(Press-News.org) Philadelphia, December 14, 2023 – The updated Canadian Cardiovascular Society (CCS)/Canadian Association of Interventional Cardiology (CAIC) antiplatelet therapy guidelines for primary and secondary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) provide recommendations based on the latest randomized evidence available in the literature. Updated by a panel of national experts, these new evidence-based guidelines appear in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology, published by Elsevier.
ASCVD, also known as ischemic heart disease (coronary artery disease), is the buildup of plaque in the heart’s arteries that can lead to death from a heart attack or sudden cardiac death. It is the second leading cause of death in Canada, according to Health Canada. Antiplatelet medications prevent the formation of blood clots following a heart attack and/or following a stent procedure or open-heart bypass surgery.
Co-chair and first author of the guidelines, Kevin Bainey, MD, MSc, Mazankowski Alberta Heart Institute, University of Alberta, explains: “Historically, doctors recommended taking aspirin daily for primary prevention for individuals over 50 years old (‘An aspirin a day keeps the doctor away.’), but routine use is now no longer advised. Recent evidence shows the bleeding risk outweighs the benefits, questioning the routine use to prevent a heart attack, particularly in individuals who have never had a heart attack – called primary prevention. We now recommend against routine use of aspirin for primary prevention.”
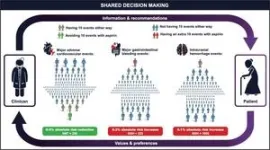
Dr. Bainey notes, “However, daily aspirin could be used for people with high risk factors for heart attack — a family history of premature coronary artery disease, diabetes, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, and smoking. The 10% risk reduction is consistent in the literature. However, we also need to recognize that bleeding can be bad. The key is to talk to your doctor to decide what’s best for you. The guidelines include a new decision-aid tool to guide those conversations in an evidence-based format.
“We really focus on individuals and determining their cardiovascular risk, their risk of bleeding, and then tailoring their antiplatelet therapy to maximize the outcomes for them. So, it’s really taking it to a different level; we’re the first in the world to endorse a shared decision-making model, engaging the person who is at risk together with their doctor.”
Dr. Bainey had this very conversation with his own father who has not had a heart attack, but has diabetes, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, and a low risk of bleeding. His dad is now taking an antiplatelet to address those risk factors.
These updated national guidelines give people who are at risk and their healthcare providers access to the latest scientific findings, which have changed considerably since the last time the guidelines were published in 2018. While the daily aspirin question is likely the most controversial topic tackled by the new guidelines, most of the topics in the guidelines focus on secondary prevention, for people who have already developed ASCVD and want to avoid further damage to their hearts.
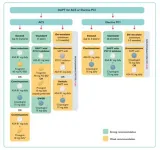
The guidelines focus on the following key topics:
Potential role of aspirin therapy for primary prevention of cardiovascular disease
Recommendations for shorter duration of dual antiplatelet therapy following percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) recognizing bleeding risk, a minimally invasive procedure to open a blocked artery
Standards for extending therapy as well as de-escalating therapy in appropriate patients
Recommendations for the use of potent P2 Y12 inhibitors (super antiplatelets) in dual antiplatelet therapy
Focus on patients with heart attacks who are medically managed without stents or open heart surgery
Discontinuation of antiplatelet therapy prior to coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) surgery and its use following CABG surgery for bypass graft protection
Importance of minimizing antithrombotic therapy in those requiring other blood thinners (oral anticoagulation for atrial fibrillation) in the context of antiplatelet therapy
The guidelines include simple illustrative diagrams and algorithms to help healthcare providers navigate through clinical scenarios for antiplatelet management.
Dr. Bainey elaborates, “It is important for us to provide clinicians with the most up-to-date contemporary evidence to improve patient care and outcomes. We are confident that these recommendations are cutting edge and contemporary, which ultimately leads to improved health and survival not only for our cardiovascular patients in Canada, but also globally.”
The updated guidelines were released in October 2023 during the CCS scientific program of Vascular 2023.
END
Updated Canadian Cardiovascular Society Guidelines advise against routinely taking aspirin daily for primary prevention of heart attack or death but acknowledge there may be a role for some people
The guidelines published in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology provide evidence-based recommendations for primary and secondary prevention of arterial plaque build-up using antiplatelet therapies
2023-12-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Rice study: AI provides more accurate analysis of prehistoric and modern animals, painting picture of ancient world
2023-12-14
A new Rice University study of the remains of prehistoric and modern African antelopes found that AI technology accurately identified animals more than 90% of the time compared to humans, who had much lower accuracy rates depending on the expert.
Composite images of teeth from five different antelope tribes analyzed and identified by artificial intelligence. Photo courtesy of Manuel Domínguez-Rodrigo.
Identifying these animals and their habits helps paint a broader picture of ancient ecosystems, and with the assistance of this new technology, it can be done with more speed and accuracy than previously done by paleontologists, ...
