(Press-News.org) An international team of researchers has found that Africa’s birds of prey are facing an extinction crisis.
The report, co-led by researchers from the School of Biology at the University of St Andrews and The Peregrine Fund, and published in the journal Nature Ecology & Evolution (4 January 2024), warns of declines among nearly 90% of 42 species examined, and suggests that more than two-thirds may qualify as globally threatened.
Led by Dr Phil Shaw from St Andrews and Dr Darcy Ogada of The Peregrine Fund, the study combines counts from road surveys conducted within four African regions at intervals of c. 20–40 years and yields unprecedented insights into patterns of change in the abundance of savanna raptor species.
It shows that large raptor species had experienced significantly steeper declines than smaller species, particularly on unprotected land, where they are more vulnerable to persecution and other human pressures. Overall, raptors had declined more than twice as rapidly outside of National Parks, Reserves and other protected areas than they had within. Worryingly, many species experiencing the steepest declines had suffered a double jeopardy, having also become much more dependent on protected areas over the course of the study.
The study’s authors conclude that unless many of the threats currently facing African raptors are addressed effectively, large, charismatic eagle and vulture species are unlikely to persist over much of the continent’s unprotected land by the latter half of this century.
The study also highlights steep declines among raptors that are currently classified as being of ‘least concern’ in the global Red List of threatened species. They include African endemics such as Wahlberg's Eagle, African Hawk-eagle, Long-crested Eagle, African Harrier-hawk and Brown Snake-eagle, as well as Dark Chanting-goshawk. All of these species have declined at rates suggesting that they may now be globally threatened.
Several other familiar, widespread raptor species are now scarce or absent from unprotected land. They include one of Africa’s most powerful raptors - the Martial Eagle - as well as the highly distinctive Bateleur.
Dr Phil Shaw commented: “Since the 1970s, extensive areas of forest and savanna have been converted into farmland, while other pressures affecting African raptors have likewise intensified. With the human population projected to double in the next 35 years, the need to extend Africa’s protected area network – and mitigate pressures in unprotected areas – is now greater than ever”.
Dr Darcy Ogada added: “Africa is at a crossroads in terms of saving its magnificent birds of prey. In many areas we have watched these species nearly disappear. One of Africa’s most iconic raptors, the Secretarybird, is on the brink of extinction. There’s no single threat imperiling these birds, it’s a combination of many human-caused ones, in other words we are seeing deaths from a thousand cuts”.
Professor Ian Newton OBE FRS, FRSE, a world-leading ornithologist who was not involved in the study, commented: “This is an important paper which draws attention to the massive declines in predatory birds which have occurred across much of Africa during recent decades. This was the continent over which, only 50 years ago, pristine populations of spectacular raptors were evident almost everywhere, bringing excitement and wonder to visitors from many parts of the world. The causes of the declines are many – from rampant habitat destruction to growing use of poisons by farmers and poachers and expanding powerline networks – all ultimately due to expansions in human numbers, livestock grazing and other activities. Let us hope that more research can be done and, more importantly, that these birds can be protected over ever more areas, measures largely dependent on the education and goodwill of local people.”
Raptors of all sizes lead an increasingly perilous existence on Africa’s unprotected land, where suitable habitat, food supplies and breeding sites have been drastically reduced, and persecution from pastoralists, ivory poachers and farmers is now widespread. Other significant threats include unintentional poisoning, electrocution on power poles and collision with powerlines and wind turbines, as well as killing for food and belief-based uses.
The late Dr Jean Marc Thiollay laid the foundation for this study in the 1970s, by initiating a remarkable long-term monitoring effort in West Africa, where the average decline rate was more than twice that of other regions. The Peregrine Fund’s Dr Ralph Buij, who has re-surveyed some of the original areas, noted that: “the human footprint is particularly high throughout West Africa’s savannas, and the near complete disappearance of many raptors outside that region’s relatively small and fragmented protected area network reflects an ecological collapse that is increasingly affecting other parts of the continent. Some raptors that occur mostly in West Africa, such as the little-known Beaudouin’s Snake-eagle, are vanishing into oblivion.”
The study’s findings highlight the importance of strengthening the protection of Africa’s natural habitats and aligns with the Convention on Biological Diversity’s COP15 goal of expanding conservation areas to cover 30% of land by 2030. They also demonstrate the need to restore natural habitats within unprotected areas, reduce the impact of energy infrastructure, improve legislation for species protection, and establish long-term monitoring and evaluation of the conservation status of African raptors. Crucially, there is a pressing need to try to increase public involvement in raptor conservation efforts.
To this end, the study’s authors have developed the African Raptor Leadership Grant to address the immediate need for more research and conservation programs. It supports educational and mentoring opportunities for emerging African scientists, boosting local conservation initiatives and knowledge of raptors across the continent. This initiative, which was launched in 2023, awarded its first grant to Joan Banda, a raptor research student at AP Leventis Ornithological Research Institute in Nigeria, who will be studying threats to African owls.
ENDS
END
Widespread population collapse of African Raptors
2024-01-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Certain combinations of gut bacteria protect stem cell transplantation patients from dangerous immune reactions
2024-01-08
After stem cell transplantation, the donated immune cells sometimes attack the patients' bodies. This is known as graft versus host disease or GvHD. Researchers at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) and the Universitätsklinikum Regensburg (UKR) have shown that GvHD is much less common when certain microbes are present in the gut. In the future, it may be possible to deliberately bring about this protective composition of the microbiome.
