(Press-News.org) Frontiers for Young Minds, the award-winning, open-access scientific journal for kids, has published the first articles in a new collection in collaboration with CERN, one of the world’s largest centers for scientific research. The collection, entitled SPARK-ing big questions: what is the future of health technology?, addresses key questions on how ground-breaking health technologies and science can improve human health for future generations.
The articles are written by researchers who attended the SPARKS! Serendipity Forum at CERN in 2022, an event for scientific and other experts to come together to collaborate, learn from each other, and address some of the complex problems facing society. As one of the largest laboratories hosting collaborative research in the world, and a leader in fields that increase our knowledge of the universe and impact our lives, including health, CERN offers a platform to host such multidisciplinary discussions and curate the serendipity that may bring about benefits to society. The collaboration between Frontiers for Young Minds and CERN enables the sharing of this information with young audiences in a way that is accessible for them.
As part of the unique Frontiers for Young Minds process, the articles have been reviewed by kids aged 8-15 to make sure the concepts are understandable for their peers. All articles are freely available on the journal website.
The first three articles in the collection are:
New Scientific Technologies: Navigating the Path of Right and Wrong, Juan Enriquez, Excel Venture Management, USA
This article explores the ethics of new technologies and how to ensure developing technologies are used to help, not harm, humans.
Doctors and Artificial Intelligence: Working Together for a Healthier Future, Jane Metcalfe, proto.life, USA
This article examines how artificial intelligence can analyze data to find patterns that humans can’t and optimize patient care using personalized medicine.
Medicine Gets Proactive: Prevention Is Better Than Cure, Michael Snyder and Ariel Ganz, Stanford University, USA
This article looks at how technology such as smartwatches and health-tracking apps can catch illnesses before humans get sick, an approach that could help humans live longer.
New articles will be added to the collection in January 2024 to help young minds engage with the topics of health literacy, open science, and bioinformatics. Together, the collection of articles will help the next generation of scientists and engaged citizens to understand and grapple with the big questions which they will have to face in their own healthcare as people continue to live longer.
To read the articles, visit the Frontiers for Young Minds website.
END
Frontiers for Young Minds and CERN ‘SPARK’ big questions in health technology
The scientific articles are written by researchers who attended the 2022 SPARKS! Serendipity Forum at CERN
2023-12-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Role of cleaning fishes in conserving biodiversity distinguished with FLAD Science Award Atlantic 2023
2023-12-15
José Ricardo Paula, researcher at the Marine and Environmental Sciences Centre, Faculty of Sciences of the University of Lisbon (Portugal), will receive 300.000 euros in funding in three years to develop a project that aims to improve the understanding of the role of cleaning mutualisms in the conservation of Atlantic biodiversity, using emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence.
In the global ocean, there are several fish species, known as cleaners, that specialize in providing ...
GYA and 30 Young Academies and Associations release statement suggesting actionable steps to connect fundamental science with sustainable development
2023-12-15
GYA and 30 Young Academies and Associations release statement suggesting actionable steps to connect fundamental science with sustainable development during Closing Ceremony of IYBSSD meeting
In a collective statement endorsed by 30 Young Academies and Associations, the Global Young Academy (GYA) underscored the pivotal role of fundamental science in achieving the United Nation Sustainable Development Goals (UN SDGs). The statement (link here) was delivered during the closing ceremony of the International Year of Basic Sciences for Sustainable Development (IYBSSD) at CERN in Switzerland on 15 December 2023.
The joint statement acknowledges the historical ...
Brief teacher training better prepares medical students for patient education & communication
2023-12-15
(Boston)—Teaching is an integral communication skill central to the practice of medicine. The art of teaching extends beyond disseminating information. The skill directly translates to health provider-patient communication, the success of which is positively correlated with improved patient outcomes.
“Teaching is a large part of medicine - patient education is critical to providing high quality patient centered care. Education helps patients understand the 'why' and 'what' of their treatments and allows them to be better participants in their ...
Local Philadelphia area business owner recognized as national champion for health equity
2023-12-15
DALLAS, December 15, 2023 — Devon Mitchell, an American Heart Association local volunteer and franchise owner at Anytime Fitness in Delaware, is the 2023 National Leaders of Impact™ Winner. Mitchell, one of the 295 leaders in cities across the country, worked to improve heart health in his community while raising funds to fuel the mission of the Association. The Leaders of Impact campaign pairs community leaders in a head-to-head competition to support the health equity work of the American ...
