(Press-News.org) With the start of a new year, smokers and vapers may have resolved to quit or cut back on the habit to improve their health. They may want to use caution, however, if their strategy involves switching from cigarettes to e-cigarettes, considered by some to be a less harmful alternative.
A new study from the University of Louisville shows the nicotine in certain types of e-cigarettes may be more harmful than others, increasing risk for irregular heartbeat, or heart arrhythmias.
A popular claim is that nicotine in e-cigarettes is relatively harmless, whereas additives and combustion products largely account for the harms of traditional cigarettes. The UofL research, which tested the effects of e-cigarettes with various types and doses of nicotine in animal models, showed that the nicotine form contained in pod-based e-cigarettes, nicotine salts, led to heart arrhythmias, particularly at higher doses.
In the study, published in Nicotine and Tobacco Research, researchers compared heart rate and heart rate variability in mice exposed to vape aerosols containing different types of nicotine. The aerosols contained either freebase nicotine, used in older types of e-cigarettes; nicotine salts, used in Juul and other pod-based e-cigarettes; or racemic freebase nicotine, simulating the recently popularized synthetic nicotine; and their effects were compared to nicotine-free e-cigarette aerosols or air. In addition, the research team delivered increasing concentrations of the nicotine over time, from 1% to 2.5% to 5%.
The nicotine salts induced cardiac arrhythmias more potently than freebase nicotine, and the cardiac arrhythmias increased with the higher concentrations of nicotine.
“This suggests the nicotine is harmful to the heart and counters popular claims that the nicotine itself is harmless,” said Alex Carll, assistant professor in UofL’s Department of Physiology, who led the study. “Our findings provide new evidence that nicotine type and concentration modify the adverse cardiovascular effects of e-cigarette aerosols, which may have important regulatory implications.”
The study also revealed that the higher levels of nicotine salts increased sympathetic nervous system activity, also known as the fight-or-flight response, by stimulating the same receptor that is inhibited by beta blockers, heart medications which are prescribed to treat cardiac arrhythmias. In the autonomic nervous system, sympathetic dominance increases the fight-or-flight response in bodily functions, including heart rate.
“The nicotine in e-cigarettes causes irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias) in a dose-dependent manner by stimulating the very receptor that many heart medications are designed to inhibit,” Carll said.
The findings conclude that inhalation of e-cig aerosols from nicotine-salt-containing e-liquids could increase cardiovascular risks by inducing sympathetic dominance and cardiac arrhythmias.
This work is part of a growing body of research on the potential toxicity and health impacts of e-cigarettes reported by the American Heart Association Tobacco Regulation and Addiction Center, for which UofL serves as the flagship institute. The team’s previous research found that exposure to e-cigarette aerosols containing certain flavors or solvent vehicles caused ventricular arrhythmias and other conduction irregularities in the heart, even without nicotine, leading Carll to speculate that the arrhythmias may not be the result of the nicotine alone, but also by the flavors and solvents included in the e-cigarettes.
The researchers concluded that, if these results are confirmed in humans, regulating nicotine salts through minimum pH standards or limits on acid additives in e-liquids may mitigate the public health risks of vaping.
Even without regulatory changes, however, the research suggests that users may reduce potential harm by opting for e-cigarettes with freebase nicotine instead of nicotine salts or using e-cigarettes with a lower nicotine content.
END
UofL study shows nicotine in e-cigarettes may not be harmless, as some claim
Pod-based e-cigarettes with higher nicotine more likely to cause irregular heartbeat
2024-01-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Maternal diabetes and overweight and congenital heart defects in offspring
2024-01-05
About The Study: This study of 620,000 children found that maternal type 1 diabetes was associated with increased risk for most types of congenital heart defects in offspring, while obesity and overweight were associated with increased risk for complex defects and outflow tract obstruction and decreased risk for ventricular septal defects. These different risk profiles of type 1 diabetes and overweight and obesity may suggest distinct underlying teratogenic mechanisms.
Authors: Riitta Turunen, M.D., Ph.D., and Emmi Helle, M.D., ...
Evaluation of changes in prices and purchases following implementation of sugar-sweetened beverage taxes across the US
2024-01-05
About The Study: Sugar-sweetened beverage (SSB) taxes in Boulder, Colorado; Philadelphia, Oakland, San Francisco, and Seattle led to substantial, consistent declines in SSB purchases following price increases associated with those taxes. Scaling SSB taxes nationally could yield substantial public health benefits.
Authors: Scott Kaplan, Ph.D., of the U.S. Naval Academy in Annapolis, Maryland, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
The evolution of photosynthesis better documented thanks to the discovery of the oldest thylakoids in fossil cyanobacteria
2024-01-05
Researchers at the University of Liège (ULiège) have identified microstructures in fossil cells that are 1.75 billion years old. These structures, called thylakoid membranes, are the oldest ever discovered. They push back the fossil record of thylakoids by 1.2 billion years and provide new information on the evolution of cyanobacteria which played a crucial role in the accumulation of oxygen on the early Earth. This major discovery is presented in the journal Nature.
Catherine Demoulin, Yannick Lara, Alexandre Lambion and Emmanuelle Javaux from the Early Life Traces & Evolution laboratory of the Astrobiology Research ...
