(Press-News.org) The São Paulo Advanced School on Technology & Innovation Strategies and Policies for Economic Development will be held from June 24 to July 05, 2024, at the University of Campinas (UNICAMP) in São Paulo state, Brazil.
Reporters are invited to register for the scientific sessions and short courses, which will present state-of-art science and results of new research.
The School provides an opportunity to learn about and debate recent developments in the economics of technological change and in science, technology and innovation (ST&I) policy studies. The programme comprises numerous seminars, intensive courses, and roundtable discussions focusing on the following topics: Economic catching-up and innovation; Innovation in Global Value Chains; Universities and regional economic development; Trade and industrial policy; and Technology Sovereignty.
The School will bring together a roster of highly regarded researchers in all these areas to participate as speakers – the up-to-date list of confirmed speakers includes Ron Boschma (Utrecht University, Netherlands), Robert Guttmann (Hofstra University, USA), William Maloney (World Bank), Roberta Rabellotti (Università di Pavia, Italy), Nicholas Vonortas (The George Washington University, USA), and Zhu Jiejin (Fudan University, China), among others.
As part of the São Paulo Advanced School on Technology & Innovation Strategies and Policies for Economic Development, UNICAMP’s Institute of Economics – which co-organizes the School in collaboration with the Institute of Geosciences (IG-UNICAMP) – will also host the 5th UNICAMP International School on Development Challenges, the IV BRICS Network University International School and the 3rd BRICS Postgraduate Forum.
How to apply and who may apply
The School is aimed at post-graduate students (doctoral and advanced masters degree candidates) as well as early career researchers, including post-doctoral researchers. Participants can expect to engage in technical visits and also networking with leading university faculty and fellow post-doctoral researchers and postgraduate degree candidates from around the world.
The São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) is supporting the event (https://bv.fapesp.br/en/auxilios/110565) through its São Paulo School of Advanced Science Program (SPSAS http://www.espca.fapesp.br/home/). Successful candidates must have a strong background in the areas covered by the School, as well as a good working knowledge of English and availability to attend the entire length of the programme.
Applications must be received by January 26, 2024. There is no registration fee and those accepted will have coverage of accommodation, food and transportation expenses for participants not resident in Campinas. The number of vacancies is 100 (50 grantees from all states of Brazil and 50 international grantees).
END
Applications open for School of Advanced Science on Technology and Innovation Strategies and Policies for Economic Development
The school will provide a set of intensive courses for postgraduate students and early-career researchers on the recent developments in the economics of technological change and in ST&I policy studies. Registrations are due on January 26, 2024
2024-01-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Ancestors of primates lived in pairs
2024-01-05
A study carried out by CNRS1 scientists working with an international team has revealed that around 70 million years ago, when dinosaurs existed, the ancestors of primates most commonly lived in pairs. Only 15% of them opted for a solitary lifestyle. This discovery — that our ancestors adopted variable forms of social organization — challenges the hitherto commonly accepted hypothesis that at the time of dinosaurs, the ancestors of primates lived alone, and that pair living evolved much later. Most likely, pair living offered significant benefits, such as easier reproduction and reduced costs of thermoregulation by huddling in pairs.
While several studies have already been conducted ...
Mysterious missing component in the clouds of Venus revealed
2024-01-05
What are the clouds of Venus made of? Scientists know it’s mainly made of sulfuric acid droplets, with some water, chlorine, and iron. Their concentrations vary with height in the thick and hostile Venusian atmosphere. But until now they have been unable to identify the missing component that would explain the clouds’ patches and streaks, only visible in the UV range.
In a new study published in Science Advances, researchers from the University of Cambridge synthesised iron-bearing sulfate minerals that are stable under the harsh chemical conditions in the Venusian clouds. Spectroscopic analysis revealed that a combination of two minerals, rhomboclase and acid ferric ...
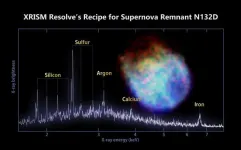
NASA/JAXA XRISM mission reveals its first look at X-ray cosmos
2024-01-05
The Japan-led XRISM (X-ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission) observatory has released a first look at the unprecedented data it will collect when science operations begin later this year.
The satellite’s science team released a snapshot of a cluster of hundreds of galaxies and a spectrum of stellar wreckage in a neighboring galaxy, which gives scientists a detailed look at its chemical makeup.
“XRISM will provide the international science community with a new glimpse of the hidden X-ray sky,” said Richard Kelley, the ...