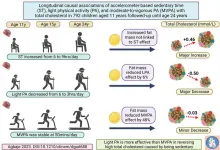
Childhood sedentariness causes elevated cholesterol but light physical activity may neutralize it
2023-12-15
Increased sedentary time from childhood through young adulthood significantly increased cholesterol levels in a new follow-up study. However, the results also showed that light physical activity (LPA) may completely reverse the adverse process. Moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA) may also reduce cholesterol levels, but its effect is diminished by body fat. The study was conducted in collaboration between the University of Bristol in the UK, the University of Exeter in the UK, and the University of Eastern ...
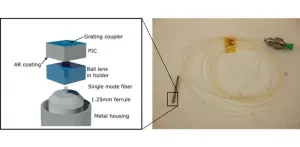
From PIC to probe
2023-12-15
Similarly as for electronics, photonic circuits can be miniaturized onto a chip, leading to a so-called photonic integrated circuit (PIC). Although these developments are more recent than for electronics, this field is rapidly evolving. One of the main issues, however, is to turn such a PIC into a functional device. This requires optical packaging and coupling strategies to bring light into and to get light out of the PIC. For example, for optical communication a connection needs to be made with optical fibers, which then transport the light ...
Prone to abandoning New Year’s resolutions? Bayes’ research suggests blaming money worries rather than being time-poor
2023-12-15
People who abandon New Year’s resolutions or other commitments can maintain the respect of their peers by blaming external factors such as lack of money, new research suggests.
Studies have found that people were more likely to be seen as having good self-control despite abandoning a commitment to live a healthier life if they claimed they did not have the money for a gym membership or expensive new cooking equipment. People who instead claimed they didn’t have the time to exercise or to replace a takeaway ...
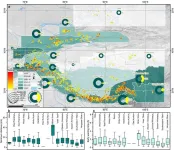
Third Pole environment researchers study the risk of glacial lake Outbursts in the Third Pole
2023-12-15
The Third Pole, which spans the Tibetan Plateau and the surrounding Himalayas, Hindu Kush, and Tianshan Mountain ranges, is extremely vulnerable to the effects of climate change. Warming temperatures and altered rainfall patterns have caused over 10,000 glaciers in the region to retreat over the past three decades, facilitating the formation of thousands of glacial lakes.
Though they appear harmless, these water bodies have a tremendous destructive potential, particularly due to their ability to cause glacial lake outburst floods (GLOFs). When triggered ...
Data scientists unveil AI framework to identify new indications for existing drugs
2023-12-15
Scientists at Klick Applied Sciences have created an artificial intelligence framework that can rapidly identify new use cases for existing therapeutics, according to findings presented Friday at the NeurIPS conference that could greatly improve the drug repurposing process and transform the pharmaceutical industry.
The team debuted their algorithm, called LOVENet, a Large Optimized Vector Embeddings Network which integrates two cutting-edge AI technologies: large language model (LLM), and structured knowledge graph technology, which mathematically represents the relationships between drugs and diseases to offer a fresh ...
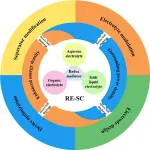
Strategies to limit redox electrolyte-enhanced carbon-based supercapacitor self-discharge
2023-12-15
The efficient storage of clean energy is a critical component to achieving carbon neutrality. Capacitors are devices that store energy by separating positive and negative electrical charge, and supercapacitors (SC) are capacitors that can store and release large amounts of energy. A specialized supercapacitor, called a redox electrolyte-enhanced SC (RE-SC), places liquid redox electrolytes, a source of ions that can be electrically charged, next to a carbon-based electrical conductor, or electrode, to achieve high energy storage density and power output. Despite this increase in performance, RE-SCs suffer from self-discharge of stored energy, limiting their practicality. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Roadmap for Europe’s biodiversity monitoring system
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
[Press-News.org] Frontiers for Young Minds and CERN ‘SPARK’ big questions in health technologyThe scientific articles are written by researchers who attended the 2022 SPARKS! Serendipity Forum at CERN