(Press-News.org) WINSTON-SALEM, NC, December 13, 2023 - The Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine (WFIRM) has received a $6 million grant from the National Institute for Diabetes, Digestive and Kidney Diseases, part of the National Institutes of Health. Alongside five other North Carolina institutions, the collaborative effort aims to address critical issues and advance research in the fields of kidney, urology and hematology. Dr. Anthony Atala, the W. Boyce professor and chair of urology at Wake Forest University School of Medicine and director of WFIRM, Dr. Ronald Falk, Nan and Hugh Cullman Eminent professor of medicine at UNC, and Dr. Thomas Ortel, professor of medicine at Duke University, are the principal investigators of the five year grant from the NIH National Institute for Diabetes, Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK). The goal of the program developed under this award, named the NC KUH Training, Research, Innovation and Outreach (TRIO), is designed to cultivate a highly skilled cohort of people and resources to advance research for patients with kidney disease, urological disorders, and hematological conditions such as sickle cell disease.
“WFIRM will be generating a regenerative medicine focus,” said Atala, who is co-principal investigator for the grant. “Our researchers have decades of expertise in the field of tissue regeneration and precision medicine through organ-on-a-chip that we are excited to contribute to the partnership.” Atala, a practicing surgeon and urologist at Atrium Health Wake Forest Baptist, will be guiding the project’s urology focus. The research team also includes Chris Porada and Dr. Graca Almeida-Porada, professors at WFIRM, as the leads for the hematology area with expertise in cell and gene therapies, and James Yoo, associate director at WFIRM, as the lead for professional development training.
This new initiative is the result of organizations across a variety of disciplines and universities who are deeply committed to advancing medical knowledge and improving patient outcomes. The multi-institutional collaboration includes the University of North Carolina School of Medicine, Duke University School of Medicine, Wake Forest University School of Medicine, East Carolina University Brody School of Medicine, Winston-Salem State University, and North Carolina Central University.
The primary objectives of this grant-funded research training initiative are to:
Provide state of the art training for students and early investigators in kidney diseases, urological disorders, and hematology conditions
Advance the understanding of these diseases through this training and collaborative program
Develop innovative diagnostic tools, therapies, and treatment options
Improve patient care and outcomes through leading-edge research and clinical trials
Foster collaborations that bring together the best minds across fields as well as their intersections
“What makes this grant different is the professional development and training components,” said Joan Schanck, chief education program officer for WFIRM and program coordinator for the grant. “These institutions have existing legacies in cutting edge research, but we are now combining that expertise with outreach programs and education efforts to increase awareness and drive progress.”
In addition, the collaborative nature of this project will create a dynamic ecosystem of researchers, clinicians, and educators working together to accelerate real life treatments for patients. For more information about this grant and the collaborative research initiative, please visit http://nckuhtrio.org.
About Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine: The Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine is recognized as an international leader in translating scientific discovery into clinical therapies, with many world firsts, including the development and implantation of the first engineered organ in a patient. Over 450 people at the institute, the largest in the world, work on more than 40 different tissues and organs. A number of the basic principles of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine were first developed at the institute. WFIRM researchers have successfully engineered replacement tissues and organs in all four categories – flat structures, tubular tissues, hollow organs and solid organs – and 16 different applications of cell/tissue therapy technologies, such as skin, urethras, cartilage, bladders, muscle, kidney, and vaginal organs, have been successfully used in human patients. The institute, which is part of Wake Forest University School of Medicine, is located in the Innovation Quarter in downtown Winston-Salem, NC, and is driven by the urgent needs of patients. The institute is making a global difference in regenerative medicine through collaborations with over 500 entities and institutions worldwide, through its government, academic and industry partnerships, its start-up entities, and through major initiatives in breakthrough technologies, such as tissue engineering, cell therapies, diagnostics, drug discovery, biomanufacturing, nanotechnology, gene editing and 3D printing.
Media Contact: Emily Gregg, egregg@wakehealth.edu
END
WFIRM and partnering institutions awarded five-year, $6 million grant on kidney, urology, and hematology research
2023-12-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Beef farming that keeps cattle on lifelong grass diets may have higher carbon footprint
2023-12-13
Beef operations that keep cattle on lifelong grass-based diets may have an overall higher carbon footprint than those that switch cattle to grain-based diets partway through their lives. Daniel Blaustein-Rejto of the Breakthrough Institute, USA, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on December 13.
Cattle on lifelong grass diets are known as “pasture finished,” while those that switch from grass to grain before slaughter are “grain finished.” Prior research has suggested that ...
Vikings in Sweden suffered from tooth decay
2023-12-13
Vikings in Sweden suffered from painful dental issues and occasionally tried to treat them, according to a study published December 13, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Carolina Bertilsson of the University of Gothenburg, Sweden and colleagues.
