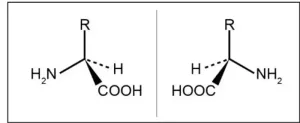
(Press-News.org) Osaka, Japan – Only recently was it discovered that amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, exist in two different forms: L- and D-forms. While all natural proteins consist exclusively of L-amino acids, the function of D-amino acids remained poorly understood, despite being present in the food we eat every day.
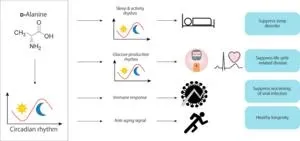
Now, a multi-institutional research team led by Osaka University has revealed a function of one D-form amino acid: D-alanine. So, what does it do, and how did they uncover its function? To understand, we need a little background information.
The circadian clock, a natural oscillation in our bodies that aligns with the 24-hour cycle of day and night, affects many biological processes. One of these is gluconeogenesis, in which new glucose can be created to maintain energy levels in lieu of carbohydrate intake. While gluconeogenesis was known to vary with circadian rhythm, the reason why was unknown.
There were some clues, however. D-alanine is found in tissues that metabolize glucose, and trace levels of D-alanine in blood and urine had been reported to vary with the circadian rhythm. Using special equipment and an advanced analytical technique, the researchers were able to detect and quantify trace levels of the rare amino acid. The team could then verify that levels of D-alanine reliably change with the circadian clock; the variations are caused by the removal of D-alanine via urine, a process controlled by the kidney. They also showed that sleep was key in regulating D-alanine levels.
“We decided to look at which genes are expressed when the kidney is exposed to D-alanine,” explains lead author of the study, Shinsuke Sakai. “We used deep-learning analysis with an iterative random-forest algorithm to identify the targeted genes. We found that D-alanine upregulates both genes linked to gluconeogenesis and genes known to be related to the circadian rhythm.”
Analysis of transcription factors, which are proteins that regulate gene expression, showed that the changes induced by D-alanine were mediated by a protein called Cry2, which is known to be a key circadian regulator. Under circadian rhythm-disturbed condition, treatment of D-alanine improved the daily rhythm.
“Through these experiments, we were able to show that D-alanine is a link between gluconeogenesis in the kidney and the circadian clock,” says senior author Tomonori Kimura, “and that D-alanine activates gluconeogenesis through the circadian transcriptional network.”
Revealing the link between D-alanine and the circadian clock represents a major step forward in our understanding of these rare D-amino acids. One exciting possibility is new treatments for diseases related to glucose, e.g., diabetes, and the circadian clock, e.g., sleep disorders.
###
The article, “D-Alanine affects the circadian clock to regulate glucose metabolism in kidney”, was published in Kidney360 at DOI: https://doi.org/10.34067/KID.0000000000000345
About Osaka University
Osaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and is now one of Japan's leading comprehensive universities with a broad disciplinary spectrum. This strength is coupled with a singular drive for innovation that extends throughout the scientific process, from fundamental research to the creation of applied technology with positive economic impacts. Its commitment to innovation has been recognized in Japan and around the world, being named Japan's most innovative university in 2015 (Reuters 2015 Top 100) and one of the most innovative institutions in the world in 2017 (Innovative Universities and the Nature Index Innovation 2017). Now, Osaka University is leveraging its role as a Designated National University Corporation selected by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to contribute to innovation for human welfare, sustainable development of society, and social transformation.
Website: https://resou.osaka-u.ac.jp/en
END
One of the keys to healthy sleep and blood sugar has been found
Researchers from Osaka University have shown that the rare D-form of the amino acid alanine underlies the link between the circadian clock and glucose regulation by the kidney
2023-12-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Artery calcification more common in night owls
2023-12-21
Artery calcification is almost twice as common in night owls compared to early birds, according to a study from the University of Gothenburg, Sweden. Circadian function appears to be particularly important during the early stages of cardiovascular disease.
Atherosclerosis involves fatty deposits accumulating on the inside of the arteries, making it harder for blood to pass through. The disease develops over a very long period of time and is not noticed until it leads to blood clots causing angina, heart attack, or stroke. Previous research has shown that people with late-night habits have an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, but this is the first study to show how circadian rhythms ...
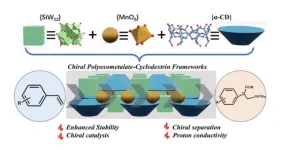
Scientists create chiral POM-based frameworks with enhanced stability and catalytic activity
2023-12-21
A team of scientists has created a chiral assembly by blending inorganic polyoxometalates and organic cyclodextrin molecules. Polyoxometalates are a class of nanomaterials with many useful applications. But the use of polyoxometalates as building blocks to construct chiral POM-based frameworks has been a long-stranding challenge for researchers. In this research, the team produced a 3D framework, constructed by coordination assembly. The resulting framework features an interlaced organic-inorganic hybrid layer.
The team has published their work in the journal, Polyoxometalates, ...
Smithsonian-led study reveals five new species of soft-furred hedgehogs from Southeast Asia
2023-12-21
A new study led by scientists at the Smithsonian’s National Museum of Natural History identifies five new species of soft-furred hedgehogs from Southeast Asia.
The study, published in the Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, used DNA analysis and physical characteristics to describe two entirely new species of soft-furred hedgehogs and elevate three subspecies to the level of species.
The two new species, named Hylomys vorax and H. macarong, are endemic to the endangered Leuser ecosystem, a tropical rainforest in North Sumatra and Southern Vietnam, respectively. The museum specimens that were vital to describing these two new species came from the natural history collections ...
