(Press-News.org)
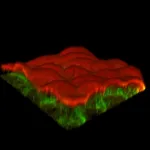
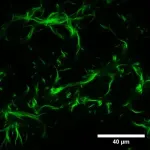
Tiny things matter – for instance, one amino acid can completely alter the architecture of the cell. Researchers at the Universities of Göttingen and Warwick investigated the structure and mechanics of the main component of the cytoskeleton of the cell: a protein known as actin. Actin is found in all living cells where it has a range of important functions – from muscle contraction to cell signalling and cell shape. This protein comes in two different varieties termed “isoforms”, which are known as gamma actin and beta actin. The difference between the two proteins is miniscule, only a few amino acids at just one part of the molecule vary. Yet this small change has a big impact on the cell. In nature, normally only mixtures of the two isoforms are found. In their study, the researchers separated out the two isoforms and analyzed them individually. The results were published in the journal Nature Communications.
The researchers studied the behaviour of networks of filaments, particularly focusing on the unique properties of the individual isoforms. They employed specialized techniques allowing them to assess the mechanics and dynamics of research models of cytoskeletal networks, drawing on expertise in biophysics at Göttingen and bioengineering at Warwick.
The results indicate that gamma actin prefers to form rigid networks near the cell's apex, while beta actin preferentially forms parallel bundles with a distinct organizational pattern. This difference is likely to be due to the stronger interaction of gamma actin with specific types of positively charged ions, rendering its networks stiffer than those formed by beta actin. “Our findings are compelling because they open up new avenues for understanding the intricate dynamics of protein networks within cells,” explains Professor Andreas Janshoff, Institute for Physical Chemistry, University of Göttingen. The research advances scientists’ understanding of fundamental cellular processes by shedding light on specific biological functions of actin, and this will have particular relevance for processes involving cellular mechanics such as growth, division and maturation of cells in tissue. “The implications of these discoveries extend to the broader field of cellular biology, offering insights that could impact many areas of research and applications, for instance in developmental biology,” adds Janshoff.
Original publication: Nietmann et al “Cytosolic actin isoforms form networks with different rheological properties that indicate specific biological function” Nature Communications, DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-43653-w
Contact:
Professor Andreas Janshoff
University of Göttingen
Institute for Physical Chemistry
Tammannstraße 6, 37077 Göttingen, Germany
Tel: +49 (0)551 39-14411
Email: ajansho@gwdg.de
www.uni-goettingen.de/en/208570.html
END
Big impacts from small changes in cell
Research at Göttingen and Warwick Universities reveals how filament interactions affect cellular networks
2023-12-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Jupiter was targeted by exoplanet hunter
2023-12-22
For the first time, an instrument to find planets light years away was used on an object in the Solar System, in a study on Jupiter's winds.
We find ourselves at a time when it has become almost commonplace to discover planets orbiting another star, with more than 5,000 already registered. The first distant worlds to incorporate this list were mainly giant planets, similar to but also very different in many ways from Jupiter and Saturn.
Astrophysicists have already begun to obtain data on the atmospheres of exoplanets, but fundamental ...
Pandemic lessons: Insights into how mobility restrictions affect healthcare costs
2023-12-22
Osaka, Japan - As the world grappled with lockdowns and restrictions brought by the COVID-19 pandemic, researchers at Osaka Metropolitan University conducted an extensive study to elucidate the link between changes in human mobility and the impact on medical costs associated with lifestyle-related diseases.
Dr. Haruka Kato and Professor Atsushi Takizawa of the Graduate School of Human Life and Ecology at Osaka Metropolitan University were concerned by the negative health effects resulting from the restriction of ...
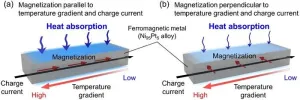
Controlling thermoelectric conversion in magnetic materials by magnetization direction
2023-12-22
1. NIMS has succeeded in directly observing the "anisotropic magneto-Thomson effect," a phenomenon in which the heat absorption/release proportional to an applied temperature difference and charge current (i.e., Thomson effect) changes anisotropically depending on the magnetization direction in magnetic materials. This research is expected to lead to further development of basic physics and materials science related to the fusion area of thermoelectrics and spintronics, as well as to development of new functionalities to control thermal energy with magnetism.
