(Press-News.org) An AI model can predict which SARS-CoV-2 variants are likely to cause new waves of infection. Current models used to predict the dynamics of viral transmission do not predict variant-specific spread. Retsef Levi and colleagues studied what factors could shape the viral spread based on analysis of 9 million SARS-CoV-2 genetic sequences collected by the Global Initiative on Sharing Avian Influenza Data (GISAID) from 30 countries, along with data on vaccination rates, infection rates, and other factors. The patterns that emerged from this analysis were used to build a machine-learning enabled risk assessment model. The model can detect 72.8% of the variants in each country that will cause at least 1,000 cases per million people in the next three months after an observation period of only one week after detection. This predictive performance increases to 80.1% after two weeks of observation. Among the strongest predictors that a variant will become infectious are the early trajectory of the infections caused by the variant, the variant’s spike mutations, and how different the mutations of a new variant are from those of the most dominant variant during the observation period. The modeling approach could potentially be extended to predict the future course of other infectious diseases as well, according to the authors.
END
Predicting COVID-19 variant waves with AI
2024-01-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cultivated kelp can now be as good as wild kelp
2024-01-02
Norway’s exports products derived from from tangle kelp (Laminoria hyperborea) and knotted kelp (Ascophyllum nodosu) to the tune of more than NOK 1 billion a year. The industry mainly extracts alginate from kelp, which is used in over 600 different products as diverse as paint, soft serve ice cream, sauces, bandages, nappies, acid reflux medicine and material for encapsulating cells and medicine. However, the market is far from saturated.
“Alginate is becoming a scarce commodity on the global market. There are great opportunities here if we could cultivate more kelp that yielded alginate of good enough quality,” says Finn Aachmann, a professor at the Norwegian ...
Researchers identify new coding mechanism that transfers information from perception to memory
2024-01-02
Our memories are rich in detail: we can vividly recall the color of our home, the layout of our kitchen, or the front of our favorite café. How the brain encodes this information has long puzzled neuroscientists.
In a new Dartmouth-led study, researchers identified a neural coding mechanism that allows the transfer of information back and forth between perceptual regions to memory areas of the brain. The results are published in Nature Neuroscience.
Prior to this work, the classic understanding of brain organization was that perceptual regions of the brain represent the world "as it is," with the ...
A novel switch to turn genes on/off on cue, a promising step toward safer gene therapy
2024-01-02
Just like a doctor adjusts the dose of a medication to the patient’s needs, the expression of therapeutic genes, those modified in a person to treat or cure a disease via gene therapy, also needs to be maintained within a therapeutic window. Staying within the therapeutic window is important as too much of the protein could be toxic, and too little could result in a small or no therapeutic effect.
Although the principle of therapeutic window has been known for a long time, there has been no strategy to implement it safely, limiting the potential applications of gene therapy in the clinic. ...
Food insecurity among low-income adults dropped nearly 5% during pandemic-era SNAP expansion
2024-01-01
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 1 January 2024
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only ...
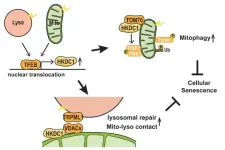
A tidy cell seems to keep aging at bay
2024-01-01
Osaka, Japan – Just as healthy organs are vital to our well-being, healthy organelles are vital to the proper functioning of the cell. These subcellular structures carry out specific jobs within the cell, for example, mitochondria power the cell and lysosomes keep the cell tidy.
Although damage to these two organelles has been linked to aging, cellular senescence, and many diseases, the regulation and maintenance of these organelles has remained poorly understood. Now, researchers at Osaka University have identified a protein, HKDC1, that plays a key role in maintaining these two organelles, thereby acting to prevent ...
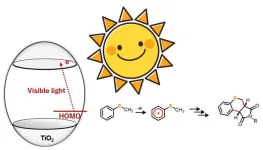
Chemical synthesis using titanium dioxide: An eco-friendly and innovative approach
2024-01-01
Heterocyclic compounds are organic molecules with a ring structure comprising at least two or more elements. In most cases, these rings are composed of carbon atoms along with one or more other elements such as nitrogen, oxygen, or sulfur. They are highly sought-after as raw materials in the chemical and pharmaceutical industry, owing to their versatility and excellent physiological activities. While several methods are available for synthesizing these compounds, most of them involve high temperature and pressure conditions, or the use of precious ...
Want to quit smoking in 2024? Cytisine can help … if you live in the right country
2024-01-01
A new study published in Addiction has found that cytisine, a low-cost, generic stop-smoking aid that has been used in eastern Europe since the 1960s, increases the chances of successful smoking cessation by more than two-fold compared with placebo and may be more effective than nicotine replacement therapy. It has a benign safety profile, with no evidence of serious safety concerns. Sounds perfect for your New Year resolution, doesn’t it? But there’s a catch: Cytisine is not licensed or marketed in most countries outside of central and eastern Europe, ...
Sodium’s high-pressure transformation can tell us about the interiors of stars, planets
2023-12-29
Travel deep enough below Earth’s surface or inside the center of the Sun, and matter changes on an atomic level.
The mounting pressure within stars and planets can cause metals to become nonconducting insulators. Sodium has been shown to transform from a shiny, gray-colored metal into a transparent, glass-like insulator when squeezed hard enough.
Now, a University at Buffalo-led study has revealed the chemical bonding behind this particular high-pressure phenomenon.
While it’s been theorized that high pressure essentially squeezes sodium’s electrons out into the spaces between atoms, researchers’ quantum chemical ...
Endocrine Society applauds Ohio governor veto of state ban on gender-affirming care for minors
2023-12-29
WASHINGTON—The Endocrine Society, the world’s oldest and largest professional medical society devoted to the study and treatment of hormone-related conditions, applauds Governor Mike Dewine’s veto of a proposed Ohio law that would have banned gender-affirming care for minors. The bill he vetoed contradicts mainstream medical practice and scientific evidence and would have taken medical decision-making out of the hands of families and their physicians and instead relied upon government officials.
More ...
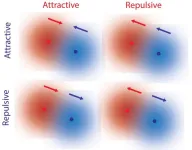
Molecules exhibit non-reciprocal interactions without external forces, new study finds
2023-12-29
Researchers from the University of Maine and Penn State discovered that molecules experience non-reciprocal interactions without external forces.
Fundamental forces such as gravity and electromagnetism are reciprocal, where two objects are attracted to each other or are repelled by each other. In our everyday experience, however, interactions don’t seem to follow this reciprocal law. For example, a predator is attracted to prey, but the prey tends to flee from the predator. Such non-reciprocal interactions are essential for complex behavior associated with living organisms. ...