(Press-News.org) Virginia Tech researchers have discovered limitations in ChatGPT’s capacity to provide location-specific information about environmental justice issues. Their findings, published in the journal Telematics and Informatics, suggest the potential for geographic biases existing in current generative artificial intelligence (AI) models.
ChatGPT is a large-language model developed by OpenAI Inc., an artificial intelligence research organization. ChatGPT is designed to understand questions and generate text responses based on requests from users. The technology has a wide range of applications from content creation and information gathering to data analysis and language translation.
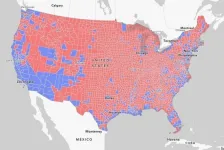
A county-by-county overview
“As a geographer and geospatial data scientist, generative AI is a tool with powerful potential,” said Assistant Professor Junghwan Kim of the College of Natural Resources and Environment. “At the same time, we need to investigate the limitations of the technology to ensure that future developers recognize the possibilities of biases. That was the driving motivation of this research.”
Utilizing a list of the 3,108 counties in the contiguous United States, the research group asked the ChatGPT interface to answer a prompt asking about the environmental justice issues in each county. The researchers selected environmental justice as a topic to expand the range of questions typically used to test the performance of generative AI tools. Asking questions by county allowed the researchers to measure ChatGPT responses against sociodemographic considerations such as population density and median household income.
Key findings indicate limitations
Surveying counties with populations as varied as Los Angeles County, California, with a population of 10,019,635, and Loving County, Texas, with a population of 83, the generative AI tool showed a capacity to identify location-specific environmental justice challenges in large, high-density population areas. However, the tool was limited in its ability to identify and provide contextualized information on local environmental justice issues.
ChatGPT was able to provide location-specific information about environmental justice issues for just 515 of the 3018 counties entered, or 17 percent.
In rural states such as Idaho and New Hampshire, more than 90 percent of the population lived in counties that could not receive local-specific information.
In states with larger urban populations such as Delaware or California, fewer than 1 percent of the population lived in counties that cannot receive specific information.
Impacts for AI developers and users
With generative AI emerging as a new gateway tool for gaining information, the testing of potential biases in modeling outputs is an important part of improving programs such as ChatGPT.
“While more study is needed, our findings reveal that geographic biases currently exist in the ChatGPT model,” said Kim, who teaches in the Department of Geography. “This is a starting point to investigate how programmers and AI developers might be able to anticipate and mitigate the disparity of information between big and small cities, between urban and rural environments.”
Kim has previously published a paper on how ChatGPT understands transportation issues and solutions in the U.S. and Canada. His Smart Cities for Good research group explores the use of geospatial data science methods and technology to solve urban social and environmental challenges.
Enhancing future capabilities of the tools
Assistant Professor Ismini Lourentzou of the College of Engineering, a co-author on the paper, cited three areas of further research for large-language models such as ChatGPT:
Refine localized and contextually grounded knowledge, so that geographical biases are reduced
Safeguard large-language models such as ChatGPT against challenging scenarios such as ambiguous user instructions or feedback
Enhance user awareness and policy so that people are better informed of the strengths and weaknesses, particularly around sensitive topics
“There are a lot of issues with the reliability and resiliency of large-language models,” said Lourentzou, who teaches in the Department of Computer Science and is an affiliate of the Sanghani Center for Artificial Intelligence and Data Analytics. “I hope our research can guide further research on enhancing the capabilities of ChatGPT and other models.”
Related stories
Generative AI poised to change the way we live according to experts
The chatbot whisperers
'Curious Conversations' podcast: Ismini Lourentzou talks about AI's potential as an assistant
END
Researchers use environmental justice questions to reveal geographic biases in ChatGPT
2023-12-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Using a fiber optic cable to study Arctic seafloor permafrost
2023-12-15
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. — The Arctic is remote, with often harsh conditions, and its climate is changing rapidly — warming four times faster than the rest of the Earth. This makes studying the Arctic climate both challenging and vital for understanding global climate change.
Scientists at Sandia National Laboratories are using an existing fiber optic cable off Oliktok Point on the North Slope of Alaska to study the conditions of the Arctic seafloor up to 20 miles from shore. Christian Stanciu, project lead, will present their latest findings on Friday, Dec. 15 at AGU’s Fall ...
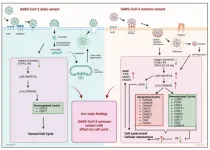
A unique pathogenic mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant: Selective induction of cellular senescence
2023-12-15
“Our findings suggest that the omicron variant, in particular, leads to premature senescence in in vitro, ex vivo, and in lung tissue models.”
BUFFALO, NY- December 15, 2023 – A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 23, entitled, “Uncovering a unique pathogenic mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant: selective induction of cellular senescence.”
