(Press-News.org) A UC Riverside study to motivate your new year’s resolutions: it demonstrates that high-fat diets affect genes linked not only to obesity, colon cancer and irritable bowels, but also to the immune system, brain function, and potentially COVID-19 risk.
While other studies have examined the effects of a high-fat diet, this one is unusual in its scope. UCR researchers fed mice three different diets over the course of 24 weeks where at least 40% of the calories came from fat. Then, they looked not only at the microbiome, but also at genetic changes in all four parts of the intestines.
One group of mice ate a diet based on saturated fat from coconut oil, another got a monounsaturated, modified soybean oil, a third got an unmodified soybean oil high in polyunsaturated fat. Compared to a low-fat control diet, all three groups experienced concerning changes in gene expression, the process that turns genetic information into a functional product, such as a protein.
“Word on the street is that plant-based diets are better for you, and in many cases that’s true. However, a diet high in fat, even from a plant, is one case where it’s just not true,” said Frances Sladek, a UCR cell biology professor and senior author of the new study.
A new Scientific Reports paper about the study documents the many impacts of high-fat diets. Some of the intestinal changes did not surprise the researchers, such as major changes in genes related to fat metabolism and the composition of gut bacteria. For example, they observed an increase in pathogenic E. coli and a suppression of Bacteroides, which helps protect the body against pathogens.
Other observations were more surprising, such as changes in genes regulating susceptibility to infectious diseases. “We saw pattern recognition genes, ones that recognize infectious bacteria, take a hit. We saw cytokine signaling genes take a hit, which help the body control inflammation,” Sladek said. ‘So, it’s a double whammy. These diets impair immune system genes in the host, and they also create an environment in which harmful gut bacteria can thrive.”
The team’s previous work with soybean oil documents its link to obesity and diabetes, both major risk factors for COVID. This paper now shows that all three high-fat diets increase the expression of ACE2 and other host proteins that are used by COVID spike proteins to enter the body.
Additionally, the team observed that high-fat food increased signs of stem cells in the colon. “You’d think that would be a good thing, but actually they can be precursors to cancer,” Sladek said.
In terms of effects on gene expression, coconut oil showed the greatest number of changes, followed by the unmodified soybean oil. Differences between the two soybean oils suggest that polyunsaturated fatty acids in unmodified soybean oil, primarily linoleic acid, play a role in altering gene expression.
Negative changes to the microbiome in this study were more pronounced in mice fed the soybean oil diet. This was unsurprising, as the same research team previously documented other negative health effects of high soybean oil consumption.
In 2015, the team found that soybean oil induces obesity, diabetes, insulin resistance, and fatty liver in mice. In 2020, the researchers team demonstrated the oil could also affect genes in the brain related to conditions like autism, Alzheimer’s disease, anxiety, and depression.
Interestingly, in their current work they also found the expression of several neurotransmitter genes were changed by the high fat diets, reinforcing the notion of a gut-brain axis that can be impacted by diet.
The researchers have noted that these findings only apply to soybean oil, and not to other soy products, tofu, or soybeans themselves. “There are some really good things about soybeans. But too much of that oil is just not good for you,” said UCR microbiologist Poonamjot Deol, who was co-first author of the current study along with UCR postdoctoral researcher Jose Martinez-Lomeli.
Also, the studies were conducted using mice, and mouse studies do not always translate to the same results in humans. However, humans and mice share 97.5% of their working DNA. Therefore, the findings are concerning, as soybean oil is the most commonly consumed oil in the United States, and is increasingly being used in other countries, including Brazil, China, and India.
By some estimates, Americans tend to get nearly 40% of their calories from fat, which mirrors what the mice were fed in this study. “Some fat is necessary in the diet, perhaps 10 to 15%. Most people though, at least in this country, are getting at least three times the amount that they need,” Deol said.
Readers should not panic about a single meal. It is the long-term high-fat habit that caused the observed changes. Recall that the mice were fed these diets for 24 weeks. “In human terms, that is like starting from childhood and continuing until middle age. One night of indulgence is not what these mice ate. It’s more like a lifetime of the food,” Deol said.
That said, the researchers hope the study will cause people to closely examine their eating habits.
“Some people think, ‘Oh, I’ll just exercise more and be okay. But regularly eating this way could be impacting your immune system and how your brain functions,” Deol said. “You may not be able to just exercise away these effects.”
END
New reasons eating less fat should be one of your resolutions
High fat impairs immune, intestinal, and brain health
2024-01-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Job ads with wide pay ranges can deter applicants
2024-01-03
PULLMAN, Wash. – As more states require employers to list compensation on job ads, a trending strategy to use very wide pay ranges could potentially harm recruitment, according to a Washington State University study.
The study, published in the Journal of Applied Psychology, found that participants in three different experiments were more likely to respond negatively to job ads with very wide pay ranges, viewing those employers as less trustworthy. Prior surveys have found that most people report they would trust organizations that include pay ranges in ...
What makes urine yellow? UMD scientists discover the enzyme responsible
2024-01-03
Researchers at the University of Maryland and National Institutes of Health have identified the microbial enzyme responsible for giving urine its yellow hue, according to a new study published in the journal Nature Microbiology on January 3, 2024.
