Advancing the generation of in-vivo chimeric lungs in mice using rat-derived stem cells
Researchers from Japan explore the conditions needed for organ regeneration and overcoming species-specific barriers to create functional organs in interspecies chimeric animals
2024-01-05
(Press-News.org)
Ikoma, Japan – Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the third leading cause of death worldwide. It is marked by lung damage that is lasting and incurable, leaving lung transplantation as the only viable treatment option. Unfortunately, finding suitable lung donors is difficult. To compensate for this shortage of donors, regenerative medicine is making strides in developing lungs from pluripotent stem cells (PSCs), using interspecies animal models.
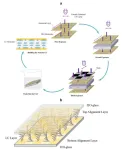
Through a biological technique known as blastocyst complementation, PSCs, and embryonic stem cells (ESCs) from one species can be injected into blastocysts of a different organ-deficient species, creating interspecies chimeric animals. This technique has enabled successful regeneration of the pancreas, heart, and kidney in rat-mouse chimeras. However, functional lung formation has still not been achieved successfully, warranting further research into the viable conditions required to generate PSC-derived organs.
Now, scientists from Nara Institute of Science and Technology (NAIST), Japan have used the reverse-blastocyst complementation (rBC) method to understand the conditions required to form lungs in rat-mouse chimeric models. In addition, they used the tetraploid-based organ complementation (TOC) method to successfully create a rat-derived lung in their mouse model. The study, published in Development, was led by Shunsuke Yuri and Ayako Isotani from NAIST.
The fibroblast growth factor 10 (Fgf10) and its interaction with the Fgf receptor 2 isoform IIIb (Fgfr2b) in the lungs are crucial for lung development. In this study, the rBC method involved injecting mutant ESCs which fail to show lung formation into wild-type (WT) embryos. This method allows for efficient detection of mutant PSCs in the recipient tissue, aiding the determination of the conditions necessary for successful lung formation in the organ-deficient animal.
The research team also found that WT ESCs provide uniform contributions across target and non-target organs in the chimeras. This helped ascertain that a certain number of WT or normal cells are required to overcome the lung development failure in Fgf10-deficient or Fgfr2b-deficient animals.
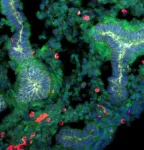
With this knowledge, they successfully produced rat-derived lungs in the Fgfr2b-deficient mouse embryos with the TOC method, without needing to produce a mutant mouse line. “Interestingly, we found that the rat epithelial cells conserved intrinsic species-specific timing in the interspecies model, resulting in an underdeveloped lung,” notes Yuri. Consequently, these lungs remained nonfunctional post-birth.
The findings of this study clearly identify the factors required and barriers to overcome for successful generation of functional lungs in rat-mouse interspecies chimeras. Speaking of the significance of these findings, Yuri concludes, “We believe that our study makes an important contribution to the literature by presenting a faster and more efficient method of exploring blastocyst complementation. These novel results can significantly advance the progress toward developing in-vivo chimeric lungs for the purpose of transplantation, which could transform the practical application of regenerative medicine.”
###
Resource
Title: Generation of rat-derived lung epithelial cells in Fgfr2b-deficient mice retains species-specific development
Authors: Shunsuke Yuri, Yuki Murase, Ayako Isotani
Journal: Development
DOI: 10.1242/dev.202081
More information about the Organ Developmental Engineering Lab can be found at the following website: https://bsw3.naist.jp/eng/courses/courses214.html
About Nara Institute of Science and Technology (NAIST)
Established in 1991, Nara Institute of Science and Technology (NAIST) is a national university located in Kansai Science City, Japan. In 2018, NAIST underwent an organizational transformation to promote and continue interdisciplinary research in the fields of biological sciences, materials science, and information science. Known as one of the most prestigious research institutions in Japan, NAIST lays a strong emphasis on integrated research and collaborative co-creation with diverse stakeholders. NAIST envisions conducting cutting-edge research in frontier areas and training students to become tomorrow's leaders in science and technology.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-01-05
A new study led by researchers from the University of Helsinki, along with colleagues at the Massachusetts General Hospital and Broad Institute of Harvard and MIT, provides significant breakthroughs in our understanding of the genetics behind gestational diabetes.
Gestational diabetes is a common pregnancy disorder annually affecting more than 16 million pregnancies worldwide, with substantial health implications for both mothers and their children. It is characterised by elevated blood sugar levels in pregnant women who did not have diabetes before becoming pregnant.
Despite the fact that gestational diabetes constitutes a major global health problem, there is remarkably ...
