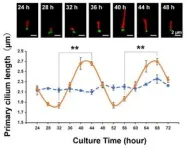
Wildflowers increasingly doing without insect pollinators
2023-12-21
(Press-News.org)
Scientists at the CNRS and the University of Montpellier1 have discovered that flowering plants growing in farmland are increasingly doing without insect pollinators. As reproduction becomes more difficult for them in an environment depleted in pollinating insects, the plants are evolving towards self-fertilisation. These findings are published in a paper in the journal New Phytologist dated December 20, 2023.
By comparing field pansies growing in the Paris region today with pansies from the same localities resurrected in the laboratory from seeds collected2 between 1992 and 2001, the research team found that today's flowers are 10% smaller, produce 20% less nectar, and are less visited by pollinators than their ancestors.
This rapid evolution is thought to be due to the decline in pollinator populations in Europe. Indeed, a study conducted in Germany showed that over 75% of the biomass of flying insects has vanished from protected areas in the last thirty years.
The study identified a vicious circle in which the decline in pollinators leads to reduced nectar production by flowers, which could in turn exacerbate the decline of these insects. It underlines the importance of implementing measures to counter this phenomenon as quickly as possible and thus safeguard the interactions between plants and pollinators, which have existed for millions of years.
Notes
1 Centre d’écologie fonctionnelle et évolutive (CNRS/Université de Montpellier/EPHE/IRD)
2 Seeds conserved by the Conservatoire botanique national de Bailleul and the Conservatoire botanique national du Bassin parisien.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-12-21
Dec. 20, 2023
Contact: Derek Smith, 734-546-3632, smitdere@umich.edu; Nicole Casal Moore, 734-709-1651, ncmoore@umich.edu
ANN ARBOR—Lights could soon use the full color suite of perfectly efficient organic light-emitting diodes, or OLEDs, that last tens of thousands of hours, thanks to an innovation from physicists and engineers at the University of Michigan.
The U-M team's new phosphorescent OLEDs, commonly referred to as PHOLEDs, can maintain 90% of the blue light intensity for 10-14 times longer than other designs that emit similar deep blue colors. That kind ...
2023-12-20
We often look to the smallest lifeforms for help solving the biggest problems: Microbes help make foods and beverages, cure diseases, treat waste and even clean up pollution. Yeast and bacteria can also convert plant sugars into biofuels and chemicals traditionally derived from fossil fuels — a key component of most plans to slow climate change.
Now University of Wisconsin–Madison researchers have engineered bacteria that can produce two chemical products at the same time from underutilized plant fiber. And unlike humans, these ...
2023-12-20
In the not-so-distant future, people might be able to tune in to their favorite news source for an update on their community health status, just as they check on the local weather forecast.
The community health status is similar to the color-coded Doppler weather data that provides meteorologists with information about rain, snow or hail, its motion and intensity, which they can use to determine specific areas where dangerous weather conditions exist. Having this information has proven to be a valuable tool to protect life and property.
“The new community ...
2023-12-20
Scientists at NTNU’s Kavli Institute for Systems Neuroscience in Norway have discovered a pattern of activity in the brain that can serve as a template for building sequential experiences.
“I believe we have found one of the brain’s prototypes for building sequences” says Professor Edvard Moser.He describes the activity pattern as “a fundamental algorithm that is intrinsic to the brain and independent of experience.”
The breakthrough discovery was published in Nature 20. December 2023.
The ability to organise elements into sequences ...
2023-12-20
A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 23, entitled, “Benidipine calcium channel blocker promotes the death of cigarette smoke-induced senescent cells and improves lung emphysema.”
Smoking is the main risk factor for many lung diseases including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Cigarette smoke (CS) contains carcinogenic and reactive oxygen species that favor DNA mutations and perturb the homeostasis and environment of cells. CS induces lung cell senescence resulting in a stable proliferation arrest and a senescence-associated ...
2023-12-20
Despite their promise, immunotherapies fail to treat many cancers, including over 80% of some of the most advanced breast cancers. And many of those patients who do respond still experience metastases eventually. New research from Stanford University and the Arc Institute has revealed a better way to predict and improve patient responses.
A team led by Lingyin Li, associate professor of biochemistry at Stanford and Arc Core Investigator, found that a protein called ENPP1 acts as an on/off switch that controls breast cancer’s ability to both resist immunotherapy and metastasize. The study, published on ...
2023-12-20
Oak Ridge National Laboratory researchers have identified the most energy-efficient 2024 model year vehicles available in the United States, including electric and hybrids, in the latest edition of the Department of Energy’s Fuel Economy Guide.
The annual online resource compares fuel costs for two-seaters up to large sedans, small and midsize station wagons, minivans, small and standard sport utility vehicles and small and standard pickup trucks. A quick reference top 10 list is searchable for make, model and class, too.
“With the national average of gasoline over $3 per gallon, drivers need to know how much they can save by ...
2023-12-20
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, DECEMBER 20, 2023
MINNEAPOLIS – Signs of injury to the brain’s white matter called white matter hyperintensities, as seen on brain scans, may be tied more strongly to vascular risk factors, brain shrinkage, and other markers of dementia in former tackle football players than in those who did not play football, according to a study published in the December 20, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
“Studies have shown that athletes exposed to repetitive head impacts can have increased white matter hyperintensity burden in their brains,” ...
2023-12-20
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- A Binghamton University team is one of just 18 nationally that will share in $100 million in U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) funding from the Technology, Innovation and Partnerships (TIP) Directorate to accelerate the pace and scale of translational research.
The Accelerating Research Translation (ART) program will provide $6 million to Binghamton as a cooperative agreement over four years to source and grow pivotal innovations that, with help from the technology transfer office, can go to market and have a positive impact on society.
“Binghamton is quickly ...
2023-12-20
When did archery arise in the Americas? And what were the effects of this technology on society?
These questions have long been debated among anthropologists and archaeologists. But a study led by a University of California, Davis, anthropologist, is shining light on this mystery.
Focusing on the Lake Titicaca Basin in the Andes mountains, anthropologists found through analysis of 1,179 projectile points that the rise of archery technology dates to around 5,000 years ago. Previous research held that archery in the Andes emerged around 3,000 years ago.
The new research indicates that the adoption of bow-and-arrow technology coincided with both the expansion of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Wildflowers increasingly doing without insect pollinators