Bugs that help bugs: How environmental microbes boost fruit fly reproduction
2023-12-21
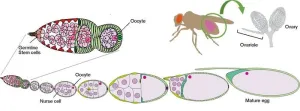
Osaka, Japan – For many of us, when we think of microbiomes, our first thoughts are probably about the beneficial microorganisms that live in our guts. But now, researchers from Japan and US have discovered how the microbes living in fruit flies can enhance their reproduction.
In a recently published study in Communications Biology, the research group has revealed that microbes in the fruit fly microbiome are involved in controlling the germline stem cells that form eggs, as well as subsequent egg maturation, in female fruit ...
Sleep deprivation makes us less happy, more anxious
2023-12-21
Sleep loss does more than just make us tired. It can undermine our emotional functioning, decrease positive moods and put us at higher risk for anxiety symptoms, according to a study published by the American Psychological Association that synthesized more than 50 years of research on sleep deprivation and mood.
“In our largely sleep-deprived society, quantifying the effects of sleep loss on emotion is critical for promoting psychological health,” said study lead author Cara Palmer, PhD, of Montana State University. “This study represents ...
KIMM develops real-time multimodal tactile detection system applicable to robots and wearable devices
2023-12-21
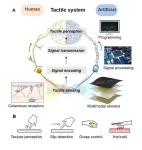
A tactile perception system capable of providing human-like multimodal tactile information to objects like robots and wearable devices that require tactile data in real time has been developed.
The research team led by Research Director Hyuneui Lim of the Nano-Convergence Manufacturing Systems Research Division and Principle Researcher Youngdo Jung of the Department of Nature-Inspired System and Application of the Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials (Chairman Seog-hyeon Ryu, hereinafter referred to as the “KIMM”), an institute under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Science and ICT, developed a real-time and ...
New 1.5-billion-pixel ESO image shows Running Chicken Nebula in unprecedented detail
2023-12-21
While many holiday traditions involve feasts of turkey, soba noodles, latkes or Pan de Pascua, this year, the European Southern Observatory (ESO) is bringing you a holiday chicken. The so-called Running Chicken Nebula, home to young stars in the making, is revealed in spectacular detail in this 1.5-billion-pixel image captured by the VLT Survey Telescope (VST), hosted at ESO’s Paranal site in Chile.
This vast stellar nursery is located in the constellation Centaurus (the Centaur), at about 6500 light-years from Earth. Young stars within this nebula emit intense radiation that makes the surrounding hydrogen gas glow in shades ...
Light exercise could be the key to reversing childhood obesity linked to sedentariness
2023-12-21
Increased sedentary time as a child through adolescence is directly linked to childhood obesity, but new research has found light physical activity may completely reverse the adverse process.
The study - conducted in collaboration with between University of Exeter, University of Eastern Finland, University of Bristol, and University of Colorado and published in Nature Communications – is the largest and longest follow-up to objectively measure physical activity and fat mass, using the University of Bristol’s Children of the 90s data (also known as the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children). ...
Are diamonds GaN’s best friend? Revolutionizing transistor technology
2023-12-21
Researchers at Osaka Metropolitan University are proving that diamonds are so much more than just a girl’s best friend. Their groundbreaking research focuses on gallium nitride (GaN) transistors, which are high-power, high-frequency semiconductor devices used in mobile data and satellite communication systems. With the increasing miniaturization of semiconductor devices, problems arise such as increases in power density and heat generation that can affect the performance, reliability, and lifetime of these devices. Therefore, effective thermal management is crucial. Diamond, ...
New study examines the relationship between the rate of wound healing, the circadian rhythm, and ‘hair’ on cells
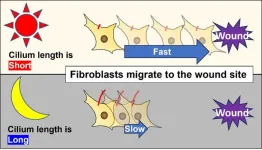
2023-12-21
Nearly every organism on Earth follows a natural circadian rhythm that is coded by your cell’s clock genes, which do exactly as you suspect from the name: regulate your body’s rhythm on a 24-hour basis. Most cells in mammalian bodies have cilia of some sort, which are hair-like structures that perform a variety of functions such as movement for motile cilia and aiding in structure in function for non-motile, or primary, cilia. The primary cilia also act as a sensory organ for the cell, a function which has illuminated ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
GLP-1 medications get at the heart of addiction: study
Global trauma study highlights shared learning as interest in whole blood resurges
Almost a third of Gen Z men agree a wife should obey her husband
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
NYCST announces Round 2 Awards for space technology projects
How the Dobbs decision and abortion restrictions changed where medical students apply to residency programs
Microwave frying can help lower oil content for healthier French fries
In MS, wearable sensors may help identify people at risk of worsening disability
Study: Football associated with nearly one in five brain injuries in youth sports
Machine-learning immune-system analysis study may hold clues to personalized medicine
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
As a whole, LGB+ workers in the NHS do not experience pay gaps compared to their heterosexual colleagues
How cocaine rewires the brain to drive relapse
Mosquito monitoring through sound - implications for AI species recognition
UCLA researchers engineer CAR-T cells to target hard-to-treat solid tumors
New study reveals asynchronous land–ocean responses to ancient ocean anoxia
Ctenophore research points to earlier origins of brain-like structures
[Press-News.org] One of the keys to healthy sleep and blood sugar has been foundResearchers from Osaka University have shown that the rare D-form of the amino acid alanine underlies the link between the circadian clock and glucose regulation by the kidney