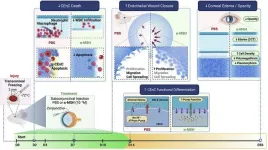
(Press-News.org) Philadelphia, January 2, 2024 – Findings from a pioneering study in The American Journal of Pathology, published by Elsevier, reveal that administration of the neuropeptide α-melanocyte–stimulating hormone (α-MSH) promotes corneal healing and restores normal eye function to an otherwise degenerating and diseased cornea by providing protection against cell death and promoting cell regeneration.
Due to a lack of currently available medical therapy, patients suffering from corneal endothelial disease, which leads to corneal swelling and potentially blindness, commonly require corneal transplantation. In fact, corneal transplantation is the most common type of transplant performed.
There is an urgent unmet need for safe and effective medical strategies for the prevention and reversal of persistent corneal edema, according to the investigators at Mass Eye and Ear of the Harvard Medical School Department of Ophthalmology. Therefore, there is a pressing need for the development of efficacious treatment for preventing, and potentially reversing, corneal edema due to corneal endothelial cell (CenC) loss following corneal injury.
This study examined the effect of local administration of α-MSH on persistent corneal edema and endothelial regeneration in an established model of injury-induced endothelial decompensation. The results show the impressive therapeutic potential of promoting the melanocortin pathway using α-MSH, thus opening new avenues of therapy.
Lead investigator Reza Dana, MD, MSc, MPH, Director of the Cornea and Refractive Surgery Service at Mass Eye and Ear, and Claes H. Dohlman Professor of Ophthalmology at Harvard Medical School, explains, "Our data, demonstrating the potent therapeutic effects of α-MSH through melanocortin receptor agonism, provide compelling evidence for the therapeutic potential of this pathway for a wide array of ocular disorders such as Fuchs Dystrophy, a common disease and indication for corneal transplantation, as well as other disorders of the corneal endothelium that lead to corneal swelling."
α-MSH is an evolutionarily conserved neuropeptide derived from the proteolysis of the pro-opiomelanocortin and exerts an array of functions through different melanocortin receptors expressed in various tissues. Findings in this seminal study show that administration of α-MSH:
Prevents corneal endothelial cell death
Restores normal endothelial function
Permits the cornea to resume normal thickness after a severe injury that normally leads to corneal thickening
Causes corneal cells to regenerate
Interventions to prevent corneal edema following ocular injury are currently limited to topical hypertonic saline and topical anti-inflammatory drugs. However, these interventions have limited efficacy, and they do not prevent CEnC decompensation.
Dr. Dana concludes: "The findings of our study suggest the therapeutic potential of α-MSH, or analogs that work by activating the melanocortin receptor system, in management of pathologies where there is a risk of corneal endothelial dysfunction, such as corneal injury or intraocular surgery. This study outlines the critical role played by neuropeptides in CEnC maintenance and offers a novel perspective on their potential application in corneal endothelial regeneration."
END
Pioneering study indicates a potential treatment for corneal endothelial disease, reducing the need for corneal transplants
Compelling evidence in The American Journal of Pathology points to the cytoprotective and proregenerative effects of a neuropeptide in promoting corneal healing after eye injury
2024-01-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Diversity of bioluminescent beetles in Brazilian savanna has declined sharply in 30 years
2024-01-02
At night in the Cerrado, Brazil’s savanna and second-largest biome, larvae of the click beetle Pyrearinus termitilluminans, which live in termite mounds, display green lanterns to capture prey attracted by the bright light.
In more than 30 years of expeditions with his students to Emas National Park and farms around the conservation unit in Goiás state to collect specimens, the phenomenon has never been so rare, said Vadim Viviani, a professor at the Federal University of São Carlos’s Science and Technology for Sustainability Center (CCTS-UFSCar) in Sorocaba, São Paulo state.
“In the 1990s, we ...
Binghamton University professor and Nobel Laureate Stanley Whittingham wins 2023 VinFuture Grand Prize
2024-01-02
Binghamton University, State University of New York Distinguished Professor and Nobel Laureate M. Stanley Whittingham has been chosen as the joint winner of the $3 million 2023 VinFuture Grand Prize in recognition of his contributions to the invention of lithium-ion batteries. The prize recognized how the combination of solar energy and lithium battery storage is overcoming climate change and was recently presented by the Prime Minister of Vietnam.
“I am truly honored to be chosen for this prestigious honor,” said Whittingham. “VinFuture’s efforts to recognize green and sustainable energy is a noble cause, and ...
