(Press-News.org) About The Study: This study of 620,000 children found that maternal type 1 diabetes was associated with increased risk for most types of congenital heart defects in offspring, while obesity and overweight were associated with increased risk for complex defects and outflow tract obstruction and decreased risk for ventricular septal defects. These different risk profiles of type 1 diabetes and overweight and obesity may suggest distinct underlying teratogenic mechanisms.
Authors: Riitta Turunen, M.D., Ph.D., and Emmi Helle, M.D., Ph.D., of the University of Helsinki, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.50579)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.50579?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=010524
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Maternal diabetes and overweight and congenital heart defects in offspring
JAMA Network Open
2024-01-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Evaluation of changes in prices and purchases following implementation of sugar-sweetened beverage taxes across the US
2024-01-05
About The Study: Sugar-sweetened beverage (SSB) taxes in Boulder, Colorado; Philadelphia, Oakland, San Francisco, and Seattle led to substantial, consistent declines in SSB purchases following price increases associated with those taxes. Scaling SSB taxes nationally could yield substantial public health benefits.
Authors: Scott Kaplan, Ph.D., of the U.S. Naval Academy in Annapolis, Maryland, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
The evolution of photosynthesis better documented thanks to the discovery of the oldest thylakoids in fossil cyanobacteria
2024-01-05
Researchers at the University of Liège (ULiège) have identified microstructures in fossil cells that are 1.75 billion years old. These structures, called thylakoid membranes, are the oldest ever discovered. They push back the fossil record of thylakoids by 1.2 billion years and provide new information on the evolution of cyanobacteria which played a crucial role in the accumulation of oxygen on the early Earth. This major discovery is presented in the journal Nature.
Catherine Demoulin, Yannick Lara, Alexandre Lambion and Emmanuelle Javaux from the Early Life Traces & Evolution laboratory of the Astrobiology Research ...
Hypertension's hidden hand: pressure-driven foam cell formation revealed as key driver of arterial disease, paving the way for new therapies
2024-01-05
A new study in Advanced Science unlocks the secrets of how high blood pressure (hypertension) fuels the progression of arterial disease. Led by Professor Thomas Iskratsch, Professor of Cardiovascular Mechanobiology & Bioengineering at Queen Mary University of London, the research team exposes a novel mechanism by which elevated pressure transforms muscle cells in the arterial wall into "foam cells" – the building blocks of plaque buildup that cripples arteries.
The study focuses on vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs), the workhorses responsible for maintaining blood vessel tone and flow. Under ...
NRL researchers receive Defense Manufacturing Technology Achievement Award
2024-01-05
WASHINGTON – U.S. Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) researchers, Kevin Cronin and Drew Rodgers, receive Technology Achievement Award for Lightweight Hydrogen Fuel Cells for Unmanned Aerial Systems (UAS) research efforts at Defense Manufacturing Conference held in Nashville, Tenn., Dec. 11, 2023.
The Department of Defense (DOD) has a critical need for increased power and endurance for persistent Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance (ISR) and transmission of radio frequency (RF) sources for communications and targeting.
“It ...
Applications open for School of Advanced Science on Technology and Innovation Strategies and Policies for Economic Development
2024-01-05
The São Paulo Advanced School on Technology & Innovation Strategies and Policies for Economic Development will be held from June 24 to July 05, 2024, at the University of Campinas (UNICAMP) in São Paulo state, Brazil.
Reporters are invited to register for the scientific sessions and short courses, which will present state-of-art science and results of new research.
The School provides an opportunity to learn about and debate recent developments in the economics of technological change and in science, technology and innovation (ST&I) policy studies. The programme comprises numerous seminars, intensive courses, and roundtable discussions focusing ...
Ancestors of primates lived in pairs
2024-01-05
A study carried out by CNRS1 scientists working with an international team has revealed that around 70 million years ago, when dinosaurs existed, the ancestors of primates most commonly lived in pairs. Only 15% of them opted for a solitary lifestyle. This discovery — that our ancestors adopted variable forms of social organization — challenges the hitherto commonly accepted hypothesis that at the time of dinosaurs, the ancestors of primates lived alone, and that pair living evolved much later. Most likely, pair living offered significant benefits, such as easier reproduction and reduced costs of thermoregulation by huddling in pairs.
While several studies have already been conducted ...
Mysterious missing component in the clouds of Venus revealed
2024-01-05
What are the clouds of Venus made of? Scientists know it’s mainly made of sulfuric acid droplets, with some water, chlorine, and iron. Their concentrations vary with height in the thick and hostile Venusian atmosphere. But until now they have been unable to identify the missing component that would explain the clouds’ patches and streaks, only visible in the UV range.
In a new study published in Science Advances, researchers from the University of Cambridge synthesised iron-bearing sulfate minerals that are stable under the harsh chemical conditions in the Venusian clouds. Spectroscopic analysis revealed that a combination of two minerals, rhomboclase and acid ferric ...
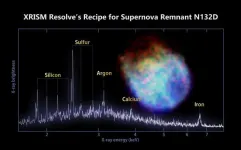
NASA/JAXA XRISM mission reveals its first look at X-ray cosmos
2024-01-05
The Japan-led XRISM (X-ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission) observatory has released a first look at the unprecedented data it will collect when science operations begin later this year.
The satellite’s science team released a snapshot of a cluster of hundreds of galaxies and a spectrum of stellar wreckage in a neighboring galaxy, which gives scientists a detailed look at its chemical makeup.
“XRISM will provide the international science community with a new glimpse of the hidden X-ray sky,” said Richard Kelley, the ...
Hainan's quest for pristine air: Charting a course to global air quality leadership by 2035
2024-01-05
Air pollution significantly impacts human health, with Hainan Province in China aiming to achieve world-leading ambient air quality by 2035, despite already having relatively good air quality in China. The existing Ambient Air Quality Standards (AAQS) offer insufficient guidance for further enhancing air quality in Hainan, which stands at the forefront of China's environmental protection efforts. Consequently, it is imperative to develop Hainan's local AAQS. This initiative, responding to WHO's strengthened guidelines, aims to address unique regional challenges in air quality ...
Asbestos: the size and shape of inhaled nanofibers could be exclusively responsible for the development of pulmonary fibrosis
2024-01-05
The pathogenic potential of inhaling the inert fibrous nanomaterials used in thermal insulation (such as asbestos or fibreglass) is actually connected not to their chemical composition, but instead to their geometrical characteristics and size. This was revealed by a study, published on 3 January 2024 in the journal Nature Nanotechnology, conducted on glass nanofibers by a French-Chinese team including a CNRS chemist.1
The reason for this is the inability of the macrophages2 naturally present in pulmonary alveolar tissue to eliminate foreign bodies that are too large. The study was initially conducted in vitro with electrochemical nanosensors, and revealed that when confronted ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Maternal diabetes and overweight and congenital heart defects in offspringJAMA Network Open