Hainan's quest for pristine air: Charting a course to global air quality leadership by 2035
2024-01-05
Air pollution significantly impacts human health, with Hainan Province in China aiming to achieve world-leading ambient air quality by 2035, despite already having relatively good air quality in China. The existing Ambient Air Quality Standards (AAQS) offer insufficient guidance for further enhancing air quality in Hainan, which stands at the forefront of China's environmental protection efforts. Consequently, it is imperative to develop Hainan's local AAQS. This initiative, responding to WHO's strengthened guidelines, aims to address unique regional challenges in air quality ...
Asbestos: the size and shape of inhaled nanofibers could be exclusively responsible for the development of pulmonary fibrosis
2024-01-05
The pathogenic potential of inhaling the inert fibrous nanomaterials used in thermal insulation (such as asbestos or fibreglass) is actually connected not to their chemical composition, but instead to their geometrical characteristics and size. This was revealed by a study, published on 3 January 2024 in the journal Nature Nanotechnology, conducted on glass nanofibers by a French-Chinese team including a CNRS chemist.1
The reason for this is the inability of the macrophages2 naturally present in pulmonary alveolar tissue to eliminate foreign bodies that are too large. The study was initially conducted in vitro with electrochemical nanosensors, and revealed that when confronted ...
Monitoring the well-being of reservoir water through an uncrewed surface vehicle
2024-01-05
In a recent tragic incident, approximately 100 elephants in Africa perished due to inadequate access to water. The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) issues a warning that around 2.5 billion people worldwide could face water scarcity by 2025. In the face of water shortages affecting not only human society but also the entire ecological community due to the climate crisis, it becomes crucial to adopt comprehensive measures for managing water quality and quantity to avert such pressing challenges.
A research team led by Professor Jonghun Kam and PhD candidate Kwang-Hun Lee from the Division of Environmental Science and ...
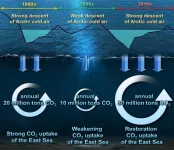
Arctic cold snap transforms into a blessing
2024-01-05
The recent cold spell has plunged the nation into a deep freeze, resulting in the closure of 247 national parks, the cancellation of 14 domestic flights, and the scrapping of 107 cruise ship voyages. While the cold snap brought relief by significantly reducing the prevalence of particulate matter obscuring our surroundings, a recent study indicates that, besides diminishing particulate matter, it is significantly contributing to the heightened uptake of carbon dioxide by the East Sea.
According to research conducted by a team of researchers ...
Feathers from deceased birds help scientists understand new threat to avian populations
2024-01-05
As concerns over the world’s declining bird population mount, animal ecologists developed an analytical approach to better understand one of the latest threats to feathered creatures: the rise of wind and solar energy facilities.
“Bird mortality has become an unintended consequence of renewable energy development,” said Hannah Vander Zanden, an assistant professor of biology at the University of Florida. “If we want to minimize or even offset these fatalities, especially for vulnerable populations, we need to identify the geographic origin of affected birds. In other words, are the dead birds local or are they coming ...
Using berry phase monopole engineering for high-temperature spintronic devices
2024-01-05
Spintronic devices are electronic devices that utilize the spin of electrons (an intrinsic form of angular momentum possessed by the electron) to achieve high-speed processing and low-cost data storage. In this regard, spin-transfer torque is a key phenomenon that enables ultrafast and low-power spintronic devices. Recently, however, spin-orbit torque (SOT) has emerged as a promising alternative to spin-transfer torque.
Many studies have investigated the origin of SOT, showing that in non-magnetic materials, a phenomenon called the spin Hall effect (SHE) is key to achieving SOT. In these materials, the existence of a “Dirac band” ...
Study shows weed makes workouts more fun, but it's no performance enhancer
2024-01-05
A bit of weed before a workout can boost motivation and make exercise more enjoyable. But if performance is the goal, it may be best to skip that joint.
That’s the takeaway of the first ever study to examine how legal, commercially available cannabis shapes how exercise feels.
The study of 42 runners, published Dec. 26 in the journal Sports Medicine, comes almost exactly 10 years after Colorado became the first state to commence legal sales of recreational marijuana, at a time when cannabis-users increasingly report mixing it with workouts.
“The bottom-line finding is that cannabis before exercise seems ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Applications open for School of Advanced Science on Technology and Innovation Strategies and Policies for Economic DevelopmentThe school will provide a set of intensive courses for postgraduate students and early-career researchers on the recent developments in the economics of technological change and in ST&I policy studies. Registrations are due on January 26, 2024