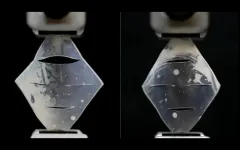
(Press-News.org) Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) on patient blood samples are useful for identifying the genetic basis of blood cell traits and their links to common diseases. While previous experiments have focused on characterizing clinical parameters such as cell count, few have evaluated the dynamic effects of factors—such as inflammation, microbiome or medications—on blood cell contributions to disease development and progression. This lack of insight into underlying biological mechanisms behind such chronic progressive conditions has hindered the advancement of targeted therapeutics.
Researchers at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, developed a framework to identify potentially hidden genetic contributors to disease by applying different stress tests to human blood cells. Using a range of physical, chemical and pharmacological stimuli, the investigators recorded evoked cellular responses and genetic variants associated with them in nearly 2,600 individuals.
The team found links between a range of blood-response characteristics and subsets of common diseases and were able to define the genetics underlying these distinct subsets of disease. In one example, they utilized the framework to identify and demonstrate a population of activated neutrophils (white blood cells) that can contribute to inflammation in cardiometabolic diseases. These findings expand the clinical measures currently available to genetically map subtypes of complex diseases.
“We were able to build on existing technology to identify new disease-associated traits,” said author Calum A. MacRae, MD, PhD, of the Division of Cardiovascular Medicine. “These tools, when combined with AI, can help improve the classification of common diseases and bring drug discovery into the clinic.”
in Nature Genetics.
END
New framework to identify genetic risk of disease could lead to targeted therapeutics
2023-12-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Newly developed material gulps down hydrogen, spits it out, protects fusion reactor walls
2023-12-14
MADISON – University of Wisconsin–Madison engineers have used a spray coating technology to produce a new workhorse material that can withstand the harsh conditions inside a fusion reactor.
The advance, detailed in a paper published recently in the journal Physica Scripta, could enable more efficient compact fusion reactors that are easier to repair and maintain.
“The fusion community is urgently looking for new manufacturing approaches to economically produce large plasma-facing components in fusion reactors,” says Mykola Ialovega, a postdoctoral researcher in nuclear engineering and engineering physics at ...
Tufts University announces Second Annual Cellular Agriculture Innovation Day
2023-12-14
Tufts University, home to the world’s largest concentration of academic researchers working on cultivated meat, will be hosting its second annual Cellular Agriculture Innovation Day on January 11, 2024. The day-long event will be held at Tufts’ Joyce Cummings Center in Medford, following a year of major developments in the industry — including regulatory approval of cultivated meat in the United States. Bringing together researchers, entrepreneurs, policymakers, and investors, Cellular Agriculture Innovation Day is an opportunity for candid ...
DOE’s Office of Science releases vision outlining the path to advancing fusion energy science and technology
2023-12-14
Washington, D.C. – The Office of Fusion Energy Sciences (FES), at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science, announced the release of its vision, Building Bridges: A Vision for the Office of Fusion Energy Sciences, during the Fusion Energy Sciences Advisory Committee hearing on December 13, 2023. This FES vision enables DOE to establish the steps needed to help advance fusion energy, including addressing key science and technology gaps in the supply chain and industry, bringing the United States one step closer to achieving net-zero emissions by 2050.
Fusion, the process that powers ...
Rubber that doesn’t grow cracks when stretched many times
2023-12-14
Researchers from the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) have increased the fatigue threshold of particle-reinforced rubber, developing a new, multiscale approach that allows the material to bear high loads and resist crack growth over repeated use. This approach could not only increase the longevity of rubber products such as tires but also reduce the amount of pollution from rubber particles shed during use.
The research is published in Nature.
Naturally occurring rubber latex is soft and stretchy. For a range of applications, including tires, hoses, and dampeners, rubbers are reinforced by ...
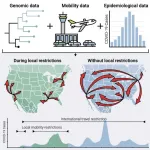
Social distancing was more effective at preventing local COVID-19 transmission than international border closures
2023-12-14
LA JOLLA, CA—Elucidating human contact networks could help predict and prevent the transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and future pandemic threats. A new study from Scripps Research scientists and collaborators points to which public health protocols worked to mitigate the spread of COVID-19—and which ones didn’t.
In the study, published online in Cell on December 14, 2023, the Scripps Research-led team of scientists investigated the efficacy of different mandates—including stay-at-home measures, social distancing and travel restrictions—at preventing local and regional transmission during different phases of the COVID-19 pandemic. They found ...
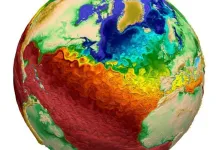
Custom software speeds up, stabilizes high-profile ocean model
2023-12-14
On the beach, ocean waves provide soothing white noise. But in scientific laboratories, they play a key role in weather forecasting and climate research. Along with the atmosphere, the ocean is typically one of the largest and most computationally demanding components of Earth system models like the Department of Energy’s Energy Exascale Earth System Model, or E3SM.
Most modern ocean models focus on two categories of waves: a barotropic system, which has a fast wave propagation speed, and a baroclinic system, which ...
Can you change a chicken into a frog, a fish or a chameleon?
2023-12-14
Gastrulation is one of the most important phases in early embryonic development. Before gastrulation, vertebrate embryos are simple two-dimensional sheets of cells. By the end of gastrulation, an embryo will have begun to differentiate distinct cell types, set up the basic axes of the body and internalize some of the precursors for organs in a three-dimensional structure. Amniotes, like chickens and humans, will have developed a primitive streak, the precursor to the brain and skin, while fish and amphibians will have developed a spherical-shaped ...
How the immune system fights to keep herpes at bay
2023-12-14
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) is extremely common, affecting nearly two-thirds of the world’s population, according to the World Health Organization.
Once inside the body, HSV establishes a latent infection that periodically awakens, causing painful blisters on the skin, typically around the nose and mouth. While a mere nuisance for most people, HSV can also lead to dangerous eye infections and brain inflammation in some people and cause life-threatening infections in newborns.
Researchers have long known ...
Drones capture new clues about how water shapes mountain ranges over time
2023-12-14
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Drones flying along miles of rivers in the steep, mountainous terrain of central Taiwan and mapping the rock properties have revealed new clues about how water helps shape mountains over geological time, according to a team led by Penn State scientists.
The researchers found a link between the size of boulders in the rivers and the steepness of the rivers. The link shows how rock properties can influence the relationship between tectonic processes happening deep underground and how mountainous landscapes ...
NIH research identifies opportunities to improve future HIV vaccine candidates
2023-12-14
WHAT:
An effective HIV vaccine may need to prompt strong responses from immune cells called CD8+ T cells to protect people from acquiring HIV, according to a new study from researchers at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, and colleagues. The study findings, appearing in Science, draw comparisons between the immune system activity of past HIV vaccine study participants and people with HIV who naturally keep the virus from replicating even in the absence of antiretroviral ...