Deciphering molecular mysteries: new insights into metabolites that control aging and disease
2024-01-02
ITHACA, NY: In a significant advancement in the field of biochemistry, scientists at the Boyce Thompson Institute (BTI) and Cornell University have uncovered new insights into a family of metabolites, acylspermidines, that could change how we understand aging and fight diseases.
The study, recently published in Nature Chemical Biology, presents an unexpected connection between spermidine, a long-known compound present in all living cells, and sirtuins, an enzyme family that regulates many life-essential functions.
Sirtuins ...
Women’s and girls’ sports: more popular than you may think
2024-01-02
COLUMBUS, Ohio – The number of Americans who watch or follow girls’ and women’s sports goes well beyond those who view TV coverage of women’s athletic events, a new study suggests.
In fact, just over half of American adults spent some time watching or following female sports in the past year, the results showed.
U.S. adults spend about one hour a week consuming female sports content, which may seem higher than expected, according to the researchers. Still, it is only a small fraction of Americans’ overall sports consumption.
The study was ...
Calcium channel blockers key to reversing myotonic dystrophy muscle weakness, study finds
2024-01-02
New research has identified the specific biological mechanism behind the muscle dysfunction found in myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1) and further shows that calcium channel blockers can reverse these symptoms in animal models of the disease. The researchers believe this class of drugs, widely used to treat a number of cardiovascular diseases, hold promise as a future treatment for DM1.
“The main finding of our study is that combined calcium and chloride channelopathy is highly deleterious and plays a central role in the function impairment of muscle found in the disease,” said John Lueck, Ph.D., an assistant professor at the University of Rochester Medical Center (URMC) in the Departments ...
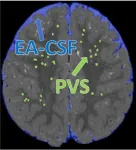
Enlarged spaces in infant brains linked to higher risk of autism, sleep problems
2024-01-02
Throughout the day and night, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pulses through small fluid-filled channels surrounding blood vessels in the brain, called perivascular spaces, to flush out neuroinflammation and other neurological waste. A disruption to this vital process can lead to neurological dysfunction, cognitive decline, or developmental delays.
For the first time, researchers Dea Garic, PhD, and Mark Shen, PhD, both at the UNC School of Medicine’s Department of Psychiatry, discovered that infants with abnormally enlarged perivascular spaces have a 2.2 times greater chance of developing autism ...
Growth hormone influences regulation of anxiety via a specific group of neurons
2024-01-02
Growth hormone (GH) acts on many tissues throughout the body, helping build bones and muscles, among other functions. It is also a powerful anxiolytic. A study conducted by researchers at the University of São Paulo (USP) in Brazil has produced a deeper understanding of the role of GH in mitigating anxiety and, for the first time, identified the population of neurons responsible for modulating the influence of GH on the development of neuropsychiatric disorders involving anxiety, depression and post-traumatic stress. An article on the study is published in the Journal of Neuroscience.
In ...
Influencers’ vulnerabilities: a double-edged sword
2024-01-02
ITHACA, N.Y. – New Cornell University-led research finds that social media platforms and the metrics that reward content creators for revealing their innermost selves to fans open creators up to identity-based harassment.
“Creators share deeply personal – often vulnerable – elements of their lives with followers and the wider public,” said Brooke Erin Duffy, associate professor of communication. “Such disclosures are a key way that influencers build intimacy with audiences and form communities. There’s a pervasive sense that internet users clamor for less polished, less idealized, ...
Designing the ‘perfect’ meal to feed long-term space travelers
2024-01-02
Imagine blasting off on a multiyear voyage to Mars, fueled by a diet of bland, prepackaged meals. As space agencies plan for longer missions, they’re grappling with the challenge of how to best feed people. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Food Science & Technology have designed the optimal “space meal”: a tasty vegetarian salad. They chose fresh ingredients that meet male astronauts’ specialized nutritional needs and can be grown in space.
Astronauts in space burn ...
Perceived time has an actual effect on physical healing
2024-01-02
Perceived time has a significant impact on the actual time it takes to heal physical wounds, according to new research by Harvard psychologists Peter Aungle and Ellen Langer.
Their study, published late last month in Nature Scientific Reports, challenges conventional beliefs about psychological influences on physical health. The findings suggest a broader range of psychological influences than is currently appreciated.
To complete their study, the authors used a standardized procedure to mildly wound volunteer subjects. Perceived time was then manipulated in the lab, with each study participant completing three ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
[Press-News.org] Pioneering study indicates a potential treatment for corneal endothelial disease, reducing the need for corneal transplantsCompelling evidence in The American Journal of Pathology points to the cytoprotective and proregenerative effects of a neuropeptide in promoting corneal healing after eye injury