(Press-News.org) The widespread use of cannabis (marijuana) and its increased potency are associated with a rise in cannabis-related psychiatric conditions, according to a new University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) review article that was recently published in the New England Journal of Medicine. It highlights the urgent need for doctors to screen for and treat patients who are experiencing symptoms of cannabis use disorder, which means they are experiencing significant problems from their use of the drug.
Nearly one in five Americans ages 12 and older used cannabis in 2021, according to the article, and more than 16 million met the criteria for cannabis use disorder as outlined in the American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Health Disorders (DSM-5-TR). Young adults ages 18 to 25 are disproportionately affected. The review found more than 14 percent of those in this age group had cannabis use disorder.
“There is a lot of misinformation in the public sphere about cannabis and its effects on psychological health with many assuming that this drug is safe to use with no side effects,” said David A. Gorelick, MD, PhD, Professor of Psychiatry at UMSOM who wrote the review article. “It is important for physicians and the public to understand that cannabis can have addictive effects and to recognize signs and symptoms in order to get properly diagnosed and treated.”
Cannabis use disorder is defined as problematic marijuana use. Symptoms include craving the drug and failing to control its use despite experiencing negative side effects like problems at work or school. It is most prevalent in people who use cannabis more than four days a week. While the primary risk factors are the frequency and duration of cannabis use, having another substance use disorder or other psychiatric condition also increases the likelihood of the diagnosis.
“Almost 50 percent of people with cannabis use disorder have another psychiatric condition such as major depression, post-traumatic stress disorder, or generalized anxiety disorder,” said Dr. Gorelick. “It’s vital that patients seek the right psychiatric treatment to address their risk factors.”
Physical signs and symptoms of cannabis use disorder can range from yellowing of the fingertips to increased depression and anxiety while using cannabis. To be properly diagnosed by a clinician, however, patients must meet two or more criteria for cannabis use disorder as outlined by the DSM-5-TR. These include doing poorly at school or work or missing important family obligations due to cannabis use. Experiencing withdrawal symptoms or cravings for cannabis are other symptoms.
Dr. Gorelick, who is also Editor-in-Chief of the Journal of Cannabis Research, conducted the extensive review to educate physicians on the array of health issues that may be associated with short-term and long-term cannabis use as a growing number of individuals use cannabis products. He also aimed to heighten public awareness around cannabis user disorder, both in terms of recognizing its symptoms and understanding treatment options.
The paper also highlighted other dangers of excessive cannabis use: Cannabis use accounts for 10 percent of all drug-related emergency room visits in the U.S. and is associated with a 30 to 40 percent increased risk of car accidents. In 2022, 18 to 25-year-olds accounted for the highest rate of cannabis-related emergency department visits.
“Approximately one in ten people who use cannabis will become addicted, and for those who start before age 18, the rate rises to one in six,” said Mark T. Gladwin, MD, the John Z. and Akiko K. Bowers Distinguished Professor and Dean, UMSOM, and Vice President for Medical Affairs, University of Maryland, Baltimore. “As use of this drug increases, we must delve deeply into basic research to understand the brain’s cannabinoid system. We must also design translational studies of therapies that target these brain mechanisms to help those with cannabis use disorder -- particularly young adults and pregnant women -- overcome their dependence on this drug.”
A key part of UMSOM’s mission is to drive innovation in the field of addiction medicine, and to learn more about neurological differences in the brain that make some people more susceptible to drug abuse and addiction. As part of this mission, the school recently opened the Kahlert Institute for Addiction Medicine, which brings together leading addiction experts to collaborate on studying the brain mechanisms underlying addiction and to train a new generation of medical practitioners in the field of addiction medicine.
“There is still a lot we don’t understand about these conditions, including why some people experience cannabis-related disorders,” said Kahlert Institute Associate Director Asaf Keller, PhD, the Donald E. Wilson, MD, MACP Distinguished Professor and Chair of Neurobiology at UMSOM. “That is what we are trying to better understand through pre-clinical research studies. We are also working on developing treatments for cannabis -related disorders.”
There are currently seven recognized disorders related to cannabis use. Some include: cannabis-induced anxiety disorder, cannabis-induced psychotic disorder, cannabis-induced sleep disorder and cannabis-induced delirium, which manifests as hyperactivity, agitation and disorientation with hallucinations. Often, their symptoms can closely resemble those of their non-cannabis-related counterpart disorders.