In 2005, excavations in Varnhem, Sweden uncovered the remains of a Christian church, nearby which was a cemetery containing thousands of Viking graves dating to the 10th-12th century AD. In this study, Bertilsson and colleagues performed clinical and radiographical examination of the dentition of individuals from this site. In total, the team analyzed over 2300 teeth ...
The methane and nitrous oxide we exhale might contribute - in a very small way - to greenhouse gas emissions, with breath analysis indicating this may comprise up to 0.1% of UK emissions of the gases
2023-12-13
The methane and nitrous oxide we exhale might contribute - in a very small way - to greenhouse gas emissions, with breath analysis indicating this may comprise up to 0.1% of UK emissions of the gases
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0295157
Article Title: Measurements of methane and nitrous oxide in human breath and the development of UK scale emissions
Author Countries: UK
Funding: The analysis was funded by the UK NERC grant E/S003614/2 ‘Detection and Attribution of Regional greenhouse gas Emissions in the UK (DAREUK)’. ...
Moms who participate in baby massage report reduced postnatal depression symptoms and better interactions with their child, per systematic review
2023-12-13
Moms who participate in baby massage report reduced postnatal depression symptoms and better interactions with their child, per systematic review
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0294156
Article Title: The effectiveness of mother-led infant massage on symptoms of maternal postnatal depression: A systematic review
Author Countries: Ireland
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Yoga nidra might be a path to better sleep and improved memory
2023-12-13
Practicing yoga nidra—a kind of mindfulness training— might improve sleep, cognition, learning, and memory, even in novices, according to a pilot study publishing in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on December 13 by Karuna Datta of the Armed Forces Medical College in India, and colleagues. After a two-week intervention with a cohort of novice practitioners, the researchers found that the percentage of delta-waves in deep sleep increased and that all tested cognitive abilities improved.
Unlike more active forms of yoga, which focus on physical postures, breathing, and muscle control, yoga nidra guides people into a state of conscious relaxation ...
Cognitive strategies for augmenting the body with a wearable, robotic arm
2023-12-13
Neuroengineer Silvestro Micera develops advanced technological solutions to help people regain sensory and motor functions that have been lost due to traumatic events or neurological disorders. Until now, he had never before worked on enhancing the human body and cognition with the help of technology.
Now in a study published in Science Robotics, Micera and his team report on how diaphragm movement can be monitored for successful control of an extra arm, essentially augmenting a healthy individual with a third – robotic – arm.
“This study opens up new and exciting opportunities, ...
Earliest evidence for domestic yak found using both archaeology, ancient DNA
2023-12-13
The high-altitude hero of the Himalayas, yak are among the few large animals that can survive the extremely cold, harsh and oxygen-poor conditions of the Tibetan Plateau. In the mountainous regions of Asia, yak and yak-cattle hybrids serve as vital sources of meat, milk, transportation and fuel. However, little is known about their history: when or where yak were domesticated.
In a study published Dec. 13 in Science Advances, an international team of researchers that includes archaeologists at Washington University in St. Louis report archaeologically and genetically confirmed evidence for domestic yak, dating back 2,500 years, by far the oldest record.
The researchers ...
Deep neural networks show promise as models of human hearing
2023-12-13
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Computational models that mimic the structure and function of the human auditory system could help researchers design better hearing aids, cochlear implants, and brain-machine interfaces. A new study from MIT has found that modern computational models derived from machine learning are moving closer to this goal.
In the largest study yet of deep neural networks that have been trained to perform auditory tasks, the MIT team showed that most of these models generate internal representations ...
Researchers create stable hybrid laser by 3D printing micro-optics onto fibers
2023-12-13
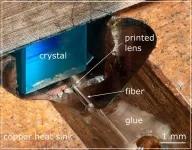
WASHINGTON — For the first time, researchers have shown that 3D-printed polymer-based micro-optics can withstand the heat and power levels that occur inside a laser. The advance enables inexpensive compact and stable laser sources that would be useful in a variety of applications, including the lidar systems used for autonomous vehicles.
“We significantly reduced the size of a laser by using 3D printing to fabricate high-quality micro-optics directly on glass fibers used inside of lasers,” said research team leader Simon Angstenberger from the 4th Physics Institute at University of Stuttgart ...
Wistar scientists enhance cell-based therapy to destroy solid tumors
2023-12-13
PHILADELPHIA—(Dec. 13, 2023)—Wistar researchers successfully tested a simple intervention that could unlock greater anti-tumor power in therapies that use T cells — an approach known as “cell-based therapy,” which uses specially designed T cells to fight cancer. Led by Dr. Hildegund C.J. Ertl — a professor in The Wistar Institute’s Vaccine & Immunotherapy Center — the team has proven an exciting concept: that the common cholesterol drug fenofibrate can boost T cells’ ability to destroy human tumors, as described in their new paper, “Treatment ...