The discovery of this enzyme, called bilirubin reductase, paves the way for further research into the gut microbiome’s role in ailments like jaundice and inflammatory bowel disease.
“This enzyme discovery finally unravels the mystery behind urine’s yellow color,” said the study’s lead author Brantley Hall, an assistant ...
Non-toxic quantum dots pave the way towards CMOS shortwave infrared image sensors for consumer electronics
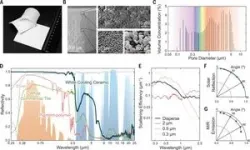
2024-01-03
Invisible to our eyes, shortwave infrared (SWIR) light can enable unprecedented reliability, function and performance in high-volume, computer vision first applications in service robotics, automotive and consumer electronics markets. Image sensors with SWIR sensitivity can operate reliably under adverse conditions such as bright sunlight, fog, haze and smoke. Furthermore, the SWIR range provides eye-safe illumination sources and opens up the possibility of detecting material properties through molecular imaging.
Colloidal quantum ...
Complex, unfamiliar sentences make the brain’s language network work harder
2024-01-03
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- With help from an artificial language network, MIT neuroscientists have discovered what kind of sentences are most likely to fire up the brain’s key language processing centers.
The new study reveals that sentences that are more complex, either because of unusual grammar or unexpected meaning, generate stronger responses in these language processing centers. Sentences that are very straightforward barely engage these regions, and nonsensical sequences of words don’t do much for them either.
For ...
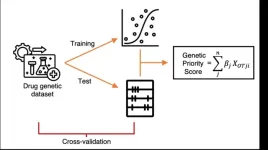
Novel genetic priority score unveiled to enhance target prioritization in drug development
2024-01-03
New York, NY [January 3, 2024]—Driven by the need for a better way to prioritize targets for drug development, the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai has led the development of a novel “genetic priority score” (GPS) that will integrate various types of human genetic data into a single easy-to-interpret score.
The findings were described in the January 3 online issue of Nature Genetics [DOI: 10.1038/s41588-023-01609-2].
Studies have shown that drugs have an increased likelihood of success in clinical trials when ...
Microbial awakening restructures high-latitude food webs as permafrost thaws
2024-01-03
Alaska is on the front lines of climate change, experiencing some of the fastest rates of warming of any place in the world. And when temperatures rise in the state’s interior—a vast high-latitude region spanning 113 million acres—permafrost there not only thaws, releasing significant amounts of its stored carbon back into the atmosphere where it further accelerates rising temperatures, but it decays. This decomposition has the potential to infuse above- and belowground food webs with carbon, which can affect ...
Bacteria load their syringes
2024-01-03
Disease-causing bacteria of the genus Salmonella or Yersinia can use tiny injection apparatuses to inject harmful proteins into host cells, much to the discomfort of the infected person. However, it is not only with a view to controlling disease that researchers are investigating the injection mechanism of these so-called type III secretion systems, also known as "injectisomes".
If the structure and function of the injectisome were fully understood, researchers would be able to hijack it to deliver specific drugs into cells, such as cancer cells. In fact, the structure of the injectisome has already been elucidated. ...
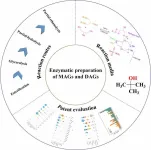
Greener and feasible production: Enzymatic methods for mono- and diacylglycerol synthesis in the food industry
2024-01-03
MAGs, predominantly in 1(3)-MAG form, and DAGs, with 1,3-DAGs as the more stable isomer, are crucial in food, cosmetic, and other industries. While MAGs are vital emulsifiers, comprising 75% of global production, DAGs are known as functional cooking oils that can reduce body fat and serum TAGs. However, their natural concentration in oils is low, prompting extensive research into their chemical and environmentally-friendly enzymatic production.
Recently, a review published in the Grain & Oil Science and Technology journal on 2 November 2023, has shed light on the advancements in enzymatic production methods with special efforts on practical and ...
Re-calibrating the sail plan for Native Hawaiians, Pacific Islanders in ocean sciences
2024-01-03
In Hawaiʻi and across much of Oceania, Pacific Islanders celebrate the connections between their islands and the ocean that surrounds them. “As descendants of the ocean, the dearth of Native Hawaiians and Pacific Islanders (NHPI) in ocean science seems inconsonant,” writes a team of authors that includes University of Hawai‘i (UH) at Mānoa faculty, students, and alumni in an article in a special issue of the journal Oceanography, “Building Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion in the Ocean Sciences. The authors ask, “Where are all our island people in the ...
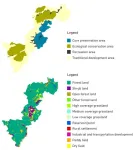
Monetized evaluation of landscape resources of national parks based on the willingness to pay of multiple interest groups
2024-01-03
In China, national parks represent the country’s most unique natural landscapes. Scientific evaluation of landscape resources is significant for preserving the authenticity and integrity of national parks. Taking Qianjiangyuan National Park System Pilot Zone as an example, this research investigated the willingness of internal group (residents and administrative staff) and external group (tourists) to pay for a hypothetical market project based on the pilot zone via Contingent Valuation Method to acquire the monetized value of landscape resources in the national park, and applied Logistic Regression to analyze the influencing factors. The results show ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
[Press-News.org] New reasons eating less fat should be one of your resolutionsHigh fat impairs immune, intestinal, and brain health