(Press-News.org) Researchers at the University of Michigan Health Rogel Cancer Center have identified a mechanism that causes severe gastrointestinal problems with immune-based cancer treatment.
They also found a way to deliver immunotherapy’s cancer-killing impact without the unwelcome side effect.
The findings are published in Science.
“This is a good example of how understanding a mechanism helps you to develop an alternative therapy that’s more beneficial. Once we identified the mechanism causing the colitis, we could then develop ways to overcome this problem and prevent colitis while preserving the anti-tumor effect,” said senior study author Gabriel Nunez, M.D., Paul de Kruif Professor of Pathology at Michigan Medicine.
Immunotherapy has emerged as a promising treatment for several types of cancer. But immune checkpoint inhibitors can also cause severe side effects, including colitis, which is inflammation in the digestive tract.
Colitis can cause severe gastrointestinal discomfort, and some patients will discontinue their cancer treatment because of it.
The problem facing researchers was that while patients were developing colitis, the laboratory mice were not. So researchers couldn’t study what was causing this side effect.
To get past this, the Rogel team, led by first author Bernard C. Lo, Ph.D., created a new mouse model, injecting microbiota from wild-caught mice into the traditional mouse model.
In this model, the mice did develop colitis after administration of antibodies used for tumor immunotherapy. Now, researchers could trace back the mechanism to see what was causing this reaction.
In fact, colitis developed because of the composition of the gut microbiota, which caused immune T cells to be hyper-activated while regulatory T cells that put the brakes on T cell activation were deleted in the gut.
This was happening within a specific domain of the immune checkpoint antibodies.
Researchers then removed that domain, which they found still resulted in a strong anti-tumor response but without inducing colitis.
“Previously, there were some data that suggested the presence of certain bacteria correlated with response to therapy. But it was not proven that microbiota were critical to develop colitis. This work for the first time shows that microbiota are essential to develop colitis from immune checkpoint inhibition,” Nunez said.
To follow up what they saw in mice, researchers reanalyzed previously reported data from studies of human cells from patients treated with immune checkpoint antibodies, which reinforced the role of regulatory T cells in inducing colitis.
The antibody they used to stop the colitis was developed by Takeda Pharmaceuticals.
The Rogel team plans additional studies to further understand the mechanisms causing colitis and seeks clinical partners to move this knowledge to a clinical trial.
Additional authors are Ilona Kryczek, Jiali Yu, Linda Vatan, Roberta Caruso, Masanori Matsumoto, Yosuke Sato, Michael H. Shaw, Naohiro Inohara, Yuying Xie, Yu Leo Lei and Weiping Zou.
Funding for this work is from National Institutes of Health grants R01 DK121504, R01 DK095782, R01 DE026728, R01 DE030691, P30 CA046592; Takeda Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Canadian Institutes of Health, Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation, National Science Foundation grant IOS-2107215.
This work was supported by these Rogel Cancer Center Shared Resources: Single Cell Spatial Analysis, Tissue and Molecular Pathology
Paper cited: “Microbiota-dependent activation of CD4+ T cells induces CTLA-4 blockade-associated colitis via Fc-gamma receptors,” Science. DOI: 10.1126/science.adh8342
END
Researchers identify why cancer immunotherapy can cause colitis
Studies in mice reveal the mechanism that induces this severe side effect and point to a solution that kills the cancer without causing gastrointestinal issues.
2024-01-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
JNM publishes procedure standard/practice guideline for FES PET imaging of breast cancer
2024-01-05
Reston, VA — The Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) and the European Association of Nuclear Medicine (EANM) have issued a new procedure standard/practice guideline for estrogen receptor imaging of breast cancer patients using FES PET. The standard/guideline, published ahead of print in The Journal of Nuclear Medicine, is intended to assist physicians in recommending, performing, interpreting, and reporting the results of 18F-FES PET studies for patients with breast cancer.
More than two million women worldwide are diagnosed with breast cancer ...
Can we fight back against Parkinson’s disease? These research volunteers hope so
2024-01-05
About three years before he retired, David Campbell noticed something weird happening as he typed. Whenever he tried to hit a letter, say “a,” he’d get “aaa,” like the keyboard was jamming or his finger was triple-tapping the key. That wasn’t the only thing that seemed off—his sense of smell was faltering. “Little things,” he says, “that I didn’t think of as being a big deal.”
A couple of weeks after he retired in fall 2020, Campbell learned the little things weren’t ...
After COP28 “insider” climate activists will become increasingly important, study suggests.
2024-01-05
Climate campaigners will increasingly adopt “insider activist” roles, working to change or challenge their organisations from the inside rather than the outside, a new study says.
Research led by the University of Exeter identifies different types of climate activists. As well as “insiders”, there are others who seek to undermine, or even damage, climate-recalcitrant organisations they are members of in the hope of change.
The study says the growing climate backlash against traditional outside climate activism and rise of corporate “greenwashing” means collaborating or ...
Protected areas for elephants work best if they are connected
2024-01-05
PRETORIA, SOUTH AFRICA – Conservation measures have successfully stopped declines in the African savanna elephant population across southern Africa, but the pattern varies locally, according to a new study.
The evidence suggests that the long-term solution to elephant survival requires not only that areas are protected but that they are also connected to allow populations to stabilize naturally, an international research team says.
Their study, published on January 5th in the peer-reviewed journal Science Advances, collected survey estimates and calculated growth rates for ...
Cult mentality: SLU professor makes monumental discovery in Italy
2024-01-05
Douglas Boin, Ph.D., a professor of history at Saint Louis University, made a major announcement at the annual meeting of the Archeological Institute of America, revealing he and his team discovered an ancient Roman temple that adds significant insights into the social change from pagan gods to Christianity within the Roman Empire.
