Cells of the future: A key to reprogramming cell identities
The dynamic journey of DNA replication timing and its impact on cellular plasticity
2023-12-20
(Press-News.org)
The intricate process of duplicating genetic information, referred to as DNA replication, lies at the heart of the transmission of life from one cell to another and from one organism to the next. This happens by not just simply copying the genetic information; a well-orchestrated sequence of molecular events has to happen at the right time. Scientists around Prof. Maria-Elena Torres-Padilla from Helmholtz Munich have recently uncovered a fascinating aspect of this process known as "replication timing" (RT) and how special this is when life commences. The new results are now published in Nature.
The process of DNA replication timing (RT) refers to the specific moments when different regions of our genetic code are duplicated. Researchers from the Institute for Epigenetics and Stem Cells at Helmholtz Munich have implemented a technique called “Repli-seq” to delve into the intimate relationship between RT and the adaptability of cells, the cellular plasticity. Intriguingly, they also uncovered a new relationship between RT and how the genes fold into three-dimensional structures inside the cell nucleus.
Starting with the earliest stage of an embryo, the zygote – the very beginning of an organism's life – researchers have created a map of RT from this single-cell stage to the stage at which the embryo implants in the mother’s womb, called a blastocyst. The unexpected discovery is that the RT in the single-celled embryo is not very ordered, leading to the suggestion that genome duplications are very flexible in these early cells. However, after the 4-cell stage, the RT becomes more defined. There is a gradual process happening, mirroring the gradual acquisition of modifications to the DNA and associated proteins, the so-called chromatin marks, that indicate the genes' activity and importance in the cell's functions.
Maria-Elena Torres-Padilla, corresponding author of the study, explains further: “This is remarkable, as this tells us that these early embryo cells have a very ‘plastic’ genome duplication program. Because these early cells are totipotent, that means, they can create every single cell in our bodies. We think that what we discovered in this study is one of the reasons why these cells are so remarkably capable of generating all the body.” The new findings about DNA replication can serve as a tool to reprogram cells. Dr. Tsunetoshi Nakatani, the first author of the study, adds: “We can envision changing the cell identity by changing its RT program into a more flexible one”.
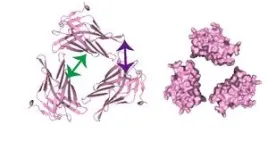
The results further show, that RNA polymerase, commonly known as the enzyme responsible for reading the genetic code and transcribing it into RNA, contributes to determining the exact RT program, providing some cues as to how to be able to manipulate such program in the future. The research team has discovered that the three-dimensional structure of the genome takes shape first, and the RT program is established consequently. This is an exciting finding, as it posits that how our genome accommodates into the three-dimensional space of the cell nucleus influences the flexibility of the RT program.
In conclusion, DNA replication timing is a fascinating piece of the puzzle in the grand narrative of life. It demonstrates how the precision of genetic replication is intimately tied to the capacity of the cells from the early embryo to generate other cell types in our body. As researchers continue to explore these connections, we gain a deeper understanding of the very essence of life's transmission, cell to cell, organism to organism, and of what makes a cell capable of generating a new body.
Original publication
Nakatani et al. (2023): The establishment of a replication timing program after fertilization reveals organizing principles of the mammalian genome. Nature. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06872-1
About Helmholtz Munich
Helmholtz Munich is a leading biomedical research center. Its mission is to develop breakthrough solutions for better health in a rapidly changing world. Interdisciplinary research teams focus on environmentally triggered diseases, especially the therapy and prevention of diabetes, obesity, allergies, and chronic lung diseases. With the power of artificial intelligence and bioengineering, researchers accelerate the translation to patients. Helmholtz Munich has more than 2,500 employees and is headquartered in Munich/Neuherberg. It is a member of the Helmholtz Association, with more than 43,000 employees and 18 research centers the largest scientific organization in Germany. More about Helmholtz Munich (Helmholtz Zentrum München Deutsches Forschungszentrum für Gesundheit und Umwelt GmbH): www.helmholtz-munich.de/en
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-12-20
A mineral found on the surface of Mars offers potential to create sustainable energy
Uses ‘waste’ product from recent NASA research to create transformative nanomaterials
Findings could play role in shaping sustainable habitation on the red planet – and clean energy production back home
Researchers at the University of Sussex have discovered the transformative potential of Martian nanomaterials, potentially opening the door to sustainable habitation on the red planet.
Using resources and techniques currently applied on the International Space Station and by NASA, Dr Conor Boland, a Lecturer in Materials Physics at the University of Sussex, led a ...
