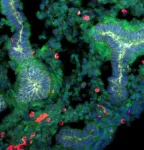
(Press-News.org) In a scientific breakthrough that aids our understanding of the internal wiring of immune cells, researchers at Monash University in Australia have cracked the code behind IKAROS, an essential protein for immune cell development and protection against pathogens and cancer.
This disruptive research, led by the eminent Professor Nicholas Huntington of Monash University’s Biomedicine Discovery Institute, is poised to reshape our comprehension of gene control networks and its impact on everything from eye colour to cancer susceptibility and design of novel therapies.
The study, published in Nature Immunology, promises pivotal insights into the mechanisms safeguarding us against infections and cancers. When the transcription factor Ikaros/Ikzf1 was deliberately obstructed, be it in preclinical models or humans, the once-mighty activity of Natural Killer (NK) cells, our immune system's frontline warriors, plummeted. Loss of this transcription factor in NK cells resulted in wide-spread dysregulation of NK cell development and function, preventing their ability to recognize and kill virus-infected cells and clear metastatic tumour cells from circulation. Aiolos/Ikzf3 and Helios/Ikzf2, related family member were found to partial compensate for the loss of Ikaros, as such when multiple IKZF-family members were inhibited, NK cells underwent rapidly death. Mechanistically, Aiolos and Ikaros were found to directly bind and activate most members of the JUN/FOS family, transcription factors known for their essential roles in human embryo development and tissue function.
This discovery opens the door to the prospect of potential novel cancer therapeutics. NK cells, our first line of defence against pathogens and internal threats like cancers, could be fortified by therapies enhancing their killing prowess by targeting IKAROS and JUN/FOS biology.
Professor Huntington notes that drugs targeting IKAROS/AIOLOS have already received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and local Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) for the treatment of B cell malignancy “but until now we haven’t understood how these drugs work, armed with this new information it could be possible to develop novel drugs targeting these complexes which may offer differentiated pharmacology and therapeutic index for treating disease,” he said. Importantly on this front, Professor Huntington’s team were able to show that IKAROS had a conserved role in healthy B cells and thus potentially B cell cancers.
END
Major breakthrough unveils immune system's guardian: IKAROS
IKAROS code cracked: insight into an essential protein for immune cell development and protection against pathogens and cancer
2024-01-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Advancing the generation of in-vivo chimeric lungs in mice using rat-derived stem cells
2024-01-05
Ikoma, Japan – Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the third leading cause of death worldwide. It is marked by lung damage that is lasting and incurable, leaving lung transplantation as the only viable treatment option. Unfortunately, finding suitable lung donors is difficult. To compensate for this shortage of donors, regenerative medicine is making strides in developing lungs from pluripotent stem cells (PSCs), using interspecies animal models.
Through a biological technique known as blastocyst complementation, PSCs, and embryonic ...
A leap forward in women's health: unlocking genetic clues to gestational diabetes
2024-01-05
A new study led by researchers from the University of Helsinki, along with colleagues at the Massachusetts General Hospital and Broad Institute of Harvard and MIT, provides significant breakthroughs in our understanding of the genetics behind gestational diabetes.
Gestational diabetes is a common pregnancy disorder annually affecting more than 16 million pregnancies worldwide, with substantial health implications for both mothers and their children. It is characterised by elevated blood sugar levels in pregnant women who did not have diabetes before becoming pregnant.
Despite the fact that gestational diabetes constitutes a major global health problem, there is remarkably ...
Soft robotic, wearable device improves walking for individual with Parkinson’s disease
2024-01-05
EMBARGO: 05 January 2024 at 05:00 (US Eastern Time)
Freezing is one of the most common and debilitating symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, a neurodegenerative disorder that affects more than 9 million people worldwide. When individuals with Parkinson’s disease freeze, they suddenly lose the ability to move their feet, often mid-stride, resulting in a series of staccato stutter steps that get shorter until the person stops altogether. These episodes are one of the biggest contributors to falls among people living with Parkinson’s disease.
Today, freezing is treated with a range of pharmacological, surgical or behavioral ...