2024-01-05
EMBARGO: 05 January 2024 at 05:00 (US Eastern Time)
Freezing is one of the most common and debilitating symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, a neurodegenerative disorder that affects more than 9 million people worldwide. When individuals with Parkinson’s disease freeze, they suddenly lose the ability to move their feet, often mid-stride, resulting in a series of staccato stutter steps that get shorter until the person stops altogether. These episodes are one of the biggest contributors to falls among people living with Parkinson’s disease.
Today, freezing is treated with a range of pharmacological, surgical or behavioral ...
2024-01-05
Liquid-crystal (LC) phase modulators are widely used in optical systems because of their advantages of low power consumption, light weight, flexible bandwidth adjustment, and non-mechanical movements. However, most LC phase modulators are polarization-sensitive, meaning that they affect the phase of light differently depending on its polarization. This can limit their performance and functionality in some applications.
There are two main approaches to realizing polarization-independent LC phase modulators. The first approach is to use polarization-independent ...
2024-01-05
Integrated optical signal distributing, processing, and sensing networks require the miniaturization of basic optical elements, such as waveguides, splitters, gratings, and optical switches. To achieve this, fabrication approaches that allow for high-resolution manufacturing are required. Curved elements like bends and ring resonators are especially challenging to fabricate, as they need even higher resolution and lower sidewall roughness. Additionally, fabrication techniques with precise control of absolute structure dimensions are imperative.
Several ...
2024-01-05
WASHINGTON — Titan’s “magic islands” are likely floating chunks of porous, frozen organic solids, a new study finds, pivoting from previous work suggesting they were gas bubbles. The study was published in Geophysical Research Letters, AGU’s journal for high-impact, short-format reports with immediate implications spanning all Earth and space sciences.
A hazy orange atmosphere 50% thicker than Earth’s and rich in methane and other carbon-based, or organic, molecules blankets Saturn’s largest moon, Titan. Its surface is covered with dark dunes of organic material and seas of liquid methane and ethane. ...
2024-01-05
Today, for the first time in human history, more than half of the world’s population lives in cities. Coincidentally, within the field of cultural heritage conservation, increasing international interest and attention over the past two decades has been focused on urban areas. This is timely because the pressure for economic development and for the prioritizing of engagement with the global economy have accompanied rapid urbanization. In many societies, economic development has privileged modernization efforts leading to the loss of traditional communities. ...
2024-01-05
Irvine, Calif., Jan 4, 2024 — With a split-second muscle contraction, the greater blue-ringed octopus can change the size and color of the namesake patterns on its skin for purposes of deception, camouflage and signaling. Researchers at the University of California, Irvine have drawn inspiration from this natural wonder to develop a technological platform with similar capabilities for use in a variety of fields, including the military, medicine, robotics and sustainable energy.
According to its inventors, new devices made possible by this ...
2024-01-05
Detecting malaria in people who aren’t experiencing symptoms is vital to public health efforts to better control this tropical disease in places where the mosquito-borne parasite is common. Asymptomatic people harboring the parasite can still transmit the disease or become ill later, after initially testing negative.
The dynamic lifecycle of this pathogen means that parasite densities can suddenly drop below the level of detection — especially when older, less sensitive tests are used. Such fluctuations can make it difficult, when testing only at a single point in time, to determine if an apparently healthy person is in fact infected.
Malaria ...
2024-01-05
Under embargo until 00:01 GMT on Friday 5 January 2024 /19:01 ET Thursday 4 January 2024
Royal Astronomical Society and University of Oxford press release
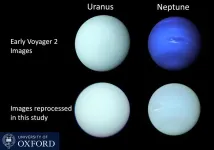
Neptune is fondly known for being a rich blue and Uranus green – but a new study has revealed that the two ice giants are actually far closer in colour than typically thought.
The correct shades of the planets have been confirmed with the help of research led by Professor Patrick Irwin from the University of Oxford, which has been published today in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
He and his team found that both worlds ...
2024-01-05
Each summer, community college students from Colorado and surrounding states converge on the CU Boulder campus to participate in an immersive nine-week research program. A recent CIRES-led study reveals that when the students head home, they don’t just take new scientific and professional skills with them—they also leave with more confidence in their ability to do science and a greater sense of belonging in the science community. The work, published last month in PLOS ONE, suggests that authentic research experiences inspire community college students’ interest in STEM careers.
“Paid, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Advancing the generation of in-vivo chimeric lungs in mice using rat-derived stem cells
Researchers from Japan explore the conditions needed for organ regeneration and overcoming species-specific barriers to create functional organs in interspecies chimeric animals