Hypertension's hidden hand: pressure-driven foam cell formation revealed as key driver of arterial disease, paving the way for new therapies
2024-01-05
A new study in Advanced Science unlocks the secrets of how high blood pressure (hypertension) fuels the progression of arterial disease. Led by Professor Thomas Iskratsch, Professor of Cardiovascular Mechanobiology & Bioengineering at Queen Mary University of London, the research team exposes a novel mechanism by which elevated pressure transforms muscle cells in the arterial wall into "foam cells" – the building blocks of plaque buildup that cripples arteries.
The study focuses on vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs), the workhorses responsible for maintaining blood vessel tone and flow. Under ...
NRL researchers receive Defense Manufacturing Technology Achievement Award
2024-01-05
WASHINGTON – U.S. Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) researchers, Kevin Cronin and Drew Rodgers, receive Technology Achievement Award for Lightweight Hydrogen Fuel Cells for Unmanned Aerial Systems (UAS) research efforts at Defense Manufacturing Conference held in Nashville, Tenn., Dec. 11, 2023.
The Department of Defense (DOD) has a critical need for increased power and endurance for persistent Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance (ISR) and transmission of radio frequency (RF) sources for communications and targeting.
“It ...
Applications open for School of Advanced Science on Technology and Innovation Strategies and Policies for Economic Development
2024-01-05
The São Paulo Advanced School on Technology & Innovation Strategies and Policies for Economic Development will be held from June 24 to July 05, 2024, at the University of Campinas (UNICAMP) in São Paulo state, Brazil.
Reporters are invited to register for the scientific sessions and short courses, which will present state-of-art science and results of new research.
The School provides an opportunity to learn about and debate recent developments in the economics of technological change and in science, technology and innovation (ST&I) policy studies. The programme comprises numerous seminars, intensive courses, and roundtable discussions focusing ...
Ancestors of primates lived in pairs
2024-01-05
A study carried out by CNRS1 scientists working with an international team has revealed that around 70 million years ago, when dinosaurs existed, the ancestors of primates most commonly lived in pairs. Only 15% of them opted for a solitary lifestyle. This discovery — that our ancestors adopted variable forms of social organization — challenges the hitherto commonly accepted hypothesis that at the time of dinosaurs, the ancestors of primates lived alone, and that pair living evolved much later. Most likely, pair living offered significant benefits, such as easier reproduction and reduced costs of thermoregulation by huddling in pairs.
While several studies have already been conducted ...
Mysterious missing component in the clouds of Venus revealed
2024-01-05
What are the clouds of Venus made of? Scientists know it’s mainly made of sulfuric acid droplets, with some water, chlorine, and iron. Their concentrations vary with height in the thick and hostile Venusian atmosphere. But until now they have been unable to identify the missing component that would explain the clouds’ patches and streaks, only visible in the UV range.
In a new study published in Science Advances, researchers from the University of Cambridge synthesised iron-bearing sulfate minerals that are stable under the harsh chemical conditions in the Venusian clouds. Spectroscopic analysis revealed that a combination of two minerals, rhomboclase and acid ferric ...
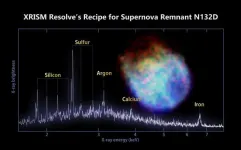
NASA/JAXA XRISM mission reveals its first look at X-ray cosmos
2024-01-05
The Japan-led XRISM (X-ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission) observatory has released a first look at the unprecedented data it will collect when science operations begin later this year.
The satellite’s science team released a snapshot of a cluster of hundreds of galaxies and a spectrum of stellar wreckage in a neighboring galaxy, which gives scientists a detailed look at its chemical makeup.
“XRISM will provide the international science community with a new glimpse of the hidden X-ray sky,” said Richard Kelley, the ...
Hainan's quest for pristine air: Charting a course to global air quality leadership by 2035
2024-01-05
Air pollution significantly impacts human health, with Hainan Province in China aiming to achieve world-leading ambient air quality by 2035, despite already having relatively good air quality in China. The existing Ambient Air Quality Standards (AAQS) offer insufficient guidance for further enhancing air quality in Hainan, which stands at the forefront of China's environmental protection efforts. Consequently, it is imperative to develop Hainan's local AAQS. This initiative, responding to WHO's strengthened guidelines, aims to address unique regional challenges in air quality ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Yale study challenges notion that aging means decline, finds many older adults improve over time
Korean researchers enable early detection of brain disorders with a single drop of saliva!
Swipe right, but safer
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
Low-intensity treadmill exercise preconditioning mitigates post-stroke injury in mouse models
How moss helped solve a grave-robbing mystery
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
GLP-1 medications get at the heart of addiction: study
Global trauma study highlights shared learning as interest in whole blood resurges
Almost a third of Gen Z men agree a wife should obey her husband
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
NYCST announces Round 2 Awards for space technology projects
How the Dobbs decision and abortion restrictions changed where medical students apply to residency programs
Microwave frying can help lower oil content for healthier French fries
In MS, wearable sensors may help identify people at risk of worsening disability
Study: Football associated with nearly one in five brain injuries in youth sports
Machine-learning immune-system analysis study may hold clues to personalized medicine
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
[Press-News.org] UofL study shows nicotine in e-cigarettes may not be harmless, as some claimPod-based e-cigarettes with higher nicotine more likely to cause irregular heartbeat