(Press-News.org) The Japan-led XRISM (X-ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission) observatory has released a first look at the unprecedented data it will collect when science operations begin later this year.
The satellite’s science team released a snapshot of a cluster of hundreds of galaxies and a spectrum of stellar wreckage in a neighboring galaxy, which gives scientists a detailed look at its chemical makeup.
“XRISM will provide the international science community with a new glimpse of the hidden X-ray sky,” said Richard Kelley, the U.S. principal investigator for XRISM at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. “We’ll not only see X-ray images of these sources, but also study their compositions, motions, and physical states.”
XRISM (pronounced “crism”) is led by JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) in collaboration with NASA, along with contributions from ESA (European Space Agency). It launched on Sept. 6, 2023.
It’s designed to detect X-rays with energies up to 12,000 electron volts and will study the universe’s hottest regions, largest structures, and objects with the strongest gravity. For comparison, the energy of visible light is 2 to 3 electron volts.
The mission has two instruments, Resolve and Xtend, each at the focus of an X-ray Mirror Assembly designed and built at Goddard.
Resolve is a microcalorimeter spectrometer developed by NASA and JAXA. It operates at just a fraction of a degree above absolute zero inside a refrigerator-sized container of liquid helium.
When an X-ray hits Resolve’s 6-by-6-pixel detector, it warms the device by an amount related to its energy. By measuring each individual X-ray’s energy, the instrument provides information previously unavailable about the source.
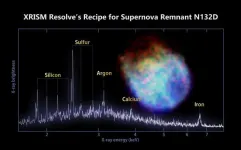
The mission team used Resolve to study N132D, a supernova remnant and one of the brightest X-ray sources in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a dwarf galaxy around 160,000 light-years away in the southern constellation Dorado. The expanding wreckage is estimated to be about 3,000 years old and was created when a star roughly 15 times the Sun’s mass ran out of fuel, collapsed, and exploded.
The Resolve spectrum shows peaks associated with silicon, sulfur, calcium, argon, and iron. This is the most detailed X-ray spectrum of the object ever obtained and demonstrates the incredible science the mission will do when regular operations begin later in 2024.
“These elements were forged in the original star and then blasted away when it exploded as a supernova,” said Brian Williams, NASA’s XRISM project scientist at Goddard. “Resolve will allow us to see the shapes of these lines in a way never possible before, letting us determine not only the abundances of the various elements present, but also their temperatures, densities, and directions of motion at unprecedented levels of precision. From there, we can piece together information about the original star and the explosion.”
XRISM’s second instrument, Xtend, is an X-ray imager developed by JAXA. It gives XRISM a large field of view, allowing it to observe an area about 60% larger than the average apparent size of the full moon.
Xtend captured an X-ray image of Abell 2319, a rich galaxy cluster about 770 million light-years away in the northern constellation Cygnus. It’s the fifth brightest X-ray cluster in the sky and is currently undergoing a major merger event.
The cluster is 3 million light-years across and highlights Xtend’s wide field of view.
“Even before the end of the commissioning process, Resolve is already exceeding our expectations,” said Lillian Reichenthal, NASA’s XRISM project manager at Goddard. “Our goal was to achieve a spectral resolution of 7 electron volts with the instrument, but now that it’s in orbit, we’re achieving 5. What that means is we’ll get even more detailed chemical maps with each spectrum XRISM captures.”
Resolve is performing exceptionally and already conducting exciting science despite an issue with the aperture door covering its detector. The door, designed to protect the detector before launch, has not opened as planned after several attempts. The door blocks lower-energy X-rays, effectively cutting the mission off at 1,700 electron volts compared to the planned 300. The XRISM team will continue to explore the anomaly and is investigating different approaches to opening the door. The Xtend instrument is unaffected.
NASA’s XRISM General Observer Facility, hosted at Goddard, is accepting proposals for observations from members of U.S. and Canadian institutions through Thursday, April 4. Cycle 1 of XRISM General Observer investigations will begin in the summer of 2024.
XRISM is a collaborative mission between JAXA and NASA, with participation by ESA. NASA’s contribution includes science participation from the Canadian Space Agency.
END
NASA/JAXA XRISM mission reveals its first look at X-ray cosmos
2024-01-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Hainan's quest for pristine air: Charting a course to global air quality leadership by 2035
2024-01-05
Air pollution significantly impacts human health, with Hainan Province in China aiming to achieve world-leading ambient air quality by 2035, despite already having relatively good air quality in China. The existing Ambient Air Quality Standards (AAQS) offer insufficient guidance for further enhancing air quality in Hainan, which stands at the forefront of China's environmental protection efforts. Consequently, it is imperative to develop Hainan's local AAQS. This initiative, responding to WHO's strengthened guidelines, aims to address unique regional challenges in air quality ...
