Monitoring the well-being of reservoir water through an uncrewed surface vehicle
2024-01-05
(Press-News.org)
In a recent tragic incident, approximately 100 elephants in Africa perished due to inadequate access to water. The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) issues a warning that around 2.5 billion people worldwide could face water scarcity by 2025. In the face of water shortages affecting not only human society but also the entire ecological community due to the climate crisis, it becomes crucial to adopt comprehensive measures for managing water quality and quantity to avert such pressing challenges.
A research team led by Professor Jonghun Kam and PhD candidate Kwang-Hun Lee from the Division of Environmental Science and Engineering at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), has implemented an advanced technique employing an uncrewed surface vehicle to concurrently assess the reservoir water depths and nitrate (NO3-) concentrations from the reservoir water surface. The findings from their research were featured in Water Resources Research, an international journal dedicated to the water environment.
Monitoring available water quantity and quality uses indicators such as water depth and nitrate concentration. Nitrates, originating from atmospheric and soil nutrients, enter streams through various pathways, posing a potential threat to aquatic ecosystems and biodiversity when their levels become excessive. Fluctuation of precipitation and water usage further impact water quality, and rising water temperatures contribute to decreased dissolved oxygen, resulting in diminished water quality.
Effective management of water resources requires the dual monitoring of nitrate concentration and water depth. However, these measurements can vary significantly based on the timing and location of assessment. Traditional water depth measurement, typically taken at a single point, introduces uncertainty in estimating the total reservoir water volume. In recent times, uncrewed devices or instruments have been introduced to address this challenge, yet simultaneous measurement of nitrate concentration and water depth has proven challenging.
The research team has achieved the simultaneous measurement of nitrate concentration and water depth using an uncrewed surface vehicle. Over the course of a year, starting in 2021, an uncrewed boat equipped with electrochemical sensors and acoustic doppler current profile sensors was employed to gauge nitrate concentration and water depth in a reservoir (Daljeonji) in Pohang, North Gyeongsang Province in South Korea. The 30 measurements revealed seasonal variations with nitrate levels ranging from 1 ton to 4 tons. Following intense rainfall, the observed nitrate amount was up to 17% lower than previous readings due to rapid water expansion. This underscores the importance of considering timing and weather conditions in water quality assessments, as measurements may lead to over- or underestimation.
Furthermore, the team successfully generated a high-resolution map illustrating the cumulative nitrate content in Daljeonji Reservior based on data collected by the uncrewed surface vehicle. Despite a one-year measurement period and the study's confinement to Pohang, its significance lies in the independent development of technology capable of simultaneous measurement of nitrate concentration and water depth.
Professor Jonghun Kam who led the research explained, "Our study has outlined both the possibilities and constraints of employing uncrewed robotics in water environment research.” He added, “It is envisioned that this research will provide a guiding framework for the development of the next generation of the Korean national water resources management system, leveraging advanced technologies like uncrewed aerial vehicles to enhance prediction accuracy and optimize water management."
The study was conducted with the support from the Group Research in Science and Engineering Program and the Ocean, Land, and Atmosphere Carbon Cycle System Research Program of the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea (2021M3I6A1086808).
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:


ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-01-05
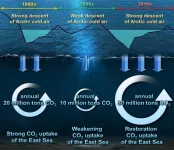
The recent cold spell has plunged the nation into a deep freeze, resulting in the closure of 247 national parks, the cancellation of 14 domestic flights, and the scrapping of 107 cruise ship voyages. While the cold snap brought relief by significantly reducing the prevalence of particulate matter obscuring our surroundings, a recent study indicates that, besides diminishing particulate matter, it is significantly contributing to the heightened uptake of carbon dioxide by the East Sea.
According to research conducted by a team of researchers ...
2024-01-05
As concerns over the world’s declining bird population mount, animal ecologists developed an analytical approach to better understand one of the latest threats to feathered creatures: the rise of wind and solar energy facilities.
“Bird mortality has become an unintended consequence of renewable energy development,” said Hannah Vander Zanden, an assistant professor of biology at the University of Florida. “If we want to minimize or even offset these fatalities, especially for vulnerable populations, we need to identify the geographic origin of affected birds. In other words, are the dead birds local or are they coming ...