Polarization-independent liquid-crystal phase modulators
2024-01-05
Liquid-crystal (LC) phase modulators are widely used in optical systems because of their advantages of low power consumption, light weight, flexible bandwidth adjustment, and non-mechanical movements. However, most LC phase modulators are polarization-sensitive, meaning that they affect the phase of light differently depending on its polarization. This can limit their performance and functionality in some applications.
There are two main approaches to realizing polarization-independent LC phase modulators. The first approach is to use polarization-independent ...
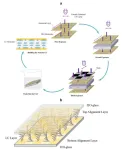
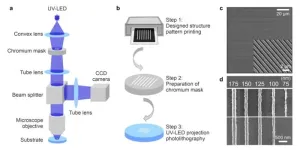
Low-cost microscope projection photolithography system for high-resolution fabrication
2024-01-05
Integrated optical signal distributing, processing, and sensing networks require the miniaturization of basic optical elements, such as waveguides, splitters, gratings, and optical switches. To achieve this, fabrication approaches that allow for high-resolution manufacturing are required. Curved elements like bends and ring resonators are especially challenging to fabricate, as they need even higher resolution and lower sidewall roughness. Additionally, fabrication techniques with precise control of absolute structure dimensions are imperative.
Several ...
Titan’s “magic islands” likely honeycombed hydrocarbon icebergs
2024-01-05
WASHINGTON — Titan’s “magic islands” are likely floating chunks of porous, frozen organic solids, a new study finds, pivoting from previous work suggesting they were gas bubbles. The study was published in Geophysical Research Letters, AGU’s journal for high-impact, short-format reports with immediate implications spanning all Earth and space sciences.
A hazy orange atmosphere 50% thicker than Earth’s and rich in methane and other carbon-based, or organic, molecules blankets Saturn’s largest moon, Titan. Its surface is covered with dark dunes of organic material and seas of liquid methane and ethane. ...
Historic urban Landscape Paradigm—A tool for balancing values and changes in the urban conservation process
2024-01-05
Today, for the first time in human history, more than half of the world’s population lives in cities. Coincidentally, within the field of cultural heritage conservation, increasing international interest and attention over the past two decades has been focused on urban areas. This is timely because the pressure for economic development and for the prioritizing of engagement with the global economy have accompanied rapid urbanization. In many societies, economic development has privileged modernization efforts leading to the loss of traditional communities. ...
UC Irvine engineers invent octopus-inspired technology that can deceive and signal
2024-01-05
Irvine, Calif., Jan 4, 2024 — With a split-second muscle contraction, the greater blue-ringed octopus can change the size and color of the namesake patterns on its skin for purposes of deception, camouflage and signaling. Researchers at the University of California, Irvine have drawn inspiration from this natural wonder to develop a technological platform with similar capabilities for use in a variety of fields, including the military, medicine, robotics and sustainable energy.
According to its inventors, new devices made possible by this ...
Classifying the natural history of asymptomatic malaria
2024-01-05
Detecting malaria in people who aren’t experiencing symptoms is vital to public health efforts to better control this tropical disease in places where the mosquito-borne parasite is common. Asymptomatic people harboring the parasite can still transmit the disease or become ill later, after initially testing negative.
The dynamic lifecycle of this pathogen means that parasite densities can suddenly drop below the level of detection — especially when older, less sensitive tests are used. Such fluctuations can make it difficult, when testing only at a single point in time, to determine if an apparently healthy person is in fact infected.
Malaria ...
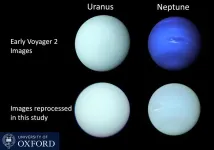
New images reveal what Neptune and Uranus really look like
2024-01-05
Under embargo until 00:01 GMT on Friday 5 January 2024 /19:01 ET Thursday 4 January 2024
Royal Astronomical Society and University of Oxford press release
Neptune is fondly known for being a rich blue and Uranus green – but a new study has revealed that the two ice giants are actually far closer in colour than typically thought.
The correct shades of the planets have been confirmed with the help of research led by Professor Patrick Irwin from the University of Oxford, which has been published today in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
He and his team found that both worlds ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
[Press-News.org] Major breakthrough unveils immune system's guardian: IKAROSIKAROS code cracked: insight into an essential protein for immune cell development and protection against pathogens and cancer