(Press-News.org) While many holiday traditions involve feasts of turkey, soba noodles, latkes or Pan de Pascua, this year, the European Southern Observatory (ESO) is bringing you a holiday chicken. The so-called Running Chicken Nebula, home to young stars in the making, is revealed in spectacular detail in this 1.5-billion-pixel image captured by the VLT Survey Telescope (VST), hosted at ESO’s Paranal site in Chile.
This vast stellar nursery is located in the constellation Centaurus (the Centaur), at about 6500 light-years from Earth. Young stars within this nebula emit intense radiation that makes the surrounding hydrogen gas glow in shades of pink.
The Running Chicken Nebula actually comprises several regions, all of which we can see in this vast image that spans an area in the sky of about 25 full Moons [1]. The brightest region within the nebula is called IC 2948, where some people see the chicken’s head and others its rear end. The wispy pastel contours are ethereal plumes of gas and dust. Towards the centre of the image, marked by the bright, vertical, almost pillar-like, structure, is IC 2944. The brightest twinkle in this particular region is Lambda Centauri, a star visible to the naked eye that is much closer to us than the nebula itself.
There are, however, many young stars within IC 2948 and IC 2944 themselves — and while they might be bright, they’re most certainly not merry. As they spit out vast amounts of radiation, they carve up their environment much like, well, a chicken. Some regions of the nebula, known as Bok globules, can withstand the fierce bombardment from the ultraviolet radiation pervading this region. If you zoom in to the image, you might see them: small, dark, and dense pockets of dust and gas dotted across the nebula.
Other regions pictured here include, to the upper right, Gum 39 and 40, and to the lower right, Gum 41. Aside from nebulae, there are countless orange, white and blue stars, like fireworks in the sky. Overall in this image, there are more wonders than can be described — zoom in and pan across, and you’ll have a feast for the eyes.
This image is a large mosaic comprising hundreds of separate frames carefully stitched together. The individual images were taken through filters that let through light of different colours, which were then combined into the final result presented here. The observations were conducted with the wide-field camera OmegaCAM on the VST, a telescope owned by the National Institute for Astrophysics in Italy (INAF) and hosted by ESO at its Paranal site in Chile’s Atacama Desert that is ideally suited for mapping the southern sky in visible light. The data that went into making this mosaic were taken as part of the VST Photometric Hα Survey of the Southern Galactic Plane and Bulge (VPHAS+), a project aimed at better understanding the life cycle of stars.
Notes
[1] This image, edge to edge, is 270 light-years wide. It would take an average chicken almost 21 billion years to run across it. That’s much longer than our Universe has been around for.
More information
The European Southern Observatory (ESO) enables scientists worldwide to discover the secrets of the Universe for the benefit of all. We design, build and operate world-class observatories on the ground — which astronomers use to tackle exciting questions and spread the fascination of astronomy — and promote international collaboration for astronomy. Established as an intergovernmental organisation in 1962, today ESO is supported by 16 Member States (Austria, Belgium, the Czech Republic, Denmark, France, Finland, Germany, Ireland, Italy, the Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland and the United Kingdom), along with the host state of Chile and with Australia as a Strategic Partner. ESO’s headquarters and its visitor centre and planetarium, the ESO Supernova, are located close to Munich in Germany, while the Chilean Atacama Desert, a marvellous place with unique conditions to observe the sky, hosts our telescopes. ESO operates three observing sites: La Silla, Paranal and Chajnantor. At Paranal, ESO operates the Very Large Telescope and its Very Large Telescope Interferometer, as well as survey telescopes such as VISTA. Also at Paranal ESO will host and operate the Cherenkov Telescope Array South, the world’s largest and most sensitive gamma-ray observatory. Together with international partners, ESO operates ALMA on Chajnantor, a facility that observes the skies in the millimetre and submillimetre range. At Cerro Armazones, near Paranal, we are building “the world’s biggest eye on the sky” — ESO’s Extremely Large Telescope. From our offices in Santiago, Chile we support our operations in the country and engage with Chilean partners and society.
Links
Photos of the survey telescopes at Paranal, including VST
For journalists: subscribe to receive our releases under embargo in your language
For scientists: got a story? Pitch your research
Contacts
Juan Carlos Muñoz Mateos
ESO Media Officer
Garching bei München, Germany
Tel: +49 89 3200 6176
Email: jmunoz@eso.org
Bárbara Ferreira
ESO Media Manager
Garching bei München, Germany
Tel: +49 89 3200 6670
Cell: +49 151 241 664 00
Email: press@eso.org
END
New 1.5-billion-pixel ESO image shows Running Chicken Nebula in unprecedented detail
2023-12-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Light exercise could be the key to reversing childhood obesity linked to sedentariness
2023-12-21
Increased sedentary time as a child through adolescence is directly linked to childhood obesity, but new research has found light physical activity may completely reverse the adverse process.
The study - conducted in collaboration with between University of Exeter, University of Eastern Finland, University of Bristol, and University of Colorado and published in Nature Communications – is the largest and longest follow-up to objectively measure physical activity and fat mass, using the University of Bristol’s Children of the 90s data (also known as the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children). ...