Asbestos: the size and shape of inhaled nanofibers could be exclusively responsible for the development of pulmonary fibrosis
2024-01-05
The pathogenic potential of inhaling the inert fibrous nanomaterials used in thermal insulation (such as asbestos or fibreglass) is actually connected not to their chemical composition, but instead to their geometrical characteristics and size. This was revealed by a study, published on 3 January 2024 in the journal Nature Nanotechnology, conducted on glass nanofibers by a French-Chinese team including a CNRS chemist.1
The reason for this is the inability of the macrophages2 naturally present in pulmonary alveolar tissue to eliminate foreign bodies that are too large. The study was initially conducted in vitro with electrochemical nanosensors, and revealed that when confronted ...
Monitoring the well-being of reservoir water through an uncrewed surface vehicle
2024-01-05
In a recent tragic incident, approximately 100 elephants in Africa perished due to inadequate access to water. The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) issues a warning that around 2.5 billion people worldwide could face water scarcity by 2025. In the face of water shortages affecting not only human society but also the entire ecological community due to the climate crisis, it becomes crucial to adopt comprehensive measures for managing water quality and quantity to avert such pressing challenges.
A research team led by Professor Jonghun Kam and PhD candidate Kwang-Hun Lee from the Division of Environmental Science and ...
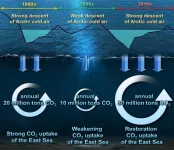
Arctic cold snap transforms into a blessing
2024-01-05
The recent cold spell has plunged the nation into a deep freeze, resulting in the closure of 247 national parks, the cancellation of 14 domestic flights, and the scrapping of 107 cruise ship voyages. While the cold snap brought relief by significantly reducing the prevalence of particulate matter obscuring our surroundings, a recent study indicates that, besides diminishing particulate matter, it is significantly contributing to the heightened uptake of carbon dioxide by the East Sea.
According to research conducted by a team of researchers ...
Feathers from deceased birds help scientists understand new threat to avian populations
2024-01-05
As concerns over the world’s declining bird population mount, animal ecologists developed an analytical approach to better understand one of the latest threats to feathered creatures: the rise of wind and solar energy facilities.
“Bird mortality has become an unintended consequence of renewable energy development,” said Hannah Vander Zanden, an assistant professor of biology at the University of Florida. “If we want to minimize or even offset these fatalities, especially for vulnerable populations, we need to identify the geographic origin of affected birds. In other words, are the dead birds local or are they coming ...
Using berry phase monopole engineering for high-temperature spintronic devices
2024-01-05
Spintronic devices are electronic devices that utilize the spin of electrons (an intrinsic form of angular momentum possessed by the electron) to achieve high-speed processing and low-cost data storage. In this regard, spin-transfer torque is a key phenomenon that enables ultrafast and low-power spintronic devices. Recently, however, spin-orbit torque (SOT) has emerged as a promising alternative to spin-transfer torque.
Many studies have investigated the origin of SOT, showing that in non-magnetic materials, a phenomenon called the spin Hall effect (SHE) is key to achieving SOT. In these materials, the existence of a “Dirac band” ...
Study shows weed makes workouts more fun, but it's no performance enhancer
2024-01-05
A bit of weed before a workout can boost motivation and make exercise more enjoyable. But if performance is the goal, it may be best to skip that joint.
That’s the takeaway of the first ever study to examine how legal, commercially available cannabis shapes how exercise feels.
The study of 42 runners, published Dec. 26 in the journal Sports Medicine, comes almost exactly 10 years after Colorado became the first state to commence legal sales of recreational marijuana, at a time when cannabis-users increasingly report mixing it with workouts.
“The bottom-line finding is that cannabis before exercise seems ...
Psychoactive drug ibogaine effectively treats traumatic brain injury in special ops military vets
2024-01-05
For military veterans, many of the deepest wounds of war are invisible: Traumatic brain injuries resulting from head trauma or blast explosions are a leading cause of post-traumatic stress disorder, anxiety, depression and suicide among veterans. Few treatments have been effective at diminishing the long-term effects of TBI, leaving many veterans feeling hopeless.
Now, Stanford researchers have discovered that the plant-based psychoactive drug ibogaine, when combined with magnesium to protect the heart, safely and effectively reduces PTSD, anxiety and depression and improves functioning in veterans with TBI. Their new study, to be published ...
Major breakthrough unveils immune system's guardian: IKAROS
2024-01-05
In a scientific breakthrough that aids our understanding of the internal wiring of immune cells, researchers at Monash University in Australia have cracked the code behind IKAROS, an essential protein for immune cell development and protection against pathogens and cancer.
This disruptive research, led by the eminent Professor Nicholas Huntington of Monash University’s Biomedicine Discovery Institute, is poised to reshape our comprehension of gene control networks and its impact on everything from eye colour to cancer susceptibility and design of novel ...
Advancing the generation of in-vivo chimeric lungs in mice using rat-derived stem cells
2024-01-05
Ikoma, Japan – Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the third leading cause of death worldwide. It is marked by lung damage that is lasting and incurable, leaving lung transplantation as the only viable treatment option. Unfortunately, finding suitable lung donors is difficult. To compensate for this shortage of donors, regenerative medicine is making strides in developing lungs from pluripotent stem cells (PSCs), using interspecies animal models.
Through a biological technique known as blastocyst complementation, PSCs, and embryonic ...