(Press-News.org)
Embargoed for release: Friday, December 15, 6:30 PM ET
Key points:
Using national data between 1993 and 2021, researchers observed that India’s national prevalence of child marriage—defined by the study as marriage before age 18—declined throughout the study period.
The decade between 2006 and 2016 saw the largest magnitude of reduction in child marriage, while the years between 2016 and 2021 saw the smallest. During these latter years, six Indian states/union territories saw increases in the prevalence of girl child marriage and eight saw increases in boy child marriage.
The study is among the first to examine how the prevalence of child marriage has changed over time at a state/union territory level.
Boston, MA—Child marriage has declined in India—but across the country, one in five girls and nearly one in six boys are still married as children, and in recent years the practice has become more prevalent in some states/union territories, according to a new study led by researchers at Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.
Child marriage is a human rights violation and a recognized form of gender- and sexual-based violence. India’s success in reaching zero child marriage is critical to achieving United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) target 5.3.
The study will be published on December 15, 2023, in The Lancet Global Health.
“This study is among the first to estimate how rates of girl and boy child marriage have changed over time at a state/union territory level. Boy child marriage in particular is often overlooked; to date, there’s been almost no research estimating its prevalence,” said lead author S. V. Subramanian, professor of population health and geography. “Our findings offer a big step forward in understanding the burden of child marriage in India—one that will be critical to effective policymaking.”
Though India legally defines child marriage as marriage before age 18 for girls and before age 21 for boys, for the purposes of the study the researchers defined it as marriage before age 18 for both sexes. Using data from all five waves of India’s National Family Health Survey, from 1993, 1999, 2006, 2016, and 2021, they estimated the number of men and women ages 20-24 who met that definition across state/union territories.
The study found that between 1993 and 2021, child marriage declined nationally. The prevalence of girl child marriage decreased from 49% in 1993 to 22% in 2021, while boy child marriage decreased from 7% in 2006 to 2% in 2021. (Using the Indian legal definition of boy child marriage, the prevalence was much higher: 29% in 2006 and 15% in 2022.) However, progress towards stopping the practice of child marriage has stalled in recent years: The largest reductions in child marriage prevalence occurred between 2006 and 2016, with the lowest magnitude of reduction occurring between 2016 and 2021. In fact, during these later years, six states/union territories (including Manipur, Punjab, Tripura, and West Bengal) saw an increase in girl child marriage and eight (including Chhattisgarh, Goa, Manipur, and Punjab) saw an increase in boy child marriage.
By 2021, the researchers counted more than 13.4 million women and more than 1.4 million men ages 20-24 who were married as children. The results showed that one in five girls and nearly one in six boys are still married below India’s legal age of marriage.
“Child marriage is a human rights violation,” said first author Jewel Gausman, research associate in the Department of Global Health and Population. “It is both a cause and a consequence of social and economic vulnerability that leads to a range of poor health outcomes. The state/union territory stagnation in reaching zero child marriage that we observed is a significant concern—and is a call for India to reignite progress.”
Rockli Kim, visiting scientist at the Harvard Center for Population and Development Studies, was also a co-author.
Funding for the study came from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation (INV-002992).
“Prevalence of Girl and Boy Child Marriage: A Repeated Cross-sectional Study Examining the Subnational Variation across States and Union Territories in India, 1993-2021,” Jewel Gausman, Rockli Kim, Akhil Kumar, Shamika Ravi, S.V. Subramanian, The Lancet Global Health, December 15, 2023, doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(23)00470-9
Visit the Harvard Chan School website for the latest news, press releases, and multimedia offerings.
###
Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health brings together dedicated experts from many disciplines to educate new generations of global health leaders and produce powerful ideas that improve the lives and health of people everywhere. As a community of leading scientists, educators, and students, we work together to take innovative ideas from the laboratory to people’s lives—not only making scientific breakthroughs, but also working to change individual behaviors, public policies, and health care practices. Each year, more than 400 faculty members at Harvard Chan School teach 1,000-plus full-time students from around the world and train thousands more through online and executive education courses. Founded in 1913 as the Harvard-MIT School of Health Officers, the School is recognized as America’s oldest professional training program in public health.
END
In a clinical trial of patients with chronic kidney disease, an experimental drug significantly reduced albuminuria — albumin in urine, a sign of kidney damage — for 50% of participants. When the experimental drug was paired with a standard-care medication, 70% of participants reportedly experienced a significant reduction in albuminuria.
The findings are published today in The Lancet. The paper’s lead author is Dr. Katherine Tuttle, a clinical professor of nephrology at the University of Washington School of Medicine and executive director for research at Providence ...