Are diamonds GaN’s best friend? Revolutionizing transistor technology
2023-12-21
Researchers at Osaka Metropolitan University are proving that diamonds are so much more than just a girl’s best friend. Their groundbreaking research focuses on gallium nitride (GaN) transistors, which are high-power, high-frequency semiconductor devices used in mobile data and satellite communication systems. With the increasing miniaturization of semiconductor devices, problems arise such as increases in power density and heat generation that can affect the performance, reliability, and lifetime of these devices. Therefore, effective thermal management is crucial. Diamond, ...
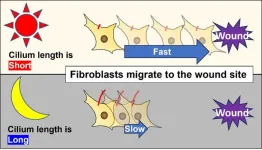
New study examines the relationship between the rate of wound healing, the circadian rhythm, and ‘hair’ on cells
2023-12-21
Nearly every organism on Earth follows a natural circadian rhythm that is coded by your cell’s clock genes, which do exactly as you suspect from the name: regulate your body’s rhythm on a 24-hour basis. Most cells in mammalian bodies have cilia of some sort, which are hair-like structures that perform a variety of functions such as movement for motile cilia and aiding in structure in function for non-motile, or primary, cilia. The primary cilia also act as a sensory organ for the cell, a function which has illuminated ...
Great British Bake Off Christmas desserts not as naughty as you may think
2023-12-21
Christmas desserts from The Great British Bake Off are more likely to use ingredients that are associated with reductions, rather than increases, in the risk of death or disease, suggests research published in the Christmas issue of The BMJ.
As the holiday season approaches, the age-old debate resurfaces: can we indulge in Christmas desserts without feeling the pang of guilt? Can we look past the negative headlines of what butter and sugar do to our bodies, and enjoy a piece of Christmas cake in heavenly peace?
To answer this Christmas conundrum, researchers set out to determine ...
Spike in morning after pill sales in the U.S. after New Year celebrations
2023-12-21
Sales of emergency contraception are estimated to rise by around 10% in the US in the week after the New Year holiday, suggesting that this period is associated with increased risks of unprotected sex compared with other holidays, finds a study published in the Christmas issue of The BMJ.
Other holidays such as Valentine’s Day and Independence Day were also associated with an increase in sales, but to a lesser extent.
Although this annual spike in sales might seem humorous, the researchers point out that as many US states have increased restrictions on abortion ...
The evolutionary timeline of diminished boric acid and urea transportation in aquaporin 10
2023-12-21
Aquaporin (Aqp) 10 water channels in humans allow the free passage of water, glycerol, urea, and boric acid across cells. However, Aqp10.2b in pufferfishes allows only the passage of water and glycerol and not urea and boric acid. Researchers from the Tokyo Institute of Technology sought to understand the evolutionary timeline that resulted in the variable substrate selection mechanisms among Aqp10s. Their results indicate that Aqp10.2 in ray-finned fishes may have reduced or lost urea and boric acid permeabilities through evolution.
Aquaporins ...
Wildflowers increasingly doing without insect pollinators
2023-12-21
Scientists at the CNRS and the University of Montpellier1 have discovered that flowering plants growing in farmland are increasingly doing without insect pollinators. As reproduction becomes more difficult for them in an environment depleted in pollinating insects, the plants are evolving towards self-fertilisation. These findings are published in a paper in the journal New Phytologist dated December 20, 2023.
By comparing field pansies growing in the Paris region today with pansies from the same localities resurrected in the laboratory from seeds collected2 between 1992 and 2001, the research team found that today's flowers are 10% smaller, produce 20% less nectar, and are less ...
Blue PHOLEDs: Final color of efficient OLEDs finally viable in lighting
2023-12-21
Dec. 20, 2023
Contact: Derek Smith, 734-546-3632, smitdere@umich.edu; Nicole Casal Moore, 734-709-1651, ncmoore@umich.edu
ANN ARBOR—Lights could soon use the full color suite of perfectly efficient organic light-emitting diodes, or OLEDs, that last tens of thousands of hours, thanks to an innovation from physicists and engineers at the University of Michigan.
The U-M team's new phosphorescent OLEDs, commonly referred to as PHOLEDs, can maintain 90% of the blue light intensity for 10-14 times longer than other designs that emit similar deep blue colors. That kind ...
Multitasking microbes: UW–Madison scientists engineer bacteria to make two valuable products from plant fiber
2023-12-20
We often look to the smallest lifeforms for help solving the biggest problems: Microbes help make foods and beverages, cure diseases, treat waste and even clean up pollution. Yeast and bacteria can also convert plant sugars into biofuels and chemicals traditionally derived from fossil fuels — a key component of most plans to slow climate change.
Now University of Wisconsin–Madison researchers have engineered bacteria that can produce two chemical products at the same time from underutilized plant fiber. And unlike humans, these ...
And now, your community health forecast…
2023-12-20
In the not-so-distant future, people might be able to tune in to their favorite news source for an update on their community health status, just as they check on the local weather forecast.
The community health status is similar to the color-coded Doppler weather data that provides meteorologists with information about rain, snow or hail, its motion and intensity, which they can use to determine specific areas where dangerous weather conditions exist. Having this information has proven to be a valuable tool to protect life and property.
“The new community ...