(Press-News.org) - Insights from Professor Sakorn Pornprasert, Dean, Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences at Chiang Mai University, on raising thalassemia awareness in Thailand.
Thalassemia, a genetic disorder affecting hemoglobin production, poses a significant public health challenge in Thailand, with a high prevalence and substantial healthcare costs. According to Thailand's Ministry of Public Health, approximately 18-24 million or 30-40 percent of the Thai population carries the thalassemia gene.
Professor Sakorn Pornprasert, Dean, Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences, Chiang Mai University, shared his views on BGI Genomics Global 2023 State of Thalassemia Awareness Report's findings related to Thailand and offer his specialized insights.
To raise awareness, the Ministry of Public Health in Thailand has implemented a policy for thalassemia prevention and control, offering free laboratory tests and prenatal diagnosis to pregnant couples, thereby reducing costs and encouraging more women to undergo screening.
With this support from the healthcare system, it makes Thai people pay less during the prenatal care. However, this health benefit covers only for those mothers carrying a fetus. Couples that plan for or entering genetic counselling and PGD still have to pay by themselves.
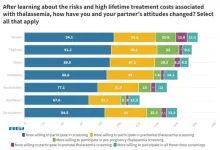
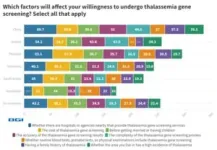
However, despite these efforts, a lower percentage of Thai women (3.9%) are willing to go for prenatal thalassemia screening compared to the global average (5.5%). Professor Pornprasert highlights the need to elevate trust in healthcare professionals to disseminate information and address concerns to build confidence in the importance and safety of prenatal screening.
At the same time, 57.4% of Thai women indicate that costs of thalassemia testing affect their willingness to go for screening, which is higher than the global average of 38.1%.
Professor Pornprasert notes that the willingness to pay is related to multiple reasons, such as the individual's financial status and the overall Thai economy. Thai women may also not be willing to pay for something that they view as "not necessary" at a certain point of time.
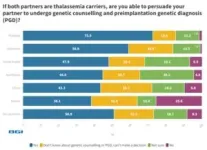
On a positive note, Thailand has a far higher percentage of women (72.5% relative to global average of 50.9%) who say they can persuade their partner to go for genetic counseling and preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) if both are thalassemia carriers.
Professor Pornprasert also believes that Thai women's proactive stance towards thalassemia is due to a cultural emphasis on unity and cooperation. In Thai culture, family and interpersonal relationships are valued, and open communication and shared decision-making are encouraged.
In conclusion, Thailand is making significant strides in thalassemia awareness and prevention. While there are still challenges to overcome, such as financial concerns and cultural barriers, the efforts of the Thai Ministry of Public Health and the proactive approach of Thai women offer a promising outlook for the prevention and control of this hereditary disease in the country.
About BGI Genomics
BGI Genomics, headquartered in Shenzhen, China, is the world's leading integrated solutions provider of precision medicine. In July 2017, as a subsidiary of BGI Group, BGI Genomics (300676.SZ) was officially listed on the Shenzhen Stock Exchange.
The company has pioneered thalassemia genetic testing services based on next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology since 2013. Expanding the availability of genetic testing has been instrumental in the screening, diagnosing, and treating thalassemia.
END
Thalassemia screening in Thailand: Medical Sciences Dean advocates for elevated trust
2023-12-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Lung nodule program provides benefits patients ineligible for lung cancer screening
2023-12-18
(Denver—December 18, 2023) – Adopting a lung nodule program (LNP) may increase the detection of early lung cancer for patients who are not eligible for lung cancer screening under existing age eligibility criteria, according to a study published in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology, an official journal of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer.
LNPs are established to follow up on lung nodules that are frequently identified during routine imaging for reasons other than suspected lung cancer or lung cancer screening.
The research was conducted by a team led by Dr. Raymond U. Osarogiagbon, MBBS, FACP, chief scientist ...
Multi-site study reveals addressable socioeconomic barriers to prenatal diagnosis of congenital heart defects
2023-12-18
Prenatal diagnosis of congenital heart defects – the most common birth defects in the United States – is associated with improved outcomes. Despite its importance, however, overall prevalence of prenatal diagnosis is low (12-50 percent). A recent multi-center study surveyed caretakers of infants who received congenital heart surgery in the Chicago area and found that social determinants or influencers of health constitute significant barriers to prenatal diagnosis from the patients’ perspective.
In ...