Stem cell transplantation can save the lives of patients suffering ...
PKU scientists and collaborators invent ultrathin optical crystal for next-generation laser tech
2024-01-08
BEIJING, Dec. 19 (Xinhua) -- A team of Chinese researchers used a novel theory to invent a new type of ultrathin optical crystal with high energy efficiency, laying the foundation for next-generation laser technology.
Prof. Wang Enge from the School of Physics, Peking University, recently told Xinhua that the Twist Boron Nitride (TBN) made by the team, with a micron-level thickness, is the thinnest optical crystal currently known in the world. Compared with traditional crystals of the same thickness, its energy efficiency is raised by 100 to 10,000 times.
Wang, also an ...
Could a drug prevent hearing loss from loud music and aging?
2024-01-08
Could a Drug Prevent Hearing Loss from Loud Music and Aging?
Researchers have found a gene that links deafness to cell death in the inner ear in humans – creating new opportunities for averting hearing loss.
A person’s hearing can be damaged by loud noise, aging and even certain medications, with little recourse beyond a hearing aid or cochlear implant.
But now, UCSF scientists have achieved a breakthrough in understanding what is happening in the inner ear during hearing loss, laying the groundwork for preventing deafness.
The research, ...
Henry Ford Health recognized for outstanding consumer experience with two prestigious Press Ganey awards
2024-01-08
DETROIT (Jan. 8, 2024) – Henry Ford Health has earned two distinguished recognitions, the HX Pinnacle of Excellence Award® and HX Guardian of Excellence Award®, both in the category of Consumer Experience and granted by Press Ganey, a leading organization focused on patient experience measurement and healthcare performance improvement. These awards reflect Henry Ford Health's unwavering commitment to providing an exceptional care experience for each of its patients and their families.
"We are immensely proud to receive the Pinnacle of Excellence and Guardian of Excellence Awards from Press Ganey,” said Bob Riney, President and ...
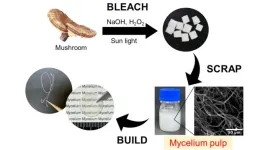
A novel strategy for extracting white mycelial pulp from fruiting mushroom bodies
2024-01-08
Mycelial fibers, the fibrous cells found in fruiting mushroom bodies, have gained momentum as a sustainable material for making leather and packaging owing to their excellent formability. Recently, a team of researchers from Shinshu University, Japan, has found a simple way of obtaining mycelial fibers, called “mycelial pulp,” from fruiting mushroom bodies and bleaching them using sunlight while keeping their mycelial structures intact.
Every year, humans generate millions of tons of waste, and almost 38% of that waste ends up in a landfill. A significant portion of it is made up of plastic or petroleum-based ...
For black adolescents, feeling connected to school has long-lasting mental health benefits
2024-01-08
School connectedness – the degree to which students feel part of their school community – influences more than grades. For Black students, it’s a protective factor against depression and aggressive behavior later in life, according to a Rutgers University-New Brunswick study.
“Our data provide fairly strong evidence for the idea that the experiences Black adolescents have in their school impacts their long-term mental health,” said Adrian Gale, an assistant professor in the Rutgers School ...
Mechanisms and management of atrial fibrillation: Updates from a Chinese Medical Journal Review
2024-01-08
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a major global health concern impacting millions and causing symptoms like palpitations, dyspnea, fatigue, dizziness, and chest discomfort. Furthermore, these symptoms reduce patients’ quality of life and lead to increased mortality and morbidity. The medical community agrees that epicardial adipose tissue (EAT), chronic inflammation, imbalances in the autonomic nervous system (ANS), stretch-induced fibrosis, and genetic alterations are the main factors that influence AF pathogenesis. Despite extensive research efforts focused on uncovering the underlying mechanisms ...
Study from ECNU Review of Education redevelops framework for teaching artificial intelligence and robotics
2024-01-08
Just like computers, the Internet, and smartphones have become commonplace in our daily lives, artificial intelligence and robotics (AIR) are the next technologies in line set to drastically change how we interact with the world and among ourselves. Various AI-driven applications are already in widespread use, such as Siri, Google Assistant, and ChatGPT, and both industrial- and consumer-grade robots are becoming increasingly capable and accessible.
In our modern societies, where people rely more and more on AIR systems to perform tasks, it’s essential to prepare children and teenagers to understand ...
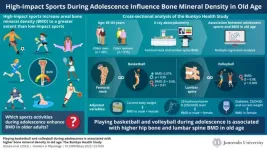
Adolescent sports activities help improve bone health in older adults, new study finds
2024-01-08
Loss of bone mineral density (BMD) with age is an important cause of osteoporosis (deterioration of bone tissue), which has been reported as one of the leading causes of falls among older adults in Japan. This leads to fractures that require long-term nursing. Prevention of osteoporosis in the aging population can thus help decrease the burden of disease and healthcare costs substantially.
Early lifestyle habits can largely influence health and disease onset in old age. In this regard, physical activities ...
Bariatric surgery may slow cognitive decline for people with obesity
2024-01-08
Within the next 10 years, it’s projected that up to 50% of United States adults will be affected by obesity, which is associated with cognitive impairment and dementia.
Investigators at Michigan Medicine found that people with obesity who underwent bariatric surgery had stable cognition two years later.
Researchers say it suggests that bariatric surgery may mitigate the natural history of cognitive decline expected in people with obesity.
The results are published in the Journal of Nutrition, Health & Aging.
“Since individuals with obesity ...