(Press-News.org) A new study from Lawson Health Research Institute and Western University published in the journal Microbiome has found changes in the microbiome in multiple locations in the body are linked to the formation of kidney stones.
The human microbiome comprises trillions of microorganisms, including healthy bacteria. In recent years, research has begun to uncover its role in health and numerous diseases.
The research team examined the gut, urinary and salivary microbiomes in 83 patients who had kidney stones and compared them to 30 healthy controls. They found changes in all three microbiomes were linked to kidney stone formation.
“Kidney stone disease has been rising in recent years, affecting roughly 10 per cent of people,” says Dr. Jeremy Burton, Lawson Scientist and Research Chair of Human Microbiome and Probiotics at St. Joseph’s Health Care London (St. Joseph’s). “While previous research has shown a connection between the gut microbiome and kidney stones in those who have taken antibiotics, we also wanted to explore the connection to other microbiomes in the hopes we can advance understanding and potential treatments.”
Study participants included people who had formed kidney stones, had not had antibiotic exposure in the last 90 days and were having the stones removed surgically at St. Joseph’s.
“Our testing – called shotgun metagenomic sequencing – allowed us to discover which bacteria were present in the gut and the genetic capabilities of those bacteria, or how it functions. We also did a simpler sequencing of the oral and urinary samples,” explains Dr. Kait Al, lead author on the study and Postdoctoral Research Fellow at Western’s Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry.
Kidney stones are most commonly formed from calcium oxalate, which is a waste product produced by the body. Historically, it was thought people with specific gut microbes, like one bacterium called Oxalobacter formigenes that breaks down oxalate, were less likely to form kidney stones. This study suggests there are other factors.
“It’s a more complex story. The microbes form a kind of network that’s stable and beneficial in healthy people, but in those with kidney stones, that network is broken down. They’re not producing the same vitamins and useful metabolites, not just in the gut but also in the urinary tract and oral cavity,” Dr. Al explains.
There was also evidence that those with kidney stones had been exposed to more antimicrobials, as they had more antibiotic-resistant genes.
“We found not only that those who got kidney stones had an unhealthy microbiome, including a gut microbiome that was more likely to excrete toxins to the kidneys, but also that they were antibiotic resistant,” explains Dr. Burton, also an Associate Professor in the Department of Microbiology and Immunology at Schulich Medicine & Dentistry.
The research team says that although more research is needed, these initial findings shed light on the overall importance of a person’s microbiome and keeping it as healthy as possible, with a microbiome-friendly diet and minimal antibiotic use potentially part of the solution.
The study was funded in part through the Weston Foundation and supported by the American Urological Association.
END
New study sheds light on the connection between the microbiome and kidney stones
2023-12-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
TTUHSC researcher studies the ability of brine shrimp to thrive in high salinity
2023-12-20
Brine shrimp of the genus Artemia are small crustaceans that can thrive in environments where sodium concentrations are as high as 25% (more than eight times typical ocean sea water). Also known by the household pet trademark ‘sea monkeys,’ these animals are abundant in inland salt lakes where brine-fly larvae are the only other animals known to exist.
The mechanisms which permit brine shrimp to tolerate some of the harshest environments are only partially understood. Previously known adaptive features include a tight protective layer (integument) to avoid water loss and the increased extrusion of sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl-) ions ...
Digital training program improves quality of life for care residents with dementia – even during the COVID-19 pandemic
2023-12-20
Quality of life for people with dementia living in residential and nursing home care substantially improved after staff took part in a digital training programme that was specially adapted to Covid-19 restrictions. The training also led to a significant drop in the prescription of potentially harmful sedative medications to residents.
The iWHELD programme supported care home staff in delivering personalised care and encouraging meaningful social interactions. Through a digital platform featuring live coaching sessions led by trained coaches, the programme supported ...
Discovery: Plants use “trojan horse” to fight mold invasions
2023-12-20
UC Riverside scientists have discovered a stealth molecular weapon that plants use to attack the cells of invading gray mold.
If you’ve ever seen a fuzzy piece of fruit in your fridge, you’ve seen gray mold. It is an aggressive fungus that infects more than 1,400 different plant species: almost all fruits, vegetables, and many flowers. It is the second most damaging fungus for food crops in the world, causing billions in annual crop losses.
