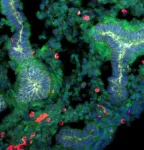
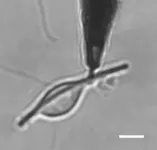
Asbestos: the size and shape of inhaled nanofibers could be exclusively responsible for the development of pulmonary fibrosis
2024-01-05
(Press-News.org)
The pathogenic potential of inhaling the inert fibrous nanomaterials used in thermal insulation (such as asbestos or fibreglass) is actually connected not to their chemical composition, but instead to their geometrical characteristics and size. This was revealed by a study, published on 3 January 2024 in the journal Nature Nanotechnology, conducted on glass nanofibers by a French-Chinese team including a CNRS chemist.1
The reason for this is the inability of the macrophages2 naturally present in pulmonary alveolar tissue to eliminate foreign bodies that are too large. The study was initially conducted in vitro with electrochemical nanosensors, and revealed that when confronted with inert nanofibers over 15 microns in length,3 the cells are unable to distend enough to entirely encapsulate them within their “digestive” vesicle. This results in leaked secretions that are very harmful for the alveolar walls, which this study detected, characterised, and quantified for the first time.4 An experiment on rats subsequently showed that regular unprotected inhalation of similar inert fibrous nanometerials, whatever they may be, causes repeated pulmonary lesions that can eventually lead to the development of fibroma.
This discovery poses a challenge for the use of inert nanofibre felts in construction, which had heretofore been deemed to be less harmful than the asbestos it replaced, but that in reality could present the same health risks for those handling it.
Notes :
1 From the Selective Activation Processes via Uni-Electronic or Radiative Energy Transfer Laboratory (CNRS/ École normale supérieure – PSL/Sorbonne Université), in collaboration with Wuhan University.
2 “Big eater” cells belonging to groups of white blood cells whose primary role is to eliminate cell debris and pathogenic biological agents throughout the body.
3 Or 0.015mm, a micron measuring 10-3 mm.
4 The ROS and RNS species (species reactive to oxygen and nitrogen) secreted by macrophages are known for attacking the bioorganic components of healthy cells, and cause inflammation and mutations that are often cancerous. While the phenomenon of “frustrated phagocytosis” had already been observed, its role in the pathogenesis of the concerned diseases had not yet been clearly established.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-01-05
In a recent tragic incident, approximately 100 elephants in Africa perished due to inadequate access to water. The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) issues a warning that around 2.5 billion people worldwide could face water scarcity by 2025. In the face of water shortages affecting not only human society but also the entire ecological community due to the climate crisis, it becomes crucial to adopt comprehensive measures for managing water quality and quantity to avert such pressing challenges.
A research team led by Professor Jonghun Kam and PhD candidate Kwang-Hun Lee from the Division of Environmental Science and ...
2024-01-05
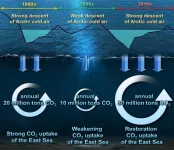
The recent cold spell has plunged the nation into a deep freeze, resulting in the closure of 247 national parks, the cancellation of 14 domestic flights, and the scrapping of 107 cruise ship voyages. While the cold snap brought relief by significantly reducing the prevalence of particulate matter obscuring our surroundings, a recent study indicates that, besides diminishing particulate matter, it is significantly contributing to the heightened uptake of carbon dioxide by the East Sea.
According to research conducted by a team of researchers ...
2024-01-05
As concerns over the world’s declining bird population mount, animal ecologists developed an analytical approach to better understand one of the latest threats to feathered creatures: the rise of wind and solar energy facilities.
“Bird mortality has become an unintended consequence of renewable energy development,” said Hannah Vander Zanden, an assistant professor of biology at the University of Florida. “If we want to minimize or even offset these fatalities, especially for vulnerable populations, we need to identify the geographic origin of affected birds. In other words, are the dead birds local or are they coming ...
2024-01-05
Spintronic devices are electronic devices that utilize the spin of electrons (an intrinsic form of angular momentum possessed by the electron) to achieve high-speed processing and low-cost data storage. In this regard, spin-transfer torque is a key phenomenon that enables ultrafast and low-power spintronic devices. Recently, however, spin-orbit torque (SOT) has emerged as a promising alternative to spin-transfer torque.
Many studies have investigated the origin of SOT, showing that in non-magnetic materials, a phenomenon called the spin Hall effect (SHE) is key to achieving SOT. In these materials, the existence of a “Dirac band” ...
2024-01-05
A bit of weed before a workout can boost motivation and make exercise more enjoyable. But if performance is the goal, it may be best to skip that joint.
That’s the takeaway of the first ever study to examine how legal, commercially available cannabis shapes how exercise feels.
The study of 42 runners, published Dec. 26 in the journal Sports Medicine, comes almost exactly 10 years after Colorado became the first state to commence legal sales of recreational marijuana, at a time when cannabis-users increasingly report mixing it with workouts.
“The bottom-line finding is that cannabis before exercise seems ...
2024-01-05
For military veterans, many of the deepest wounds of war are invisible: Traumatic brain injuries resulting from head trauma or blast explosions are a leading cause of post-traumatic stress disorder, anxiety, depression and suicide among veterans. Few treatments have been effective at diminishing the long-term effects of TBI, leaving many veterans feeling hopeless.
Now, Stanford researchers have discovered that the plant-based psychoactive drug ibogaine, when combined with magnesium to protect the heart, safely and effectively reduces PTSD, anxiety and depression and improves functioning in veterans with TBI. Their new study, to be published ...
2024-01-05
In a scientific breakthrough that aids our understanding of the internal wiring of immune cells, researchers at Monash University in Australia have cracked the code behind IKAROS, an essential protein for immune cell development and protection against pathogens and cancer.
This disruptive research, led by the eminent Professor Nicholas Huntington of Monash University’s Biomedicine Discovery Institute, is poised to reshape our comprehension of gene control networks and its impact on everything from eye colour to cancer susceptibility and design of novel ...
2024-01-05
Ikoma, Japan – Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the third leading cause of death worldwide. It is marked by lung damage that is lasting and incurable, leaving lung transplantation as the only viable treatment option. Unfortunately, finding suitable lung donors is difficult. To compensate for this shortage of donors, regenerative medicine is making strides in developing lungs from pluripotent stem cells (PSCs), using interspecies animal models.
Through a biological technique known as blastocyst complementation, PSCs, and embryonic ...
2024-01-05
A new study led by researchers from the University of Helsinki, along with colleagues at the Massachusetts General Hospital and Broad Institute of Harvard and MIT, provides significant breakthroughs in our understanding of the genetics behind gestational diabetes.
Gestational diabetes is a common pregnancy disorder annually affecting more than 16 million pregnancies worldwide, with substantial health implications for both mothers and their children. It is characterised by elevated blood sugar levels in pregnant women who did not have diabetes before becoming pregnant.
Despite the fact that gestational diabetes constitutes a major global health problem, there is remarkably ...
2024-01-05
EMBARGO: 05 January 2024 at 05:00 (US Eastern Time)
Freezing is one of the most common and debilitating symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, a neurodegenerative disorder that affects more than 9 million people worldwide. When individuals with Parkinson’s disease freeze, they suddenly lose the ability to move their feet, often mid-stride, resulting in a series of staccato stutter steps that get shorter until the person stops altogether. These episodes are one of the biggest contributors to falls among people living with Parkinson’s disease.
Today, freezing is treated with a range of pharmacological, surgical or behavioral ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Asbestos: the size and shape of inhaled nanofibers could be exclusively responsible for the development of pulmonary fibrosis