2. The Thomson effect has long been known as one of the fundamental ...
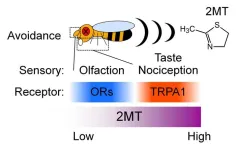
Stinky, bitter, and painful: A novel insect repellent attacks multiple sensory pathways
2023-12-22
Okazaki, Japan – crop damage in agriculture and the transmission of vector-borne diseases by insect pests have become worldwide threat nowadays. Chemical treatments such as insecticides and repellents have been a major strategy against insect pests for centuries. Due to limited understanding of mechanisms of insect avoidance behavior, however, development of insect repellents has been delayed. To discover compounds that effectively repel insect pests, it is important to focus on key molecules associated with sensory, particularly aversive, responses. In this study, researchers ...
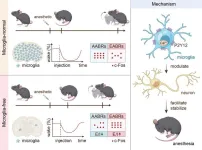
Microglia act as a “facilitator and stabilizer” for anesthesia
2023-12-22
Though it may be a surprise to the millions of people who undergo general anesthesia every year for medical procedures, the biological mechanism for how different anesthetics block consciousness is still not fully understood. However, researchers may be one step closer after uncovering the way small immune cells in the brain called microglia are impacted by general anesthesia.
The research was presented in a paper published in eLife on 22/Dec/2023.
“We found that microglia play an important role in regulating the body’s response to general anesthesia. ...
3D-printed flat-bone-mimetic bioceramic scaffolds for cranial restoration
2023-12-22
The cranial bone in the human body performs very important functions, such as protecting the brain and enabling the passage of the cranial nerves that are essential to physiological functioning. Critical-sized cranial defects can disrupt both the physical and psychological well-being of patients. Restoration of critical-sized cranial defects by cranioplasty is challenging for reconstructive surgeons, who prefer to use autologous bone grafts. The acquisition of autologous bone requires additional surgeries concomitant with risks such as free flap loss, infection, deep venous thrombosis, and nerve injury. These limitations necessitate the development ...
TTUHSC's Reddy elected fellow by the National Academy of Inventors
2023-12-22
P. Hemachandra Reddy, Ph.D., a professor in the Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center (TTUHSC) School of Medicine’s Department of Internal Medicine who has researched healthy aging, dementia and other neurodegenerative diseases for more than 20 years, recently was named to the 2023 class of Fellows for the National Academy of Inventors (NAI).
The NAI is a member organization comprised of U.S. and international universities and governmental and nonprofit research institutes with more than 4,600 individual inventor members and fellows spanning more than 300 institutions worldwide. ...
Light colour is less important for the internal clock than originally thought
2023-12-22
Vision is a complex process. The visual perception of the environment is created by a combination of different wavelengths of light, which are decoded as colours and brightness in the brain. Photoreceptors in the retina first convert the light into electrical impulses: with sufficient light, the cones enable sharp, detailed, and coloured vision. Rods only contribute to vision in low light conditions allowing for different shades of grey to be distinguished but leaving vision much less precise. The electrical nerve impulses are finally transmitted to ganglion cells in the retina and then via the optic nerve to the visual cortex in the ...
Scientists develop ‘flying dragon’ robot to fight fires from a distance
2023-12-22
Imagine a flying dragon that doesn’t spout fire, but instead extinguishes it with blasts of water. Thanks to a team of Japanese researchers, this new kind of beast may soon be recruited to firefighter teams around the world, to help put out fires that are too dangerous for their human teammates to approach.
The blueprint of this novel firefighter robot, called the Dragon Firefighter, has now been published in Frontiers in Robotics and AI. And as it has been published as Open Science, roboticists around the world may freely ...
Sunday sales reign supreme and other takeaways from review of farmers market transactions
2023-12-21
CORNELL UNIVERSITY MEDIA RELATIONS OFFICE
FOR RELEASE: Dec. 21, 2023
Kaitlyn Serrao
607-882-1140
kms465@cornell.edu
ITHACA, N.Y. – Cornell researchers partnered with New York livestock farmers to analyze transactions at farmers markets, finding that sales were better on Sundays, early in the morning, and during certain months of the year. The study, which researchers believe is the first peer-reviewed analysis of customer-level transaction data at farmers markets, gives new insights into how farmers can make markets more profitable for them.
The researchers and farmers used point-of-sale devices that record sales ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Big impacts from small changes in cellResearch at Göttingen and Warwick Universities reveals how filament interactions affect cellular networks