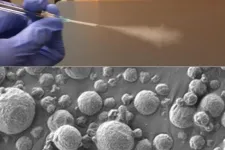
(Press-News.org) CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Using a new technology developed at MIT, diagnosing lung cancer could become as easy as inhaling nanoparticle sensors and then taking a urine test that reveals whether a tumor is present.
The new diagnostic is based on nanosensors that can be delivered by an inhaler or a nebulizer. If the sensors encounter cancer-linked proteins in the lungs, they produce a signal that accumulates in the urine, where it can be detected with a simple paper test strip.
This approach could potentially replace or supplement the current gold standard for diagnosing lung cancer, low-dose computed tomography (CT). It could have an especially significant impact in low- and middle-income countries that don’t have widespread availability of CT scanners, the researchers say.
“Around the world, cancer is going to become more and more prevalent in low- and middle-income countries. The epidemiology of lung cancer globally is that it’s driven by pollution and smoking, so we know that those are settings where accessibility to this kind of technology could have a big impact,” says Sangeeta Bhatia, the John and Dorothy Wilson Professor of Health Sciences and Technology and of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at MIT, and a member of MIT’s Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research and the Institute for Medical Engineering and Science.
Bhatia is the senior author of the paper, which appears today in Science Advances. Qian Zhong, an MIT research scientist, and Edward Tan, a former MIT postdoc, are the lead authors of the study.
Inhalable particles
To help diagnose lung cancer as early as possible, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that heavy smokers over the age of 50 undergo annual CT scans. However, not everyone in this target group receives these scans, and the high false-positive rate of the scans can lead to unnecessary, invasive tests.
Bhatia has spent the last decade developing nanosensors for use in diagnosing cancer and other diseases, and in this study, she and her colleagues explored the possibility of using them as a more accessible alternative to CT screening for lung cancer.
These sensors consist of polymer nanoparticles coated with a reporter, such as a DNA barcode, that is cleaved from the particle when the sensor encounters enzymes called proteases, which are often overactive in tumors. Those reporters eventually accumulate in the urine and are excreted from the body.
Previous versions of the sensors, which targeted other cancer sites such as the liver and ovaries, were designed to be given intravenously. For lung cancer diagnosis, the researchers wanted to create a version that could be inhaled, which could make it easier to deploy in lower resource settings.
“When we developed this technology, our goal was to provide a method that can detect cancer with high specificity and sensitivity, and also lower the threshold for accessibility, so that hopefully we can improve the resource disparity and inequity in early detection of lung cancer,” Zhong says.
To achieve that, the researchers created two formulations of their particles: a solution that can be aerosolized and delivered with a nebulizer, and a dry powder that can be delivered using an inhaler.
Once the particles reach the lungs, they are absorbed into the tissue, where they encounter any proteases that may be present. Human cells can express hundreds of different proteases, and some of them are overactive in tumors, where they help cancer cells to escape their original locations by cutting through proteins of the extracellular matrix. These cancerous proteases cleave DNA barcodes from the sensors, allowing the barcodes to circulate in the bloodstream until they are excreted in the urine.
In the earlier versions of this technology, the researchers used mass spectrometry to analyze the urine sample and detect DNA barcodes. However, mass spectrometry requires equipment that might not be available in low-resource areas, so for this version, the researchers created a lateral flow assay, which allows the barcodes to be detected using a paper test strip.
The researchers designed the strip to detect up to four different DNA barcodes, each of which indicates the presence of a different protease. No pre-treatment or processing of the urine sample is required, and the results can be read about 20 minutes after the sample is obtained.
“We were really pushing this assay to be point-of-care available in a low-resource setting, so the idea was to not do any sample processing, not do any amplification, just to be able to put the sample right on the paper and read it out in 20 minutes,” Bhatia says.
Accurate diagnosis
The researchers tested their diagnostic system in mice that are genetically engineered to develop lung tumors similar to those seen in humans. The sensors were administered 7.5 weeks after the tumors started to form, a time point that would likely correlate with stage 1 or 2 cancer in humans.
In their first set of experiments in the mice, the researchers measured the levels of 20 different sensors designed to detect different proteases. Using a machine learning algorithm to analyze those results, the researchers identified a combination of just four sensors that was predicted to give accurate diagnostic results. They then tested that combination in the mouse model and found that it could accurately detect early-stage lung tumors.
For use in humans, it’s possible that more sensors might be needed to make an accurate diagnosis, but that could be achieved by using multiple paper strips, each of which detects four different DNA barcodes, the researchers say.
The researchers now plan to analyze human biopsy samples to see if the sensor panels they are using would also work to detect human cancers. In the longer term, they hope to perform clinical trials in human patients. A company called Sunbird Bio has already run phase 1 trials on a similar sensor developed by Bhatia’s lab, for use in diagnosing liver cancer and a form of hepatitis known as nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
In parts of the world where there is limited access to CT scanning, this technology could offer a dramatic improvement in lung cancer screening, especially since the results can be obtained during a single visit.
“The idea would be you come in and then you get an answer about whether you need a follow-up test or not, and we could get patients who have early lesions into the system so that they could get curative surgery or lifesaving medicines,” Bhatia says.
###
The research was funded by the Johnson & Johnson Lung Cancer Initiative, the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, the Koch Institute Support (core) Grant from the National Cancer Institute, and the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences.
