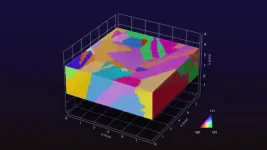
(Press-News.org) Researchers at Nagoya University in Japan have used artificial intelligence to discover a new method for understanding small defects called dislocations in polycrystalline materials, materials widely used in information equipment, solar cells, and electronic devices, that can reduce the efficiency of such devices. The findings were published in the journal Advanced Materials.
Almost every device that we use in our modern lives has a polycrystal component. From your smartphone to your computer to the metals and ceramics in your car. Despite this, polycrystalline materials are tough to utilize because of their complex structures. Along with their composition, the performance of a polycrystalline material is affected by its complex microstructure, dislocations, and impurities.
A major problem for using polycrystals in industry is the formation of tiny crystal defects caused by stress and temperature changes. These are known as dislocations and can disrupt the regular arrangement of atoms in the lattice, affecting electrical conduction and overall performance. To reduce the chances of failure in devices that use polycrystalline materials, it is important to understand the formation of these dislocations.
A team of researchers at Nagoya University, led by Professor Noritaka Usami and including Lecturer Tatsuya Yokoi and Associate Professor Hiroaki Kudo and collaborators, used a new AI to analyse image data of a material widely used in solar panels, called polycrystalline silicon. The AI created a 3D model in virtual space, helping the team to identify the areas where dislocation clusters were affecting the material’s performance.
After identifying the areas of the dislocation clusters, the researchers used electron microscopy and theoretical calculations to understand how these areas formed. They revealed stress distribution in the crystal lattice and found staircase-like structures at the boundaries between the crystal grains. These structures appear to cause dislocations during crystal growth. “We found a special nanostructure in the crystals associated with dislocations in polycrystalline structures,” Usami said.
Along with its practical implications, this study may have important implications for the science of crystal growth and deformation as well. The Haasen-Alexander-Sumino (HAS) model is an influential theoretical framework used to understand the behavior of dislocations in materials. But Usami believes that they have discovered dislocations that the Haasen-Alexander-Sumino model missed.
Another surprise was to follow soon after, as when the team calculated the arrangement of the atoms in these structures, they found unexpectedly large tensile bond strains along the edge of the staircase-like structures that triggered dislocation generation.
As explained by Usami, "As experts who have been studying this for years, we were amazed and excited to finally see proof of the presence of dislocations in these structures. It suggests that we can control the formation of dislocation clusters by controlling the direction in which the boundary spreads”.
"By extracting and analyzing the nanoscale regions through polycrystalline materials informatics, which combines experiment, theory, and AI, we made this clarification of phenomena in complex polycrystalline materials possible for the first time," Usami continued. “This research illuminates the path towards establishing universal guidelines for high-performance materials and is expected to contribute to the creation of innovative polycrystalline materials. The potential impact of this research extends beyond solar cells to everything from ceramics to semiconductors. Polycrystalline materials are widely used in society, and the improved performance of these materials has the potential to revolutionize society.”
END
Artificial intelligence unravels mysteries of polycrystalline materials
2023-12-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Asian Fund for Cancer Research Limited unveils inspiring new logo and slogan, signifying a global commitment to advancing cancer research - from Asia to the world.
2023-12-20
The Asian Fund for Cancer Research (AFCR) is thrilled to unveil its fresh brand logo and slogan, marking a pivotal moment in the organization's quest to advance breakthroughs in cancer globally. The redesigned emblem and impactful slogan firmly establish AFCR as a prominent voice in the ongoing battle against cancer, extending its influence beyond Asia.
"Advancing Cancer Breakthroughs from Asia to the World"
This compelling slogan powerfully encapsulates AFCR's unwavering commitment to drive innovation and foster collaboration in cancer research ...
Beetroot juice supplement lowers blood pressure and improves exercise capacity in people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
2023-12-20
A 12-week course of daily beetroot juice supplement for people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) lowered blood pressure and improved how far patients could walk in six minutes in research published today (Wednesday) in the European Respiratory Journal [1].
COPD is a serious lung condition affecting around 400 million people worldwide [2]. COPD which includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema, causes breathing difficulties and severely limits people’s capacity for physical activity. It also increases the risk ...
Finding that statins could slow dementia stimulates further research
2023-12-20
Blood fat-lowering statins could slow the progression of Alzheimer's disease, at least for some patients. This is the result of a new study led by Karolinska Institutet published in Alzheimer Research and Therapy. But the researchers are cautious in their interpretations and see the results as a first step in a research journey that may eventually provide the answer.