A new paper in the journal Cell Host & Microbe describes how plants send tiny, innocuous-seeming lipid “bubbles” filled with RNA across enemy lines, into the cells of the aggressive mold. Once ...
Could an electric nudge to the head help your doctor operate a surgical robot?
2023-12-20
People who received gentle electric currents on the back of their heads learned to maneuver a robotic surgery tool in virtual reality and then in a real setting much more easily than people who didn’t receive those nudges, a new study shows.
The findings offer the first glimpse of how stimulating a specific part of the brain called the cerebellum could help health care professionals take what they learn in virtual reality to real operating rooms, a much-needed transition in a field that increasingly relies on digital simulation training, said author and Johns Hopkins University roboticist Jeremy ...
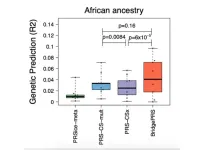
Mount Sinai researchers develop novel method to improve disease prediction across diverse ancestries
2023-12-20
A team of scientists from Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai has developed a groundbreaking statistical technique, “BridgePRS,” to enhance disease prediction in people of non-European ancestry, particularly those of African descent. This development represents a substantial step towards reducing health care inequities and a future of more personalized and precise medical interventions based on genetic information. Details of their work were published in Nature Genetics on Wednesday, December 20.
Current polygenic risk scores (PRS), essential tools for predicting disease risk encoded in our ...
How researchers are “CReATiNG” synthetic chromosomes faster and cheaper
2023-12-20
A groundbreaking new technique invented by researchers at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Science may revolutionize the field of synthetic biology. Known as CReATiNG (Cloning Reprogramming and Assembling Tiled Natural Genomic DNA), the method offers a simpler and more cost-effective approach to constructing synthetic chromosomes. It could significantly advance genetic engineering and enable a wide range of advances in medicine, biotechnology, biofuel production and even space exploration.
CReATiNG works by cloning and reassembling natural DNA segments from yeast, allowing scientists to create synthetic chromosomes that can replace their native counterparts in cells. ...
IOP Publishing expands open access in Asia Pacific region with its first Read and Publish agreement in Taiwan
2023-12-20
IOP Publishing (IOPP) has secured its first ‘Read and Publish’ transformative agreement in Taiwan, demonstrating its dedication to expanding open access (OA) to research in the Asia-Pacific (APAC) region and at scale globally.
The three-year transformative agreement with the Physics Research Promotion Centre, which is part of the National Science and Technology Council (NSTC), will enable 20 Taiwanese universities to offer their researchers unlimited OA publishing at no cost to them. The agreement will also allow authors to retain copyright ...
Mediterranean diet ‘a straightforward approach’ among many nutritional options for improving the chance of success in IVF
2023-12-20
Adjuvant therapies to help infertile women conceive by IVF - especially those whose treatments have been unsuccessful in the past - are now a common feature both before and during the treatment cycle. Now, a new analysis of the evidence for many nutritional supplements and diets thought to improve outcome in IVF has concluded that adopting a Mediterranean diet during treatment would offer a single ‘straightforward approach’ with good evidence of benefit in contrast to that of a Western diet.
Evidence from studies of nine commonly used nutritional supplements was found to be inconsistent and not always of good quality. The analysis, by Professor Roger ...
Could gamma brain stimulation help combat Alzheimer’s disease?
2023-12-20
A review in the Journal of Internal Medicine explores the potential of non-invasive interventions such as light, sound, and magnets to stimulate gamma brain waves for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Such strategies may be beneficial because Alzheimer’s disease is characterized by reduced fast brain oscillations in the gamma range (30–100 Hz).
The authors note that recent studies reveal that it is feasible and safe to induce 40 Hz brain activity in patients with Alzheimer’s disease through a range of methods. Also, preliminary evidence suggests that such treatment can yield beneficial ...
How does the inability to burp affect daily life?
2023-12-20
The inability to burp—called retrograde cricopharyngeus dysfunction (R-CPD)—is caused by failure of the throat’s cricopharyngeal muscle to relax to allow the outward passage of gas. An interview-based study in Neurogastroenterology & Motility that included 199 adults affected by the condition reveals the impact of R-CPD on quality of life.
Most participants reported abdominal bloating, socially awkward gurgling noises, excessive flatulence, and difficulty vomiting. Only half discussed their symptoms with their primary care clinician, and 90% felt they did not receive ...