2023-12-20
Three winners have been selected in the 2023 Faces of Biology Photo Contest, sponsored by the American Institute of Biological Sciences (AIBS) and the Society for Integrative and Comparative Biology (SICB).
“Photography is an effective tool to help communicate the process of scientific research,” said Scott Glisson, CEO of AIBS. “This contest provides a visual forum for expression, inspiration, and technical skill that can have a positive impact on how the public views research and science.
The competition showcases, in a personal way, biological research in its many forms and settings. With the images, we ...
2023-12-20
CAMBRIDGE, MA – Using a type of artificial intelligence known as deep learning, MIT researchers have discovered a class of compounds that can kill a drug-resistant bacterium that causes more than 10,000 deaths in the United States every year.
In a study appearing today in Nature, the researchers showed that these compounds could kill methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) grown in a lab dish and in two mouse models of MRSA infection. The compounds also show very low toxicity against human cells, making them particularly good drug candidates.
A key innovation of the new study is that the researchers were also able to figure out ...
2023-12-20
The mammalian nose is a work of evolutionary art. Its millions of nerve cells, each tailored with just one of thousands of specific odor-chemical receptors encoded in the genome, can collectively distinguish a trillion distinct scents. Those sensations, in turn, inform many behaviors, from assessing food options to discerning friends from foes to sparking memories.
Today, in the journal Nature, a research team led by scientists at Columbia’s Zuckerman Institute describes a previously undetected mechanism in mice—starring the genetic molecule RNA—that could explain how each sensory cell, or neuron, in mammalian noses becomes tailored to detect a specific ...
2023-12-20
About The Study: Compared with prior decades, the number of new dermatologic drug approvals by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) increased between 2012 and 2022. Nearly half of these drugs were considered first in class or first in indication, and several were deemed clinically useful or to have high added therapeutic benefit by health technology assessment organizations in Germany, Canada, or France.
Authors: Ravi Gupta, M.D., M.S.H.P., of the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine ...
2023-12-20
Taking inspiration from the human brain, researchers have developed a new synaptic transistor capable of higher-level thinking.
Designed by researchers at Northwestern University, Boston College and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), the device simultaneously processes and stores information just like the human brain. In new experiments, the researchers demonstrated that the transistor goes beyond simple machine-learning tasks to categorize data and is capable of performing associative learning.
Although previous studies have leveraged similar strategies to develop brain-like computing devices, those transistors cannot function outside cryogenic temperatures. The new ...
2023-12-20
About The Study: This pilot pragmatic clinical trial included 243 homebound older adults with self- or proxy-reported dementia found a lower although nonsignificant likelihood of nursing home placement among those receiving daily-delivered meals compared with those receiving drop-shipped frozen meals. While this study was not powered to detect meaningful, statistically significant differences in nursing home placement, its feasibility and initial results warrant exploration in an adequately powered trial.
Authors: Kali S. Thomas, Ph.D., of the Brown University School of Public Health in Providence, Rhode Island, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed ...
2023-12-20
The human brain continues to be built after we are born for far longer than previously recognized, suggests research by Shawn Sorrells, assistant professor of neuroscience in the Kenneth P. Dietrich School of Arts and Sciences. Sorrells’s research on postnatal brain development, published today inthe journal Nature, shines light on fundamental processes that contribute to the development of important brain functions, such as learning, memory and spatial navigation.
The new research suggests that a subset of inhibitory neurons within the entorhinal cortex, or EC -- an area of the brain essential for forming memories -- continue ...
2023-12-20
In less time than it will take you to read this article, an artificial intelligence-driven system was able to autonomously learn about certain Nobel Prize-winning chemical reactions and design a successful laboratory procedure to make them. The AI did all that in just a few minutes — and nailed it on the first try.
"This is the first time that a non-organic intelligence planned, designed and executed this complex reaction that was invented by humans," says Carnegie Mellon University chemist and ...
2023-12-20
Alloys, which are materials such as steel that are made by combining two or more metallic elements, are among the underpinnings of contemporary life. They are essential for buildings, transportation, appliances and tools — including, very likely, the device you are using to read this story. In applying alloys, engineers have faced an age-old trade-off common in most materials: Alloys that are hard tend to be brittle and break under strain, while those that are flexible under strain tend to dent easily.
Possibilities for sidestepping that trade-off arose about 20 years ago, when researchers first developed medium- and high-entropy alloys, stable materials that combine ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Cells of the future: A key to reprogramming cell identities
The dynamic journey of DNA replication timing and its impact on cellular plasticity