(Press-News.org) A new study led by researchers from the University of Helsinki, along with colleagues at the Massachusetts General Hospital and Broad Institute of Harvard and MIT, provides significant breakthroughs in our understanding of the genetics behind gestational diabetes.
Gestational diabetes is a common pregnancy disorder annually affecting more than 16 million pregnancies worldwide, with substantial health implications for both mothers and their children. It is characterised by elevated blood sugar levels in pregnant women who did not have diabetes before becoming pregnant.
Despite the fact that gestational diabetes constitutes a major global health problem, there is remarkably little research into its molecular causes.
The study now published is the largest genome-wide association study of gestational diabetes conducted to date, including more than 12,000 patients and 131,000 female controls from the Finnish genomics initiative FinnGen.
This groundbreaking research, published in Nature Genetics, has nearly tripled the number of known genetic areas associated with gestational diabetes, identifying a total of 13 distinct chromosomal regions linked to the condition.
Using recently-developed analysis methods, the researchers were able to show that there are two distinct classes of genetic variants related to gestational diabetes: Those that are shared with type 2 diabetes and those that are predominantly associated with the gestational form of diabetes only.
“Our results suggest that gestational diabetes has a unique genetic basis that is partially separate from type 2 diabetes, challenging previous assumptions about the shared genetic underpinnings of the two conditions,” says Dr. Elisabeth Widén from the Institute for Molecular Medicine Finland (FIMM), University of Helsinki, who led the study.
The study's results also provide important insights into potential physiological mechanisms related to the development of diabetes during pregnancy. These mechanisms involve adaptive changes in the brain, as well as altered insulin sensitivity in the mother. The hypothalamus emerged as one key focus, with some of the risk genes identified active in brain cell types known to be important for adaptive responses to maintain blood sugar regulation during pregnancy.
“Biobank-based studies such as FinnGen, with deep and lifelong clinical data, facilitate large-scale studies of many women’s and reproductive health phenotypes in which research funding has been badly lacking” said Dr. Mark Daly, former director of FIMM and a geneticist at the Massachusetts General Hospital and Broad Institute who jointly supervised the study. “It is exciting to see this work bearing fruit in important and understudied diseases.”
Although the study primarily focused on a Finnish population, the findings have broader implications. The majority of the risk variants are common, highlighting the potential relevance of these discoveries to diverse populations at risk for gestational diabetes.
Putting the spotlight on a very common pregnancy disorder that has remained understudied for years, the work is of high relevance for women’s health in general. Also, the results enhance the overall understanding of dysregulation of glucose metabolism more broadly.
“By providing novel data on critical genetic factors and pathways, our study has the potential to transform attitudes and approaches not only towards gestational diabetes research but towards research targeting pregnancy-related health outcomes overall, ultimately benefitting the health of mothers and their newborns,” Dr. Widén concludes.
END
A leap forward in women's health: unlocking genetic clues to gestational diabetes
The largest genetic study of gestational diabetes to date has led to a discovery of nine novel genetic regions linked to this severe and common pregnancy complication
2024-01-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Soft robotic, wearable device improves walking for individual with Parkinson’s disease
2024-01-05
EMBARGO: 05 January 2024 at 05:00 (US Eastern Time)
Freezing is one of the most common and debilitating symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, a neurodegenerative disorder that affects more than 9 million people worldwide. When individuals with Parkinson’s disease freeze, they suddenly lose the ability to move their feet, often mid-stride, resulting in a series of staccato stutter steps that get shorter until the person stops altogether. These episodes are one of the biggest contributors to falls among people living with Parkinson’s disease.
Today, freezing is treated with a range of pharmacological, surgical or behavioral ...
Polarization-independent liquid-crystal phase modulators
2024-01-05
Liquid-crystal (LC) phase modulators are widely used in optical systems because of their advantages of low power consumption, light weight, flexible bandwidth adjustment, and non-mechanical movements. However, most LC phase modulators are polarization-sensitive, meaning that they affect the phase of light differently depending on its polarization. This can limit their performance and functionality in some applications.
There are two main approaches to realizing polarization-independent LC phase modulators. The first approach is to use polarization-independent ...
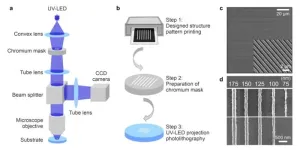
Low-cost microscope projection photolithography system for high-resolution fabrication
2024-01-05
Integrated optical signal distributing, processing, and sensing networks require the miniaturization of basic optical elements, such as waveguides, splitters, gratings, and optical switches. To achieve this, fabrication approaches that allow for high-resolution manufacturing are required. Curved elements like bends and ring resonators are especially challenging to fabricate, as they need even higher resolution and lower sidewall roughness. Additionally, fabrication techniques with precise control of absolute structure dimensions are imperative.
Several ...
Titan’s “magic islands” likely honeycombed hydrocarbon icebergs
2024-01-05
WASHINGTON — Titan’s “magic islands” are likely floating chunks of porous, frozen organic solids, a new study finds, pivoting from previous work suggesting they were gas bubbles. The study was published in Geophysical Research Letters, AGU’s journal for high-impact, short-format reports with immediate implications spanning all Earth and space sciences.
A hazy orange atmosphere 50% thicker than Earth’s and rich in methane and other carbon-based, or organic, molecules blankets Saturn’s largest moon, Titan. Its surface is covered with dark dunes of organic material and seas of liquid methane and ethane. ...