END
Inhalable sensors could enable early lung cancer detection
The diagnostic, which requires only a simple urine test to read the results, could make lung cancer screening more accessible worldwide
2024-01-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A new approach can address antibiotic resistance to Mycobacterium abscessus
2024-01-05
(Memphis, Tenn.—January 5, 2024) Scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital are tackling Mycobacterium abscessus (Mab) antibiotic resistance. This naturally antibiotic-resistant pathogen is becoming more prevalent, highlighting the urgent need for novel therapeutics. To address this, the scientists designed new versions of the drug spectinomycin that overcome efflux, the main mechanism driving resistance. The work was published today in Proceedings of the National Academy of Science.
Mab infections are increasingly found ...
nTIDE December 2023 Jobs Report: People with disabilities maintain strong employment levels through end of year, staying at historic highs
2024-01-05
East Hanover, NJ – January 5, 2023 – Following a historic high in November, slight declines were seen in the employment-to-population ratio and the labor force participation rate in December 2023 for people with and without disabilities. However, numbers still remain near the record levels achieved the previous month, according to today’s National Trends in Disability Employment – semi-monthly update (nTIDE), issued by Kessler Foundation and the University of New Hampshire’s Institute on Disability (UNH-IOD).
Month-to-Month nTIDE Numbers (comparing November 2023 to December 2023)
Based on data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) Jobs ...
New study reveals crucial 'housekeeping' genetic elements and their potent role to fight cancer
2024-01-05
Technological advancements have enabled scientists to comprehensively explore genetic control elements, unraveling the complexities of gene activation mechanisms in our genetic code. New evidence challenges the simplistic view that cis-regulatory elements (CREs) are mere on/off switches for genes, emphasizing their ability to exhibit complex behaviors, such as the simultaneous enhancement of gene activity and initiation of gene transcription, e.g., simultaneous enhancer and promoter activities. These switches aren't only important for the enhancement ...
Mixed forests protect coastal areas from tsunami impacts better than monoculture forests
2024-01-05
Coastal forests in Japan had predominantly been afforested with black pine (Pinus thunbergii), a shade-tolerant tree species that can withstand dry land ecosystems and harsh coastal environments. This afforestation initiative, dating back to the Edo period (1603~1867), aimed to mitigate the deleterious effects of robust winds and sand blowing. Subsequent to the Great East Japan Earthquake in 2011, interest shifted to the potential protective effects of coastal forests in reducing the destructive power of tsunamis.
The Great East Japan Earthquake tsunami damaged a total of 2,800 hectares (ha; 10,000 square meters) of ...
IDOR participated in a study evaluating selpercatinib for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer
2024-01-05
D'Or Institute for Research and Education (IDOR) played an important role in the phase III LIBRETTO-431 multicenter study, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of selpercatinib compared to control treatment, which consisted of platinum-based chemotherapy associated or not with pembrolizumab (immune checkpoint inhibitor) in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The research was published in the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM), one of the most important scientific publications in the medical field, and included Dr. Milena Perez Mak, IDOR researcher and clinical oncologist at ...
Novel compound protects against infection by virus that causes COVID-19, preliminary studies show
2024-01-05
Compounds that obstruct the "landing gear" of a range of harmful viruses can successfully protect against infection by the virus that causes COVID-19, a study published today and led by Dana-Farber Cancer Institute scientists shows. Based on the findings, researchers have launched a human clinical trial of one such compound made by chemically stabilizing a key coronavirus peptide.
If the compound, called a stapled lipopeptide, proves effective as a nasal spray in the trial, it could be the basis for a new drug modality to prevent or treat COVID-19, say the authors of the study, posted online today in the journal Nature ...
Speech Accessibility Project begins recruiting people with ALS
2024-01-05
The Speech Accessibility Project has expanded its recruitment and is inviting U.S. and Puerto Rican adults living with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis to participate.
Those interested in participating can sign up online.
Funded by Big Tech companies Amazon, Apple, Google, Meta, and Microsoft, the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign aims to train voice recognition technologies to understand people with diverse speech patterns and disabilities.
The project began recruiting people with Parkinson’s disease last ...
UofL study shows nicotine in e-cigarettes may not be harmless, as some claim
2024-01-05
With the start of a new year, smokers and vapers may have resolved to quit or cut back on the habit to improve their health. They may want to use caution, however, if their strategy involves switching from cigarettes to e-cigarettes, considered by some to be a less harmful alternative.
A new study from the University of Louisville shows the nicotine in certain types of e-cigarettes may be more harmful than others, increasing risk for irregular heartbeat, or heart arrhythmias.
A popular claim is that nicotine in ...
Maternal diabetes and overweight and congenital heart defects in offspring
2024-01-05
About The Study: This study of 620,000 children found that maternal type 1 diabetes was associated with increased risk for most types of congenital heart defects in offspring, while obesity and overweight were associated with increased risk for complex defects and outflow tract obstruction and decreased risk for ventricular septal defects. These different risk profiles of type 1 diabetes and overweight and obesity may suggest distinct underlying teratogenic mechanisms.
Authors: Riitta Turunen, M.D., Ph.D., and Emmi Helle, M.D., ...
Evaluation of changes in prices and purchases following implementation of sugar-sweetened beverage taxes across the US
2024-01-05
About The Study: Sugar-sweetened beverage (SSB) taxes in Boulder, Colorado; Philadelphia, Oakland, San Francisco, and Seattle led to substantial, consistent declines in SSB purchases following price increases associated with those taxes. Scaling SSB taxes nationally could yield substantial public health benefits.
Authors: Scott Kaplan, Ph.D., of the U.S. Naval Academy in Annapolis, Maryland, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
[Press-News.org] Inhalable sensors could enable early lung cancer detectionThe diagnostic, which requires only a simple urine test to read the results, could make lung cancer screening more accessible worldwide