A new study shows that people with Alzheimer's dementia deteriorated more slowly in their cognitive functions if they were also treated with a lipid-lowering ...
Potentially harmful ‘trip-killers’ to cut short ‘bad’ drug trips, emerging concern, warn doctors
2023-12-20
The use of potentially harmful ‘trip-killers’ to cut short ‘bad drug trips’ after taking psychedelics, such as LSD or magic mushrooms, is an emerging concern, warn doctors in a research letter, published online in Emergency Medicine Journal.
Their analysis of relevant threads on the social media platform Reddit, shows that drugs such as benzodiazepines (sedatives) and antipsychotics are the options most frequently recommended, but warnings about their potential side effects are rarely included, they highlight.
The intensity of a psychedelic drug trip can cause distress, agitation, ...
3 potentially unique acoustic features of healing music that transcend genre identified
2023-12-20
There are three potentially unique acoustic features of healing music that transcend musical genres, suggests research published in the open access journal General Psychiatry.
The findings might help to personalise playlists for patients, using artificial intelligence to analyse individual physiological and psychological responses, and help to evaluate the effectiveness of existing music therapies, suggest the researchers.
Despite evidence of the therapeutic effects of music for mental health issues, such as anxiety, depression, and post traumatic stress disorder, there’s no consensus on what defines healing ...
Diabetes drug may significantly lower women’s risk of substantial weight gain after giving up smoking
2023-12-20
The diabetes drug dulaglutide (Trulicity) may significantly lower a woman’s risk of substantial weight gain after she has given up smoking, finds a secondary analysis of clinical trial data, published in the open access journal BMJ Nutrition Prevention & Health.
Women seem to be 5 times as likely as men to put on a lot of weight after they’ve stubbed out what they intend to be their last cigarette, the analysis suggests.
Women seem to have higher smoking relapse rates than men. And it’s been suggested that one of the possible explanations for this is that they may be more concerned about ...
Antimicrobial resistance leads to more deaths and illnesses in the WHO African region than anywhere else
2023-12-20
SEATTLE, Wash., Dec. 19, 2023 ‑‑ Over 1.05 million deaths were associated with antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and 250,000 deaths were attributable to AMR in the WHO African region, posing an unprecedented health threat. That’s according to a new study published in The Lancet Global Health today.
The number of deaths linked to AMR in the WHO African region is higher than those caused by both HIV/AIDS (639,554) and malaria (594,348), marking a pivotal shift in the health challenges facing the region. Despite the relatively low prevalence of resistance, the WHO African region had the highest burden of AMR mortality, which ...
Groundbreaking discovery at Museums Victoria Research Institute rewrites our understanding of whale evolution
2023-12-20
Groundbreaking new research from the Museums Victoria Research Institute has turned upside down our previous understanding of the evolution of the largest animals ever––baleen whales.
Palaeontologists Dr James Rule (Monash University and Natural History Museum, London) and Dr Erich Fitzgerald (Museums Victoria Research Institute) have co-authored the open access paper ‘Giant baleen whales emerged from a cold southern cradle’, published today in the prestigious journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B.
Until now, it was believed that the beginning of the Ice Age in the ...
Scientists provide recipe to halve pollution from food production
2023-12-20
A major report for the United Nations has put forward solutions to halve nitrogen pollution from agriculture and the food system in Europe, including reducing meat and dairy consumption, fertiliser use and food waste.
Nitrogen, which is vital for plant growth, is present in animal excreta and synthetic fertilisers that are applied to land to boost crop production. But excessive and inefficient use of this nutrient means up to 80% of it leaks into the environment, mostly in various polluting forms of nitrogen: ammonia and nitrogen oxides, which are harmful air pollutants; ...
Huntsman Cancer Institute investigator receives award for metastatic breast cancer research
2023-12-20
Alana Welm, Ph.D., senior director of basic science at Huntsman Cancer Institute and professor of oncological sciences at the University of Utah (the U), received the 2023 American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Outstanding Investigator Award for Breast Cancer Research.
“Dr. Welm is an exceptionally talented and internationally-recognized scientist, applying her discoveries to the development of improved breast cancer therapies,” says Neli Ulrich, Ph.D., MS, chief scientific officer and executive director of the comprehensive cancer center at Huntsman Cancer Institute and professor of population health sciences at the U. “She has a highly productive research ...