To properly diagnosis patients for cannabis use disorder, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that adolescents and adults be screened for cannabis use disorder (and other substance use disorders) in primary care settings as long as services for accurate diagnosis, treatment and appropriate care can be offered or referred. Screening is best done with a standalone or within a larger health questionnaire during a healthcare visit. While the FDA has not approved any medication as effective for the treatment of cannabis use disorder, certain therapies can help those with cannabis use disorder manage symptoms and reduce or stop their cannabis use. These include: Cognitive Interactive Therapy (CBT) and Motivational Enhancement Therapy (MET), which help patients to manage thoughts and behaviors that trigger their use of cannabis and to better understand why they use cannabis. Adolescents may gain additional benefits from family-based treatment options.
Therapy is becoming more widely available through telehealth services, but the stigma around mental illness and addiction and the shortage of mental healthcare professionals still create barriers to treatment for many patients, Gorelick said.
About the University of Maryland School of Medicine
Now in its third century, the University of Maryland School of Medicine was chartered in 1807 as the first public medical school in the United States. It continues today as one of the fastest growing, top-tier biomedical research enterprises in the world -- with 46 academic departments, centers, institutes, and programs, and a faculty of more than 3,000 physicians, scientists, and allied health professionals, including members of the National Academy of Medicine and the National Academy of Sciences, and a distinguished two-time winner of the Albert E. Lasker Award in Medical Research. With an operating budget of more than $1.2 billion, the School of Medicine works closely in partnership with the University of Maryland Medical Center and Medical System to provide research-intensive, academic, and clinically based care for nearly 2 million patients each year. The School of Medicine has more than $500 million in extramural funding, with most of its academic departments highly ranked among all medical schools in the nation in research funding. As one of the seven professional schools that make up the University of Maryland, Baltimore campus, the School of Medicine has a total population of nearly 9,000 faculty and staff, including 2,500 students, trainees, residents, and fellows. The School of Medicine, which ranks as the 8th highest among public medical schools in research productivity (according to the Association of American Medical Colleges profile) is an innovator in translational medicine, with 606 active patents and 52 start-up companies. In the latest U.S. News & World Report ranking of the Best Medical Schools, published in 2023, the UM School of Medicine is ranked #10 among the 92 public medical schools in the U.S., and in the top 16 percent (#32) of all 192 public and private U.S. medical schools. The School of Medicine works locally, nationally, and globally, with research and treatment facilities in 36 countries around the world. Visit medschool.umaryland.edu
END
UM School of Medicine review highlights rise in psychiatric disorders linked to increased cannabis use
Review article published in New England Journal of Medicine finds 16 million Americans have cannabis use disorder
2023-12-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
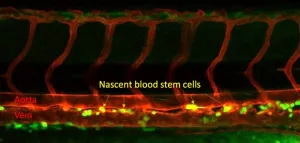
Immune system plays crucial step in creating blood stem cells
2023-12-20
AMES, Iowa – A microbial sensor that helps identify and fight bacterial infections also plays a key role in the development of blood stem cells, valuable new insight in the effort to create patient-derived blood stem cells that could eliminate the need for bone marrow transplants.
The discovery by a research team led by Raquel Espin Palazon, an assistant professor of genetics, development and cell biology at Iowa State University, was published last month in Nature Communications. It builds on prior ...
New grant gives South Carolina life sciences companies a chance to accelerate
2023-12-19
The Medical University of South Carolina is one of nine leading research universities across six states partnering with Innosphere Ventures on its Regional Life Sciences Incubator. Innosphere Ventures is a Colorado-based life sciences incubator with proven methods for propelling startups to successful market entry. Funding from a $2 million three-year Build to Scale Venture Challenge grant from the U.S. Department of Commerce will create a regional incubator that will offer its partnering institutions and selected startups ...
Predicting prenatal care to improve pregnancy outcomes
2023-12-19
Socioeconomic factors, like education and location, can affect access to life-saving prenatal care services. Researchers at Boston Children’s Hospital are taking steps towards implementing strategies that improve access to prenatal care: estimating how many pregnant people attend the recommended number of visits and identifying pregnant people who are at high risk of failing to attend. This could help policymakers allocate resources to populations not getting enough prenatal care and could, in turn, improve health outcomes for mothers and babies.
Led by Grace Chan, M.D., Ph.D., Attending Physician in the Intermediate Care Program at Boston ...
