(Press-News.org) Air pollution significantly impacts human health, with Hainan Province in China aiming to achieve world-leading ambient air quality by 2035, despite already having relatively good air quality in China. The existing Ambient Air Quality Standards (AAQS) offer insufficient guidance for further enhancing air quality in Hainan, which stands at the forefront of China's environmental protection efforts. Consequently, it is imperative to develop Hainan's local AAQS. This initiative, responding to WHO's strengthened guidelines, aims to address unique regional challenges in air quality assessment, like high background pollutant levels and other complex environmental factors. The development of these tailored standards is crucial for further improving air quality and health outcomes in Hainan and can serve as a model for other regions seeking to surpass national benchmarks and achieve global air quality leadership.
In a landmark study published in Eco-Environment & Health on 28 October 2023, a team from Tsinghua University and several other Chinese institutions presents a comprehensive approach to developing local AAQS tailored for Hainan Province, China. This initiative is part of Hainan's broader effort to enhance its ecological environment and achieve world-class air quality by 2035.
The study began by looking at air quality standards from different countries and regions, focusing on how they measure and limit pollution. For Hainan, the researchers suggested new, realistic goals for reducing common pollutants, considering health effects over both short and long periods. They used these goals, along with local data and international guidelines, to create Hainan's own standards.
To predict if Hainan can meet these goals, the researchers used a computer program called the Community Multiscale Air Quality (CMAQ) model. This program helped them see how the air quality might change by 2035 with different ways of controlling pollution. They found that with strong policies, Hainan could indeed meet these new, stricter air quality goals by 2035.
Lead researcher Bin Zhao from Tsinghua University emphasizes, "Developing local AAQS is critical for regions like Hainan, where the standard needs to reflect local conditions while aiming for global leadership in air quality. Our research is a step towards achieving that delicate balance."
The pioneering work of establishing local AAQS in Hainan Province represents a significant step towards a healthier environment and serves as a model for regions worldwide. As the province moves towards implementing these standards, it embarks on a path to achieving world-leading air quality by 2035.
The study estimates that adhering to the new standards could prevent thousands of premature deaths annually by 2035 due to reduced long-term exposure to PM2.5 and O3. This proactive approach not only promises a healthier future for Hainan's residents but also sets a precedent for other regions to develop their own localized air quality standards.
###
References
DOI
10.1016/j.eehl.2023.10.002
Original Source URL
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eehl.2023.10.002
Funding information
The National Key R&D Program of China (2022YFC3700702); The Energy Foundation, and the Tsinghua-Toyota Joint Research Institute Inter-disciplinary Program.
About Eco-Environment & Health
Eco-Environment & Health (EEH) is an international and multidisciplinary peer-reviewed journal designed for publications on the frontiers of the ecology, environment and health as well as their related disciplines. EEH focuses on the concept of "One Health" to promote green and sustainable development, dealing with the interactions among ecology, environment and health, and the underlying mechanisms and interventions. Our mission is to be one of the most important flagship journals in the field of environmental health.
END
Hainan's quest for pristine air: Charting a course to global air quality leadership by 2035
2024-01-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Asbestos: the size and shape of inhaled nanofibers could be exclusively responsible for the development of pulmonary fibrosis
2024-01-05
The pathogenic potential of inhaling the inert fibrous nanomaterials used in thermal insulation (such as asbestos or fibreglass) is actually connected not to their chemical composition, but instead to their geometrical characteristics and size. This was revealed by a study, published on 3 January 2024 in the journal Nature Nanotechnology, conducted on glass nanofibers by a French-Chinese team including a CNRS chemist.1
The reason for this is the inability of the macrophages2 naturally present in pulmonary alveolar tissue to eliminate foreign bodies that are too large. The study was initially conducted in vitro with electrochemical nanosensors, and revealed that when confronted ...
Monitoring the well-being of reservoir water through an uncrewed surface vehicle
2024-01-05
In a recent tragic incident, approximately 100 elephants in Africa perished due to inadequate access to water. The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) issues a warning that around 2.5 billion people worldwide could face water scarcity by 2025. In the face of water shortages affecting not only human society but also the entire ecological community due to the climate crisis, it becomes crucial to adopt comprehensive measures for managing water quality and quantity to avert such pressing challenges.
A research team led by Professor Jonghun Kam and PhD candidate Kwang-Hun Lee from the Division of Environmental Science and ...