Working women feel unsupported by Christian congregations — even more progressive ones
2023-12-14
As church membership declines across the United States, a new study from Rice University’s Boniuk Institute for the Study and Advancement of Religious Tolerance finds that working women do not feel supported by their clergy and churches, regardless of whether they’re involved with a more conservative or liberal congregation.
“The Limits of Congregational Support for Working Women” is part of a larger study of faith at work funded by Lilly Endowment Inc. It ...
SNAP recipients may struggle to meet dietary goals, especially in food deserts
2023-12-14
The Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) is the nation’s largest nutrition program, helping 41 million participants afford “nutritious food essential to health and well-being.”
But a new study from the University of Notre Dame found that SNAP participants in low-income households may not be able to meet the nutrition levels set by the Dietary Guidelines for Americans (DGA).
The case study set out to examine whether SNAP participants would be able to afford a healthy diet based on DGA’s recommended nutritional values. The DGA was created by the U.S. Departments of Agriculture and Health and Human ...
Researchers pave the way for next generation COVID-19 immunization strategies
2023-12-14
BOSTON – The global COVID-19 vaccination campaign saved an estimated 20 million lives. However, while current COVID-19 vaccines provide protection against developing severe disease, they do little to prevent infection and transmission.
Findings published in the journal Nature by physician-scientists at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) and colleagues suggest that it may be possible to improve protection against COVID-19 by delivering the vaccine directly to the respiratory tract— the primary site of entry in SARS-CoV-2 infection.
“The ...
Improving treatment for opioid use disorder
2023-12-14
In the fatal world of opioid use disorder (OUD), pharmacotherapy, or using a prescribed medication to treat drug dependence, has emerged as the gold standard of treatment. Among the trio of FDA-approved medications to treat OUD, buprenorphine is the newest highly effective drug that can suppress and reduce cravings for opioids. It is also the first medication that physicians can prescribe without requiring a special waiver from the DEA, enabling outpatient use and substantially increasing treatment accessibility.
Despite its widespread usage, with 1 million buprenorphine prescriptions filled in 2018, it is not without side effects. When taken sublingually (under ...
Thinking about God inspires risk-taking for believers, York University study finds
2023-12-14
Thursday Dec. 14, 2023, Toronto – Does thinking about faith make religious people more likely to take leaps? A new study lead by York University’s Faculty of Health says yes, finding that participants were more likely to take risks when thinking about God as a benevolent protector.
“While the theoretical link between a belief in God and risk taking has been around for a while, the methods previous studies employed to test this weren’t the strongest, based on current best ...
Internationally renowned oncologist to lead breast cancer program and translational research integration at UCLA Health
2023-12-14
Dr. Aditya Bardia, a renowned breast medical oncologist and physician scientist who specializes in developing novel targeted and personalized therapies, has joined the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA and the UCLA Health Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center where he will assume several leadership roles across the institution. These will include the directorship of the Breast Cancer Clinical and Research Programs and the position of assistant chief of Translational Research in the division of hematology/oncology, department of medicine. He will also be named director of Translational Research Integration and co-director ...
Researchers reveal full structure of ‘ancient genetic parasite’ implicated in human diseases
2023-12-14
Research published today in Nature sheds light on a small part of the so-called “dark genome” — the 98 per cent of the human genome whose biological function is largely not known.
In the study, an international multidisciplinary team reported the first high-resolution images and structural details of a genetic element known as LINE-1 (video here), which inserts itself into the human genome and is implicated in diseases such as cancer, autoimmune disorders and neurodegeneration, and even aging. The work provides a target for ...
A promising pairing: Scientists demonstrate new combination of materials for quantum science
2023-12-14
Quantum information scientists are always on the hunt for winning combinations of materials, materials that can be manipulated at the molecular level to reliably store and transmit information.
Following a recent proof-of-principle demonstration, researchers are adding a new combination of compounds to the quantum materials roster.
In a study reported in ACS Photonics, researchers combined two nanosized structures — one made of diamond and one of lithium niobate — onto a single chip. They then sent light from the diamond ...
Move over Blitzen: geese outpace reindeer impacts on Arctic ecosystems
2023-12-14
In the frigid seas halfway between mainland Norway and the North Pole, two types of animals browse the palatable vegetation of a high-tundra archipelago, munching on thick moss, cropped grasses and low-lying shrubs. New research from a group led by Matteo Petit Bon from the Quinney College of Natural Resources is working to untangle the ecosystem impacts that two major players — geese and reindeer — have on a changing and vulnerable Arctic system.
Reindeer have been year-round residents on the islands of Svalbard for thousands of years, but at one point were almost completely gone. Svalbard ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
[Press-News.org] Updated Canadian Cardiovascular Society Guidelines advise against routinely taking aspirin daily for primary prevention of heart attack or death but acknowledge there may be a role for some peopleThe guidelines published in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology provide evidence-based recommendations for primary and secondary prevention of arterial plaque build-up using antiplatelet therapies