2024-01-05
Spintronic devices are electronic devices that utilize the spin of electrons (an intrinsic form of angular momentum possessed by the electron) to achieve high-speed processing and low-cost data storage. In this regard, spin-transfer torque is a key phenomenon that enables ultrafast and low-power spintronic devices. Recently, however, spin-orbit torque (SOT) has emerged as a promising alternative to spin-transfer torque.
Many studies have investigated the origin of SOT, showing that in non-magnetic materials, a phenomenon called the spin Hall effect (SHE) is key to achieving SOT. In these materials, the existence of a “Dirac band” ...
2024-01-05
A bit of weed before a workout can boost motivation and make exercise more enjoyable. But if performance is the goal, it may be best to skip that joint.
That’s the takeaway of the first ever study to examine how legal, commercially available cannabis shapes how exercise feels.
The study of 42 runners, published Dec. 26 in the journal Sports Medicine, comes almost exactly 10 years after Colorado became the first state to commence legal sales of recreational marijuana, at a time when cannabis-users increasingly report mixing it with workouts.
“The bottom-line finding is that cannabis before exercise seems ...
2024-01-05
For military veterans, many of the deepest wounds of war are invisible: Traumatic brain injuries resulting from head trauma or blast explosions are a leading cause of post-traumatic stress disorder, anxiety, depression and suicide among veterans. Few treatments have been effective at diminishing the long-term effects of TBI, leaving many veterans feeling hopeless.
Now, Stanford researchers have discovered that the plant-based psychoactive drug ibogaine, when combined with magnesium to protect the heart, safely and effectively reduces PTSD, anxiety and depression and improves functioning in veterans with TBI. Their new study, to be published ...
2024-01-05
In a scientific breakthrough that aids our understanding of the internal wiring of immune cells, researchers at Monash University in Australia have cracked the code behind IKAROS, an essential protein for immune cell development and protection against pathogens and cancer.
This disruptive research, led by the eminent Professor Nicholas Huntington of Monash University’s Biomedicine Discovery Institute, is poised to reshape our comprehension of gene control networks and its impact on everything from eye colour to cancer susceptibility and design of novel ...
2024-01-05
Ikoma, Japan – Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the third leading cause of death worldwide. It is marked by lung damage that is lasting and incurable, leaving lung transplantation as the only viable treatment option. Unfortunately, finding suitable lung donors is difficult. To compensate for this shortage of donors, regenerative medicine is making strides in developing lungs from pluripotent stem cells (PSCs), using interspecies animal models.
Through a biological technique known as blastocyst complementation, PSCs, and embryonic ...
2024-01-05
A new study led by researchers from the University of Helsinki, along with colleagues at the Massachusetts General Hospital and Broad Institute of Harvard and MIT, provides significant breakthroughs in our understanding of the genetics behind gestational diabetes.
Gestational diabetes is a common pregnancy disorder annually affecting more than 16 million pregnancies worldwide, with substantial health implications for both mothers and their children. It is characterised by elevated blood sugar levels in pregnant women who did not have diabetes before becoming pregnant.
Despite the fact that gestational diabetes constitutes a major global health problem, there is remarkably ...
2024-01-05
EMBARGO: 05 January 2024 at 05:00 (US Eastern Time)
Freezing is one of the most common and debilitating symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, a neurodegenerative disorder that affects more than 9 million people worldwide. When individuals with Parkinson’s disease freeze, they suddenly lose the ability to move their feet, often mid-stride, resulting in a series of staccato stutter steps that get shorter until the person stops altogether. These episodes are one of the biggest contributors to falls among people living with Parkinson’s disease.
Today, freezing is treated with a range of pharmacological, surgical or behavioral ...
2024-01-05
Liquid-crystal (LC) phase modulators are widely used in optical systems because of their advantages of low power consumption, light weight, flexible bandwidth adjustment, and non-mechanical movements. However, most LC phase modulators are polarization-sensitive, meaning that they affect the phase of light differently depending on its polarization. This can limit their performance and functionality in some applications.
There are two main approaches to realizing polarization-independent LC phase modulators. The first approach is to use polarization-independent ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Monitoring the well-being of reservoir water through an uncrewed surface vehicle