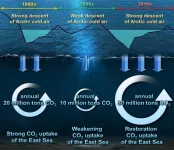
Arctic cold snap transforms into a blessing
2024-01-05
The recent cold spell has plunged the nation into a deep freeze, resulting in the closure of 247 national parks, the cancellation of 14 domestic flights, and the scrapping of 107 cruise ship voyages. While the cold snap brought relief by significantly reducing the prevalence of particulate matter obscuring our surroundings, a recent study indicates that, besides diminishing particulate matter, it is significantly contributing to the heightened uptake of carbon dioxide by the East Sea.
According to research conducted by a team of researchers ...
Feathers from deceased birds help scientists understand new threat to avian populations
2024-01-05
As concerns over the world’s declining bird population mount, animal ecologists developed an analytical approach to better understand one of the latest threats to feathered creatures: the rise of wind and solar energy facilities.
“Bird mortality has become an unintended consequence of renewable energy development,” said Hannah Vander Zanden, an assistant professor of biology at the University of Florida. “If we want to minimize or even offset these fatalities, especially for vulnerable populations, we need to identify the geographic origin of affected birds. In other words, are the dead birds local or are they coming ...
Using berry phase monopole engineering for high-temperature spintronic devices
2024-01-05
Spintronic devices are electronic devices that utilize the spin of electrons (an intrinsic form of angular momentum possessed by the electron) to achieve high-speed processing and low-cost data storage. In this regard, spin-transfer torque is a key phenomenon that enables ultrafast and low-power spintronic devices. Recently, however, spin-orbit torque (SOT) has emerged as a promising alternative to spin-transfer torque.
Many studies have investigated the origin of SOT, showing that in non-magnetic materials, a phenomenon called the spin Hall effect (SHE) is key to achieving SOT. In these materials, the existence of a “Dirac band” ...
Study shows weed makes workouts more fun, but it's no performance enhancer
2024-01-05
A bit of weed before a workout can boost motivation and make exercise more enjoyable. But if performance is the goal, it may be best to skip that joint.
That’s the takeaway of the first ever study to examine how legal, commercially available cannabis shapes how exercise feels.
The study of 42 runners, published Dec. 26 in the journal Sports Medicine, comes almost exactly 10 years after Colorado became the first state to commence legal sales of recreational marijuana, at a time when cannabis-users increasingly report mixing it with workouts.
“The bottom-line finding is that cannabis before exercise seems ...
Psychoactive drug ibogaine effectively treats traumatic brain injury in special ops military vets
2024-01-05
For military veterans, many of the deepest wounds of war are invisible: Traumatic brain injuries resulting from head trauma or blast explosions are a leading cause of post-traumatic stress disorder, anxiety, depression and suicide among veterans. Few treatments have been effective at diminishing the long-term effects of TBI, leaving many veterans feeling hopeless.
Now, Stanford researchers have discovered that the plant-based psychoactive drug ibogaine, when combined with magnesium to protect the heart, safely and effectively reduces PTSD, anxiety and depression and improves functioning in veterans with TBI. Their new study, to be published ...
Major breakthrough unveils immune system's guardian: IKAROS
2024-01-05
In a scientific breakthrough that aids our understanding of the internal wiring of immune cells, researchers at Monash University in Australia have cracked the code behind IKAROS, an essential protein for immune cell development and protection against pathogens and cancer.
This disruptive research, led by the eminent Professor Nicholas Huntington of Monash University’s Biomedicine Discovery Institute, is poised to reshape our comprehension of gene control networks and its impact on everything from eye colour to cancer susceptibility and design of novel ...
Advancing the generation of in-vivo chimeric lungs in mice using rat-derived stem cells
2024-01-05
Ikoma, Japan – Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the third leading cause of death worldwide. It is marked by lung damage that is lasting and incurable, leaving lung transplantation as the only viable treatment option. Unfortunately, finding suitable lung donors is difficult. To compensate for this shortage of donors, regenerative medicine is making strides in developing lungs from pluripotent stem cells (PSCs), using interspecies animal models.
Through a biological technique known as blastocyst complementation, PSCs, and embryonic ...
A leap forward in women's health: unlocking genetic clues to gestational diabetes
2024-01-05
A new study led by researchers from the University of Helsinki, along with colleagues at the Massachusetts General Hospital and Broad Institute of Harvard and MIT, provides significant breakthroughs in our understanding of the genetics behind gestational diabetes.
Gestational diabetes is a common pregnancy disorder annually affecting more than 16 million pregnancies worldwide, with substantial health implications for both mothers and their children. It is characterised by elevated blood sugar levels in pregnant women who did not have diabetes before becoming pregnant.
Despite the fact that gestational diabetes constitutes a major global health problem, there is remarkably ...