JMIR Medical Education accepted for MEDLINE indexing
2023-12-19
JMIR Publications is pleased to announce that JMIR Medical Education has passed the Scientific Quality Review for MEDLINE and has been accepted for inclusion in MEDLINE, which is the U.S. National Library of Medicine's premier bibliographic database.
JMIR Medical Education was already indexed in PubMed. MEDLINE is a more selective subset of PubMed, consisting of the top 5,200 biomedical journals, and indexing in MEDLINE also means that articles are now also indexed with NLM Medical Subject Headings (MeSH terms) and other metadata.
Selection for MEDLINE is a result of a thorough review ...
Fish display distinct individual behaviours when swimming to find food
2023-12-19
Fish from the same species can evolve their sense of smell and display individual foraging ‘personalities’ to successfully find food in different habitats, according to new research.
In the study, published today as a Reviewed Preprint in eLife, researchers developed a high-throughput behavioural assay to test spontaneous swimming and differences in the sense of smell of individual Mexican cavefish larvae. eLife editors described the work as important, presenting compelling evidence that the surface and cave morphs of the fish show different olfactory preferences and odour sensitivities, and that individual fish show substantial variability in their spontaneous ...
Protein allows poison dart frogs to accumulate toxins safely
2023-12-19
Scientists have identified the protein that helps poison dart frogs safely accumulate their namesake toxins, according to a study published today in eLife.
The findings solve a long-standing scientific mystery and may suggest potential therapeutic strategies for treating humans poisoned with similar molecules.
Alkaloid compounds, such as caffeine, make coffee, tea and chocolate delicious and pleasant to consume, but can be harmful in large amounts. In humans, the liver can safely metabolise modest ...
Toxic chemicals found in oil spills and wildfire smoke detected in killer whales
2023-12-19
Toxic chemicals produced from oil emissions and wildfire smoke have been found in muscle and liver samples from Southern Resident killer whales and Bigg’s killer whales.
A study published today in Scientific Reports is the first to find polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in orcas off the coast of B.C., as well as in utero transfer of the chemicals from mother to fetus.
“Killer whales are iconic in the Pacific Northwest—important culturally, economically, ecologically and more. Because they are able to metabolically process PAHs, these are most likely recent exposures. Orcas are our canary in the coal ...
Schar school researchers to receive funding for nonprofit employment data project
2023-12-19
Schar School Researchers To Receive Funding For Nonprofit Employment Data Project
Alan Abramson, Professor, Government and Politics; Mirae Kim, Associate Professor, Nonprofit Studies; and Stefan Toepler, Professor, Nonprofit Studies, are set to receive funding for: "Nonprofit Employment Data Project."
The researchers will produce a comprehensive report on nonprofit employment in the United States, based on new data that is expected to be released by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) early in 2024. The researchers will also arrange for the transfer of the Nonprofit Works interactive database application, which is currently hosted by Johns ...
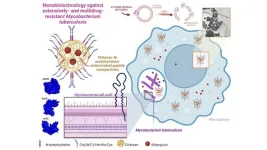
Nanoparticles with antibacterial action shorten duration of tuberculosis treatment
2023-12-19
A low-cost technology involving nanoparticles loaded with antibiotics and other antimicrobial compounds that can be used in multiple attacks on infections by the bacterium responsible for most cases of tuberculosis has been developed by researchers at São Paulo State University (UNESP) in Brazil and is reported in an article published in the journal Carbohydrate Polymers. Results of in vitro tests suggest it could be the basis for a treatment strategy to combat multidrug bacterial resistance.
According ...
Marzougui & Kan developing crashworthy tangent end treatment for low-speed & curbed roadways
2023-12-19
Marzougui & Kan Developing Crashworthy Tangent End Treatment For Low-Speed & Curbed Roadways
Dhafer Marzougui, Associate Professor, Physics and Astronomy, and Cing-Dao Kan, Professor/Director, Center for Collision Safety and Analysis, received $749,954 from the National Cooperative Highway Research Program for: "Development of a Crashworthy Tangent End Treatment for Low-Speed and Curbed Roadways."
This funding began in Nov. 2023 and will end in Nov. 2026.
###
About George Mason University
George Mason University is Virginia's largest public research university. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] UM School of Medicine review highlights rise in psychiatric disorders linked to increased cannabis useReview article published in New England Journal of Medicine finds 16 million Americans have cannabis use disorder