Wildfires increasing across eastern U.S., new study reveals
2023-12-18
In a new analysis of data spanning more than three decades in the eastern United States, a team of scientists found a concerning trend – an increasing number of wildfires across a large swath of America.
“It’s a serious issue that people aren’t paying enough attention to: We have a rising incidence of wildfires across several regions of the U.S., not only in the West,” said Victoria Donovan, lead author of the study and an assistant professor of forest management at the UF/IFAS ...
Nurse aide turnover linked to scheduling decisions
2023-12-18
Long-term care facilities that scheduled part-time Certified Nursing Assistants (CNAs) with more hours and more consistently with the same co-workers had reduced turnover, according to research led by Washington State University. The findings could help address staffing challenges that affect millions of patients at long-term care facilities nationwide.
Using a model based on real scheduling data of thousands of nurse aides, the researchers estimated that a one-hour increase in CNAs’ weekly hours worked could reduce turnover by 1.9%. Also, the analysis found that by scheduling ...
TAMEST names Nidhi Sahni, Ph.D., as the Recipient of the 2024 Mary Beth Maddox Award & Lectureship
2023-12-18
AUSTIN/HOUSTON – TAMEST (Texas Academy of Medicine, Engineering, Science and Technology) has announced Nidhi Sahni, Ph.D., The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, as the recipient of the 2024 Mary Beth Maddox Award and Lectureship in cancer research. She was chosen for her role in identifying novel biomarkers and drug targets, which are expected to have a significant impact on cancer by translating into more effective prognosis and therapy for the disease.
The Mary Beth Maddox Award and Lectureship recognizes women scientists in Texas bringing new ideas and innovations to the fight ...
Do genes that code athletic heart enlargement carry a risk of future heart problems?
2023-12-18
A new landmark study involving 281 elite athletes from Australia and Belgium has revealed one in six have measures that would normally suggest reduced heart function.
Genetic analysis published in Circulation conducted by scientists in Australia and Belgium revealed those athletes also had an enrichment of genes associated with heart muscle disease.
Thus, a genetic predisposition may be ‘stressed’ by exercise to cause profound heart changes. The international collaboration will continue to monitor the athletes over the long-term to determine the consequences on their heart health.
Associate Professor Andre la Gerche, who heads the HEART Laboratory that is jointly ...
ASU research reveals regions in U.S. where heat adaptation and mitigation efforts can most benefit future populations
2023-12-18
Tempe, Ariz., December 18, 2023 – Extreme heat waves, once considered rare, are now frequent and severe in cities due to climate change. Phoenix faced such a brutal heat wave in July of 2023 when it endured 31 consecutive days of high temperatures of at least 110 F. The severity of the heat wave triggered a state of emergency. In June of 2021, the town of Lytton, B.C., Canada, hit a blistering 121 F, leading to a fire that burnt most of the village. This pattern repeated in Europe in 2022, where heat caused fatal illnesses, wildfires and damaged infrastructure, highlighting ...
Global inventory of sound production brings us one step closer to understanding aquatic ecosystems
2023-12-18
Scientists looking to uncover the mysteries of the underwater world have more valuable information at their fingertips thanks to an international team that has produced an inventory of species confirmed or expected to produce sound underwater.
Led by Audrey Looby from the University of Florida Department of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, the Global Library of Underwater Biological Sounds working group collaborated with the World Register of Marine Species to document 729 aquatic mammals, other tetrapods, fishes, and invertebrates that produce active or passive sounds. In addition, the inventory includes another 21,911 species that ...
Early-life diseases linked to lifelong childlessness
2023-12-18
Led by Aoxing Liu and senior authors Melinda Mills, Andrea Ganna and an international team, the study examined the link between 414 early-life diseases and lifetime childlessness in over 2.5 million individuals born in Finland and Sweden.
In many Western European and East Asian countries, up to 15-20% of individuals born around 1970 are now childless. Although multiple social, economic and individual preferences have been studied, there has been limited research examining the contribution of different diseases to being childless over a lifetime, particularly those diseases with onset prior to the peak reproductive age.
Dr Aoxing Liu, lead author ...
Some coral species might be more resilient to climate change than previously thought
2023-12-18
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Some coral species can be resilient to marine heat waves by “remembering” how they lived through previous ones, research by Oregon State University scientists suggests.
The study, funded by the National Science Foundation, also contains evidence that the ecological memory response is likely linked to the microbial communities that dwell among the corals.
The findings, published today in Global Change Biology, are important because coral reefs, crucial to the functioning ...