“We found three walls of a monumental structure that evidence suggests belonged to a Roman temple that dates to Constantine's period,” Boin said. “It dates to the fourth century AD and it would ...
Inhalable sensors could enable early lung cancer detection
2024-01-05
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Using a new technology developed at MIT, diagnosing lung cancer could become as easy as inhaling nanoparticle sensors and then taking a urine test that reveals whether a tumor is present.
The new diagnostic is based on nanosensors that can be delivered by an inhaler or a nebulizer. If the sensors encounter cancer-linked proteins in the lungs, they produce a signal that accumulates in the urine, where it can be detected with a simple paper test strip.
This approach could potentially replace or supplement the current gold standard for diagnosing lung cancer, low-dose computed tomography (CT). It ...
A new approach can address antibiotic resistance to Mycobacterium abscessus
2024-01-05
(Memphis, Tenn.—January 5, 2024) Scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital are tackling Mycobacterium abscessus (Mab) antibiotic resistance. This naturally antibiotic-resistant pathogen is becoming more prevalent, highlighting the urgent need for novel therapeutics. To address this, the scientists designed new versions of the drug spectinomycin that overcome efflux, the main mechanism driving resistance. The work was published today in Proceedings of the National Academy of Science.
Mab infections are increasingly found ...
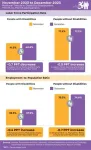
nTIDE December 2023 Jobs Report: People with disabilities maintain strong employment levels through end of year, staying at historic highs
2024-01-05
East Hanover, NJ – January 5, 2023 – Following a historic high in November, slight declines were seen in the employment-to-population ratio and the labor force participation rate in December 2023 for people with and without disabilities. However, numbers still remain near the record levels achieved the previous month, according to today’s National Trends in Disability Employment – semi-monthly update (nTIDE), issued by Kessler Foundation and the University of New Hampshire’s Institute on Disability (UNH-IOD).
Month-to-Month nTIDE Numbers (comparing November 2023 to December 2023)
Based on data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) Jobs ...
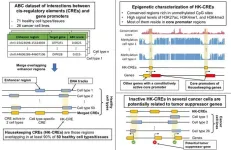
New study reveals crucial 'housekeeping' genetic elements and their potent role to fight cancer
2024-01-05
Technological advancements have enabled scientists to comprehensively explore genetic control elements, unraveling the complexities of gene activation mechanisms in our genetic code. New evidence challenges the simplistic view that cis-regulatory elements (CREs) are mere on/off switches for genes, emphasizing their ability to exhibit complex behaviors, such as the simultaneous enhancement of gene activity and initiation of gene transcription, e.g., simultaneous enhancer and promoter activities. These switches aren't only important for the enhancement ...
Mixed forests protect coastal areas from tsunami impacts better than monoculture forests
2024-01-05
Coastal forests in Japan had predominantly been afforested with black pine (Pinus thunbergii), a shade-tolerant tree species that can withstand dry land ecosystems and harsh coastal environments. This afforestation initiative, dating back to the Edo period (1603~1867), aimed to mitigate the deleterious effects of robust winds and sand blowing. Subsequent to the Great East Japan Earthquake in 2011, interest shifted to the potential protective effects of coastal forests in reducing the destructive power of tsunamis.
The Great East Japan Earthquake tsunami damaged a total of 2,800 hectares (ha; 10,000 square meters) of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The unprecedented transformation in energy: The Third Energy Revolution toward carbon neutrality
Building on the far side: AI analysis suggests sturdier foundation for future lunar bases
Far-field superresolution imaging via k-space superoscillation
10 Years, 70% shift: Wastewater upgrades quietly transform river microbiomes
Why does chronic back pain make everyday sounds feel harsher? Brain imaging study points to a treatable cause
Video messaging effectiveness depends on quality of streaming experience, research shows
Introducing the “bloom” cycle, or why plants are not stupid
The Lancet Oncology: Breast cancer remains the most common cancer among women worldwide, with annual cases expected to reach over 3.5 million by 2050
Improve education and transitional support for autistic people to prevent death by suicide, say experts
GLP-1 drugs like Ozempic could cut risk of major heart complications after heart attack, study finds
Study finds Earth may have twice as many vertebrate species as previously thought
NYU Langone orthopedic surgeons present latest clinical findings and research at AAOS 2026
New journal highlights how artificial intelligence can help solve global environmental crises
Study identifies three diverging global AI pathways shaping the future of technology and governance
Machine learning advances non targeted detection of environmental pollutants
ACP advises all adults 75 or older get a protein subunit RSV vaccine
New study finds earliest evidence of big land predators hunting plant-eaters
Newer groundwater associated with higher risk of Parkinson’s disease
New study identifies growth hormone receptor as possible target to improve lung cancer treatment
Routine helps children adjust to school, but harsh parenting may undo benefits
IEEE honors Pitt’s Fang Peng with medal in power engineering
SwRI and the NPSS Consortium release new version of NPSS® software with improved functionality
Study identifies molecular cause of taste loss after COVID
Accounting for soil saturation enhances atmospheric river flood warnings
The research that got sick veterans treatment
Study finds that on-demand wage access boosts savings and financial engagement for low-wage workers
Antarctica has lost 10 times the size of Greater Los Angeles in ice over 30 years
Scared of spiders? The real horror story is a world without them
New study moves nanomedicine one step closer to better and safer drug delivery
Illinois team tests the costs, benefits of agrivoltaics across the Midwest
[Press-News.org] Researchers identify why cancer immunotherapy can cause colitisStudies in mice reveal the mechanism that induces this severe side effect and point to a solution that kills the cancer without causing gastrointestinal issues.