(Press-News.org) Martin Taylor, MD, PhD, a physician investigator in the Department of Pathology at Massachusetts General Hospital and an instructor in Pathology at Harvard Medical School, is the lead corresponding author of a new study in Nature, Structural Analysis and Inhibition of Human LINE-1 ORF2 Protein Reveals Novel Adaptations and Functions.
What Question Were You Investigating?
About a fifth of the human genome is half a million copies of a transposon, a virus-like element known as LINE-1 (L1). L1 was ignored as “junk DNA” for years but is increasingly recognized to contribute to the pathology of autoimmunity, cancer, neurodegeneration, and aging. However, we don’t know how big a contribution L1 makes or how it works, limiting our ability to target it.
We sought out to determine the structure and mechanisms of its critical multifunctional ORF2p reverse transcriptase.
What Methods Did You Use?
Lab models - cryo-electron microscopy, X-ray crystallography, biochemistry, pharmacology, cell-based imaging (immunofluorescence), computational modeling of evolution.
What Did You Find?
We determined the first structures of the LINE-1 ORF2 multifunctional reverse transcriptase protein (ORF2p) in multiple states by both cryo-EM and crystallography, and these together with biochemical and cell-based analyses provided key mechanistic insights into polymerization, insertion, and activation of the innate immune system and shed light on LINE-1's evolutionary history.
We find an unexpected mechanism for innate immune activation by LINE-1, whereby it directly synthesizes DNA in the cytosol, which is then sensed by cGAS/STING.
We also show which reverse transcriptase inhibitors do and do not inhibit LINE-1, and the structure allows us to understand their potencies.
What Are the Implications?
The work will facilitate rational drug design targeting LINE-1 and may lead to novel therapies and strategies to prevent cancer, autoimmune disease, and neurodegeneration and other diseases of aging.
We also have a better understanding of how LINE-1 works mechanistically, which will allow future studies to determine how it causes disease. In particular, the new findings of direct innate immune activation explain associations of LINE-1 with cytosolic double stranded nucleic acids in models of aging and cancer and open new areas of research.
What’s Next?
We will use our knowledge of LINE-1 and existing HIV-1 inhibitors that inhibit it to study LINE-1 in disease models in mice.
We will build on our structural and mechanistic knowledge to understand how each step of the LINE-1 replication cycle works in detail in cells, to understand how this streamlined parasite co-opts host factors to replicate, and how the cell attempts to shut it down.
Finally, we will build on our discovery of ORF2p cytosolic priming,reverse transcription, and innate immune activation to understand it in detail, which may allow new therapies based on this activity.
END
Research spotlight: Structural analysis and inhibition of human LINE-1 ORF2 protein reveals novel adaptations and functions
2023-12-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
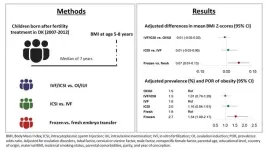
Assisted reproductive technologies not associated with body mass index in children, except when using frozen embryos – according to new Danish study
2023-12-19
Assisted reproductive technologies not associated with body mass index in children, except when using frozen embryos – according to new Danish study
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Medicine: http://journals.plos.org/plosmedicine/article?id=10.1371/journal.pmed.1004324
Article Title: Overweight or obesity in children born after assisted reproductive technologies in Denmark: A population-based cohort study
Author Countries: ...
Novel approach emerging for rescuing limbs at risk
2023-12-19
Across the United States, about 2 million people are living with an amputation and another 185,000 amputations occur every year, according to the Amputee Coalition, a Washington DC-based support group. About 54% of these lost limbs were caused by vascular disease, including diabetes and peripheral arterial disease (PAD).
And as more people are diagnosed with diabetes, in the US and worldwide, the number of amputations keeps rising.
Now, experts at Cincinnati Children’s in collaboration with colleagues from Kanazawa University in Japan, have uncovered a new way to prompt blood vessel ...
Socialization for success: Two recent studies expand our understanding of how early social housing helps dairy calves thrive
2023-12-19
Philadelphia, December 19, 2023 – Dairy industry professionals continuously work to ensure the highest possible welfare for dairy calves, including fine-tuning their housing to improve overall health, well-being, and performance. Two new studies in JDS Communications are illuminating our understanding of paired housing in the critical newborn and pre-weaned stages of dairy lives by showing that housing designed to facilitate early socialization can build behavior skills, shape calf personalities, and ultimately, set up animals ...