Historic urban Landscape Paradigm—A tool for balancing values and changes in the urban conservation process
2024-01-05
Today, for the first time in human history, more than half of the world’s population lives in cities. Coincidentally, within the field of cultural heritage conservation, increasing international interest and attention over the past two decades has been focused on urban areas. This is timely because the pressure for economic development and for the prioritizing of engagement with the global economy have accompanied rapid urbanization. In many societies, economic development has privileged modernization efforts leading to the loss of traditional communities. ...
UC Irvine engineers invent octopus-inspired technology that can deceive and signal
2024-01-05
Irvine, Calif., Jan 4, 2024 — With a split-second muscle contraction, the greater blue-ringed octopus can change the size and color of the namesake patterns on its skin for purposes of deception, camouflage and signaling. Researchers at the University of California, Irvine have drawn inspiration from this natural wonder to develop a technological platform with similar capabilities for use in a variety of fields, including the military, medicine, robotics and sustainable energy.
According to its inventors, new devices made possible by this ...
Classifying the natural history of asymptomatic malaria
2024-01-05
Detecting malaria in people who aren’t experiencing symptoms is vital to public health efforts to better control this tropical disease in places where the mosquito-borne parasite is common. Asymptomatic people harboring the parasite can still transmit the disease or become ill later, after initially testing negative.
The dynamic lifecycle of this pathogen means that parasite densities can suddenly drop below the level of detection — especially when older, less sensitive tests are used. Such fluctuations can make it difficult, when testing only at a single point in time, to determine if an apparently healthy person is in fact infected.
Malaria ...
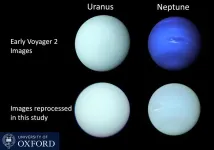
New images reveal what Neptune and Uranus really look like
2024-01-05
Under embargo until 00:01 GMT on Friday 5 January 2024 /19:01 ET Thursday 4 January 2024
Royal Astronomical Society and University of Oxford press release
Neptune is fondly known for being a rich blue and Uranus green – but a new study has revealed that the two ice giants are actually far closer in colour than typically thought.
The correct shades of the planets have been confirmed with the help of research led by Professor Patrick Irwin from the University of Oxford, which has been published today in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
He and his team found that both worlds ...
Students build science identity through immersive research experience
2024-01-05
Each summer, community college students from Colorado and surrounding states converge on the CU Boulder campus to participate in an immersive nine-week research program. A recent CIRES-led study reveals that when the students head home, they don’t just take new scientific and professional skills with them—they also leave with more confidence in their ability to do science and a greater sense of belonging in the science community. The work, published last month in PLOS ONE, suggests that authentic research experiences inspire community college students’ interest in STEM careers.
“Paid, ...
Bipolar disorder linked to early death more than smoking
2024-01-04
Having bipolar disorder – a serious mental illness that can cause both manic and depressed moods – can make life more challenging.
It also comes with a higher risk of dying early. Now, a study puts into perspective just how large that risk is, and how it compares with other factors that can shorten life.
In two different groups, people with bipolar disorder were four to six times more likely as people without the condition to die prematurely, the study finds.
By contrast, people who had ever smoked were about twice as likely to die prematurely than those ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Ochsner MD Anderson uses groundbreaking TIL therapy to treat advanced melanoma in adults
A heatshield for ‘never-wet’ surfaces: Rice engineering team repels even near-boiling water with low-cost, scalable coating
Skills from being a birder may change—and benefit—your brain
Waterloo researchers turning plastic waste into vinegar
Measuring the expansion of the universe with cosmic fireworks
How horses whinny: Whistling while singing
US newborn hepatitis B virus vaccination rates
When influencers raise a glass, young viewers want to join them
Exposure to alcohol-related social media content and desire to drink among young adults
Access to dialysis facilities in socioeconomically advantaged and disadvantaged communities
Dietary patterns and indicators of cognitive function
New study shows dry powder inhalers can improve patient outcomes and lower environmental impact
Plant hormone therapy could improve global food security
A new Johns Hopkins Medicine study finds sex and menopause-based differences in presentation of early Lyme disease
Students run ‘bee hotels’ across Canada - DNA reveals who’s checking in
SwRI grows capacity to support manufacture of antidotes to combat nerve agent, pesticide exposure in the U.S.
University of Miami business technology department ranked No. 1 in the nation for research productivity
Researchers build ultra-efficient optical sensors shrinking light to a chip
Why laws named after tragedies win public support
Missing geomagnetic reversals in the geomagnetic reversal history
EPA criminal sanctions align with a county’s wealth, not pollution
“Instead of humans, robots”: fully automated catalyst testing technology developed
Lehigh and Rice universities partner with global industry leaders to revolutionize catastrophe modeling
Engineers sharpen gene-editing tools to target cystic fibrosis
Pets can help older adults’ health & well-being, but may strain budgets too
First evidence of WHO ‘critical priority’ fungal pathogen becoming more deadly when co-infected with tuberculosis
World-first safety guide for public use of AI health chatbots
Women may face heart attack risk with a lower plaque level than men
Proximity to nuclear power plants associated with increased cancer mortality
Women’s risk of major cardiac events emerges at lower coronary plaque burden compared to men
[Press-News.org] A leap forward in women's health: unlocking genetic clues to gestational diabetesThe largest genetic study of gestational diabetes to date has led to a discovery of nine novel genetic regions linked to this severe and common pregnancy complication