HOUSTON – (Dec. 15, 2023) – Materials with enhanced thermal conductivity are critical for the development of advanced devices to support applications in communications, clean energy and aerospace. But in order to engineer materials with this property, scientists need to understand how phonons, or quantum units of the vibration of atoms, behave in a particular substance.
“Phonons are quite important for studying new materials because they govern several material properties such as thermal conductivity and carrier properties,” said Fuyang Tay, a graduate student in applied physics working with the Rice ...
The National Science Foundation has awarded Lehigh University $6 million to increase the translation of scientific discoveries by faculty, graduate students and postdoctoral researchers into prototypes, products and programs that will benefit society.
The NSF’s Directorate for Technology Innovation and Partnerships (founded in 2022) provided the four-year award to an interdisciplinary, university-wide team led by John Coulter, senior associate dean for research in the P.C. Rossin College of Engineering and Applied Science, as part of the new federal Accelerating Research Translation (ART) program.
The award ...
Vinod Namboodiri, joint faculty member of Lehigh University’s College of Health and P.C. Rossin College of Engineering and Applied Science, has been awarded Phase 2 funding from the National Science Foundation’s (NSF) Convergence Accelerator to further develop a digital app to help persons with disabilities navigate indoor environments successfully.
MABLE: Mapping for Accessibility in BuiLt Environments provides persons with disabilities independence to experience large events, conferences and educational programs. Using crowdsensing, AI and robotics, MABLE empowers individuals with responsive ...
In a first-of-its-kind study for North America, scientists accumulated a list of potential invasive species for Florida, and researchers deemed 40 pose the greatest threat.
A team of experts, led by University of Florida scientists, evaluated terrestrial, aquatic and marine species with characteristics that make them particularly adept at invasion. Their list includes 460 vertebrates, invertebrates, algae and plants.
“Invasive species management tends to be reactive, instead of preventative,” said Deah Lieurance, ...
Virginia Tech researchers have discovered limitations in ChatGPT’s capacity to provide location-specific information about environmental justice issues. Their findings, published in the journal Telematics and Informatics, suggest the potential for geographic biases existing in current generative artificial intelligence (AI) models.
ChatGPT is a large-language model developed by OpenAI Inc., an artificial intelligence research organization. ChatGPT is designed to understand questions and generate text responses based on requests from users. The technology has a wide range of applications from content creation and information gathering to data analysis and language translation.
A ...
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. — The Arctic is remote, with often harsh conditions, and its climate is changing rapidly — warming four times faster than the rest of the Earth. This makes studying the Arctic climate both challenging and vital for understanding global climate change.
Scientists at Sandia National Laboratories are using an existing fiber optic cable off Oliktok Point on the North Slope of Alaska to study the conditions of the Arctic seafloor up to 20 miles from shore. Christian Stanciu, project lead, will present their latest findings on Friday, Dec. 15 at AGU’s Fall ...
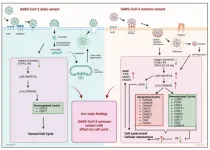
“Our findings suggest that the omicron variant, in particular, leads to premature senescence in in vitro, ex vivo, and in lung tissue models.”
BUFFALO, NY- December 15, 2023 – A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 23, entitled, “Uncovering a unique pathogenic mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant: selective induction of cellular senescence.”
SARS-CoV-2 variants are constantly emerging with a variety of changes in the conformation of the spike ...
The University of Chicago Medicine Comer Children’s Hospital will be among the first in the country to offer gene therapy for sickle cell disease in patients 12 years and older, after federal regulators approved two new treatments on December 8, 2023.
Thousands of patients with sickle cell disease experience vaso-occlusive crises (VOCs), which are often painful and frequently require hospitalization. The two new potentially curative treatments show promise for eliminating VOCs and offer an alternative to bone marrow transplants, which can be arduous and carry risk of rejection even if a matching donor is found.
People ...
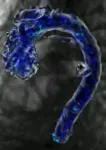
Northwestern University researchers have developed the first physics-based metric to predict whether or not a person might someday suffer an aortic aneurysm, a deadly condition that often causes no symptoms until it ruptures.
In the new study, the researchers forecasted abnormal aortic growth by measuring subtle “fluttering” in a patient’s blood vessel. As blood flows through the aorta, it can cause the vessel wall to flutter, similar to how a banner ripples in the breeze. While stable flow predicts normal, natural growth, unstable flutter is highly predictive of future abnormal growth and potential rupture, the researchers found.
Called ...