shows that this is not worth wasting the sugary stuff.
"Emergency physician Elise Tiebie, the driving force behind this project, saw online that this was really a rumour, from tip websites to Wikipedia as well as an anecdote in a British newspaper about paramedics saving a life by using cola. I've even heard doctors recommending it,” says Arjan Bredenoord, Professor of Gastroenterology at ...
McGovern Medical School names new neurosurgery chair; Tandon takes on role at UTHealth Houston Neurosciences
2023-12-11
Jacques Morcos, MD, a renowned neurosurgeon from University of Miami Health System, will join UTHealth Houston as the new chair of the Vivian L. Smith Department of Neurosurgery with McGovern Medical School at UTHealth Houston, effective today.
Morcos will also serve as co-director of UTHealth Houston Neurosciences alongside Louise McCullough, MD, PhD, chair of the Department of Neurology, and will be appointed as the Nancy, Clive and Pierce Runnells Distinguished Chair in Neuroscience.
Nitin Tandon, MD, former chair ad interim of the neurosurgery department, ...
Study: Women-led groups were key to food security during COVID-19 in India
2023-12-11
In March of 2020, India’s government announced a strict lockdown with just four hours notice, including a ban on the informal and traditional food outlets that 80 to 90 percent of Indians rely on for their main source of food.
In a new paper, “Applying the six-dimensional food security framework to examine a fresh fruit and vegetable program implemented by self-help groups during the COVID-19 lockdown in India,” published in the journal World Development, researchers from the Alliance of Bioversity International and CIAT looked at the effects of a government-backed women’s self-help group program in the state of Odisha, India and how it impacted the six ...
Researchers combine biopolymers derived from the ocean to replace synthetic plastic films
2023-12-11
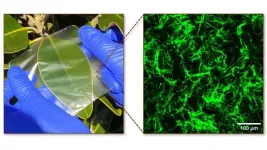
Materials with enhanced structure derived from crustaceans and seaweed could be part of a next-generation answer to the challenge of replacing petroleum-based plastic films, according to new research from North Carolina State University.
Combining chitosan, a biopolymer that makes crab shells hard, with agarose, a biopolymer extracted from seaweed that is used to make gels, creates unique biopolymer composite films with enhanced strength. The films are also biodegradable, have antibacterial properties, repel water and are transparent. The findings could eventually lead to sustainable packaging films for food ...
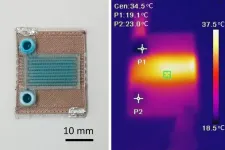
Scientists 3D print self-heating microfluidic devices
2023-12-11
MIT researchers have used 3D printing to produce self-heating microfluidic devices, demonstrating a technique which could someday be used to rapidly create cheap, yet accurate, tools to detect a host of diseases.
Microfluidics, miniaturized machines that manipulate fluids and facilitate chemical reactions, can be used to detect disease in tiny samples of blood or fluids. At-home test kits for Covid-19, for example, incorporate a simple type of microfluidic.
But many microfluidic applications require chemical reactions that must be performed at specific temperatures. These more complex microfluidic devices, which are typically manufactured in a clean ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
How AI is integrated into clinical workflow lowers medical liability perception
New biotech company to accelerate treatments for heart disease
One gene makes the difference: research team achieves breakthrough in breeding winter-hardy faba beans
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
[Press-News.org] Stem cell study reveals how infantile cystinosis causes kidney failure – and how to cure itResearch demonstrates how the genetic defect causing this rare, congenital disease could be repaired through CRISPR