SARS-CoV-2 variants are constantly emerging with a variety of changes in the conformation of the spike ...
UChicago Medicine among the first in the country to offer newly approved sickle cell gene therapies
2023-12-15
The University of Chicago Medicine Comer Children’s Hospital will be among the first in the country to offer gene therapy for sickle cell disease in patients 12 years and older, after federal regulators approved two new treatments on December 8, 2023.
Thousands of patients with sickle cell disease experience vaso-occlusive crises (VOCs), which are often painful and frequently require hospitalization. The two new potentially curative treatments show promise for eliminating VOCs and offer an alternative to bone marrow transplants, which can be arduous and carry risk of rejection even if a matching donor is found.
People ...
Unstable ‘fluttering’ predicts aortic aneurysm
2023-12-15
Northwestern University researchers have developed the first physics-based metric to predict whether or not a person might someday suffer an aortic aneurysm, a deadly condition that often causes no symptoms until it ruptures.
In the new study, the researchers forecasted abnormal aortic growth by measuring subtle “fluttering” in a patient’s blood vessel. As blood flows through the aorta, it can cause the vessel wall to flutter, similar to how a banner ripples in the breeze. While stable flow predicts normal, natural growth, unstable flutter is highly predictive of future abnormal growth and potential rupture, the researchers found.
Called ...
Microbiome insights found in poop help predict infections in liver transplant patients
2023-12-15
In a new study, researchers at the University of Chicago were able to predict postoperative infections in liver transplant patients by analyzing molecules in their poop. Their analysis represents a key leap forward in exploring the connection between the gut microbiome — the bacteria that inhabit the human body — and overall health.
“Antibiotic resistance is growing every year and getting worse. Without antibiotics that work, we can't do things like perform surgeries, protect premature infants or treat cancer,” said Christopher Lehmann, MD, ...
A new tool to better model future wildfire impacts in the United States
2023-12-15
SAN FRANCISCO – Wildfire management systems outfitted with remote sensing technology could improve first responders’ ability to predict and respond to the spread of deadly forest fires.
To do this, researchers at The Ohio State University are testing the use of Synthetic Aperture Radar, or SAR, to help with wildfire detection.
For many ecosystems, fires are vital tools that help to clear away plant waste, provide safer habitats for smaller species and burn off disease. Yet as Earth continues to experience warmer, drier conditions, the likelihood and severity of large, uncontrolled fire incidents that result in widespread ...
Navigating climate challenges: UVA engineers and environmental scientists aid Virginia’s eastern shore
2023-12-15
Because of warming waters and melting glaciers, the sea level at Virginia’s Eastern Shore has risen almost 3 inches since 2016, and the projected trajectory looks ominous. The region, sandwiched between the Chesapeake Bay and the Atlantic Ocean, has one of the highest rates of relative sea-level rise on the Atlantic coast. The Virginia Institute of Marine Science’s Center for Coastal Resource Management projects a relative sea-level rise between 4.5 to 7 feet by 2100, which is three to four times the global average.
Hampton, Virginia — its neighbor across the bay — ranks second only to New Orleans as the largest population center ...
Using AI to pinpoint hidden sources of clean energy underground
2023-12-15
SAN FRANCISCO – As efforts to transition away from fossil fuels strengthen the hunt for new sources of low-carbon energy, scientists have developed a deep learning model to scan the Earth for surface expressions of subsurface reservoirs of naturally occurring free hydrogen.
Researchers used the algorithm to help narrow down the potential whereabouts of ovoids or semicircular depressions (SCDs) in the ground that form near areas associated with natural or “gold hydrogen” deposits. Though these circular ...
A study from IMDEA Software researchers reveals hidden fortunes and surprising overestimations in cybercrime revenue
2023-12-15
To what extent methodological limitations and incomplete data impact the revenue estimations of cybercriminal groups using the Bitcoin blockchain was largely unknown. A new study, conducted by IMDEA Software Institute researchers Gibran Gomez, Kevin van Liebergen, and Juan Caballero challenges existing figures regarding cybercriminals' Bitcoin earnings to date. The study, entitled "Cybercrime Bitcoin Revenue Estimations: Quantifying the Impact of Methodology and Coverage", recently presented at the ...
Department of Defense grant boosts study of pressure, humidity on thermal energy storage
2023-12-15
Under the Defense University Research Instrumentation Program, Dr. Patrick Shamberger and a research team from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering received a grant from the U.S. Department of Defense (DOD) to acquire instrumentation for thermal energy storage research.
The grant, administered through the Office of Naval Research, will support the acquisition of a high-sensitivity multi-modal calorimeter for advanced research and education on tunable energy storage materials. This equipment will allow cutting-edge research to study the capability of pressure and humidity to control how well these materials can store ...