Sirtuin 6 activation rescues the age-related decline in DNA damage repair in chondrocytes
2023-12-19
“[...] the biological mechanisms linking aging and osteoarthritis prevalence remain largely unknown.”
BUFFALO, NY- December 19, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 23, entitled, “Sirtuin 6 activation rescues the age-related decline in DNA damage repair in primary human chondrocytes.”
While advanced age is widely recognized as the greatest risk factor for osteoarthritis (OA), the biological mechanisms behind this connection remain unclear. Previous work has ...
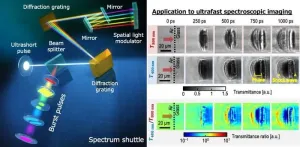
Innovative optical technique for simultaneously producing and shaping gigahertz burst pulses
2023-12-19
The generation and manipulation of high-repetition pulses hold great promise across various applications, including high-speed photography, laser processing, and acoustic wave generation. Gigahertz (GHz) burst pulses, with intervals ranging from ~0.01 to ~10 nanoseconds, are particularly valued for visualizing ultrafast phenomena and improving laser processing efficiency.
While methods for producing GHz burst pulses exist, challenges persist, such as low throughput of pulse energy, poor tunability of pulse intervals, and the complexity ...
3D material found to break down antidepressant that contaminates water bodies worldwide
2023-12-19
An article published in the Chemical Engineering Journal describes a strategy to produce a material based on zinc oxide (ZnO) capable of degrading sertraline, an antidepressant that has been detected, like other drugs, in groundwater worldwide and is considered an emerging pollutant. This kind of substance has certain physicochemical properties that hinder removal by conventional wastewater treatment methods.
The research was supported by FAPESP and conducted in Brazil by scientists at the Center for Development of Functional Materials (CDMF), the Brazilian ...
High Performance Computing Center of the University of Stuttgart and Hewlett Packard Enterprise to build exascale supercomputer
2023-12-19
The University of Stuttgart and Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) have announced an agreement to build two new supercomputers at the High-Performance Computing Center of the University of Stuttgart (HLRS).
In the first stage, a transitional supercomputer, called Hunter, will begin operation in 2025. This will be followed in 2027 with the installation of Herder, an exascale system that will provide a significant expansion of Germany’s high-performance computing (HPC) capabilities. Hunter and Herder will offer researchers ...
Gentle x-ray imaging of small living specimens
2023-12-19
X-ray imaging visualizes hidden structures and processes in living cells and organisms. The radiation that consists of highly energy-rich electromagnetic waves, however, has an ionizing effect and may damage the genetic material. This limits the possible observation period. While conventional X-ray images of soft tissue are of low contrast, phase contrast methods produce far better image contrasts at a reduced radiation dose. With higher resolution, however, gentle imaging becomes increasingly difficult, as a higher dose is required. Moreover, ...
Pushing compressed sensing to real-time edge applications
2023-12-19
Recently, a research team led by Prof. Sun Zhong at Peking University reported an analog hardware solution for real-time compressed sensing recovery, which has been published as an article titled "In-memory analog solution of compressed sensing recovery in one step" in Science Advances. In this work, a design based on a resistive memory (also known as memristor) array for performing instantaneous matrix-matrix-vector multiplication (MMVM) is first introduced. Based on this module, then an analog matrix computing circuit that solves compressed sensing (CS) recovery in one step (within few microseconds) is disclosed.
CS ...
The science behind snowflakes
2023-12-19
Tim Garrett has devoted his scientific career to characterizing snowflakes, the protean particles of ice that form in clouds and dramatically change as they fall to Earth.
Now the University of Utah atmospheric scientist is unlocking the mystery of how snowflakes move in response to air turbulence that accompanies snowfall using novel instrumentation developed on campus. And after analyzing more than half a million snowflakes, what his team has discovered has left him astonished.
Rather than something incomprehensibly complicated, predicting how snowflakes move proved to be surprisingly ...